Phillip Levine, an economics professor at Wellesley College, has been studying college financial aid and students’ higher ed spending habits for more than a decade. When his children first started applying to college about 15 years ago, he was amazed by how difficult it was to get a clear answer on how much it was really going to cost them—and he was a trained economist.
Imagine, he thought, how the average family felt reading through interminable webpages and offer letters explaining the detailed price breakdowns, differences in tuition and fees, added expected costs, and loans versus grants. Then he tried to imagine how parents who’d never gone to college might feel.
Since then, Levine has worked on a number of college cost transparency initiatives. His most recent project is the Instant Net Price Estimator, a streamlined digital tool that he hopes will make it easier for colleges to break through the noise and deliver a clear estimate to families.
As public skepticism about the value of a postsecondary degree grows and $100,000 sticker prices make front-page news, colleges are in the market for a simple way to let families know that their degrees can be affordable. Washington University in St. Louis became the first institution to adopt the tool and served as a kind of pilot program this application cycle. Interest from colleges has grown swiftly: This fall, an additional 19 institutions will introduce Levine’s calculator on their websites, and he anticipates that number will triple next academic year.
Levine spoke with Inside Higher Ed about his new tool, how low-income students get stuck in the financial aid “funnel” and how colleges can be better communicators in a time of widespread public distrust of higher ed. The conversation has been edited for length and clarity.
Q: Walk me through the genesis of this idea. What were you hoping to achieve?
A: I don’t think it’s a state secret that college pricing is complicated. If you go to any college website and look at the financial aid webpage, there’s tons of stuff there trying to explain how much they charge, but they overshoot it in terms of what people are looking for. You’re taking a high school kid and their family and giving them a Ph.D.-level course in financial aid. Not surprisingly, they don’t usually get it.
I think about the admissions process like a funnel: You give me a little information, I’ll give you a basic answer that’s pretty imprecise. You give me more information, I’ll give you a better answer that’s a little more precise. You can keep going down the process until eventually, you know, ultimately you fill out the FAFSA or the CSS Profile.
To maximize access, that funnel needs to have a very wide mouth at the top; in financial aid language, what that means is you need to communicate extremely quickly to as wide an audience as possible that college is not $100,000. It doesn’t even matter exactly what it is. But if you can’t get people off of the ledge at the $100,000 number—the mainstream media puts out stories all the time that college costs a million dollars a year, so their perception is that it’s extremely expensive. All you want them to do at the beginning stages is to be like, “Hey, maybe this is something I can afford.” Then you need to lead them through the rest of the funnel.
Ultimately, the financial aid process really is complicated because we have this concept of what a family can afford to pay, and there’s no right answer to that question, but we have all these complicated formulas that are trying to find it anyway. Over time, colleges have been trying to do a better job of getting past that point, just not very successfully. What I’ve been working on for the last 10 or 15 years is to make an easier entry point, and this tool is even higher up the funnel than what I’ve been working on in the past.
It takes three seconds to get a sense of what college is going to cost you, and in particular to get you over that hurdle that it’s probably not $100,000. My goal is within a matter of literally a few seconds to give people a sense that college is very unlikely to be as expensive as they fear. And then you can start having a more substantive conversation. Otherwise, you close the door on the poor kids, way before they’re into the process.
Q: Colleges have been trying to do this kind of thing on their own for a while. What makes your tool an improvement on institutional efforts?
A: Colleges understand that this is a problem. But to be quite honest, the only people who actually understand the way the financial aid system works are the people in the financial aid office, and they don’t speak English, so to speak. It’s an unbelievably complicated process, very complex, and now they have to explain it to a regular person, and they can’t do that. It’s not their fault; they try, they’re just not successful. There’s a handful of people in the admissions office who understand it, too, but not many. And once you get past those two audiences, nobody else at the college understands it, including the public affairs people.
I got started on this because when my kids were looking at colleges, I just wanted to know whether I was eligible for any financial aid, yeah. And I realized how unbelievably hard it was to figure it out. Back then [around 2010] it was actually impossible to figure out. Things have evolved a lot since then.
Q: Like you said, there are other tools out there now. What makes this one different?
A: I’m just trying to push it to the next stage of development. I’m an economist; I can speak geek as well as anyone. But as I started doing this, I’m learning more and more about how you sell a product, which is basically what you’re doing with college cost. I’m realizing how little time you have to communicate a message.
I’m in a weird position, because I’m doing the research on the pricing issues, and I’m developing the tools. It was in one of the Brookings [Institution] papers I wrote when these ideas were just kind of coming together and we were thinking about how you do the graphics. And it just kind of came together that we can visually display this information in a simulator, what I really refer to as a simple game. So I thought, if I can do it for a Brookings paper, why can’t I do this for a school or a family? And about that time, Washington University [in St. Louis] came to me looking for assistance on some other issues, and I pitched this to them, and they bought into it. So they paid for the development, and it’s been up and running there since December. If you go to most schools’ webpages, including my own, there’s stuff there, but you gotta read forever. And you know as well as I do that nobody reads that much anymore.
That’s what I’m trying to accomplish with this: just get the ball rolling with something that speaks to where students are.
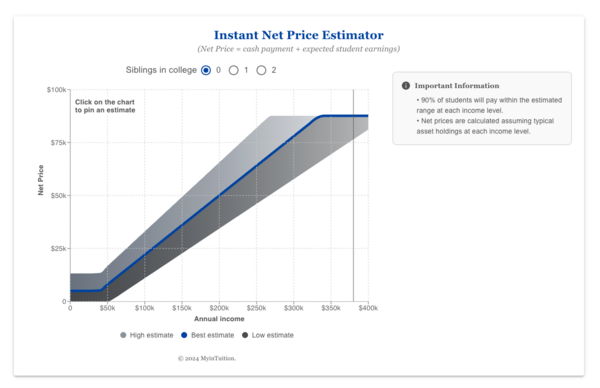
A demo version of Levine’s Instant Net Price Estimator, which can be customized to fit colleges’ specific needs and profiles.
Screenshot from myintuition.org
Q: I assume the calculator doesn’t factor in things like merit aid?
A: You want it as simple as possible. So you just slide your input and it essentially just tells you what the average cost is going to be for you based on income, and tells you the range, which may be very broad. At Washington University, they don’t give a lot of merit aid, so, like, it would not be a big deal there, but at schools that do a lot of merit aid, that range could also include merit. They can factor that into the calculator.
But mainly, you just want the light bulb to go off of, “Oh, maybe I can afford this.” And then maybe they’re willing to go spend some time reading instead of getting scared off right from the start. Their initial instinct is, there’s no way I can afford to go to Washington University. And it’s the school’s job in terms of marketing to communicate to people. The problem, in my mind, is that the door is closed so early for so many people that you need to be able to just let them get through that first door in the process. There’s still a lot of hurdles you have to get through after that, yeah, but if you don’t make it through the first one, you don’t even approach any of the others.
Q: There’s been legislation introduced at the federal level and passed in many states to mandate that colleges take certain steps toward cost transparency. Do you think there’s a good understanding of what that takes among policymakers?
A: Clearly, policymakers have figured out that transparency is an issue, and they’re right. But their intentions are often better than their proposals. The net price calculator law [a federal law mandating institutions include a price calculator on their websites by 2011], for instance, was very well intended. But it’s easy to see the big picture problem; to then come up with a solution that actually works, you have to have a little bit more inside baseball. The net price calculator law is a perfect example. It was so well intended, they completely had the right idea, and they blew it. I obviously don’t know all of the details of all the different state laws, but I’ve seen proposals, and generally I look at them and go, right idea, wrong solution.
Q: Have there been any good policy solutions?
A: The College Cost Transparency Initiative. It’s much better if the schools can fix this problem on their own, because they know what they’re doing. It’s a tiny step, and you have to already apply and get accepted before you get your letter. And then it tells you, in a more clear way than it used to. It’s lower on the funnel, really at the bottom. But it’s a good step.
[Levine later clarified that he sat on the technical advisory committee for the CCTI.]
Q: Has there been a lot of interest in your instant price calculator from other colleges? And what kinds of colleges seem to be most invested in these transparency efforts?
A: Nineteen more colleges will roll it out in the fall. It’s a small range right now, from relatively wealthy to very wealthy. I think at the very high end of higher ed, the Ivies and such, where they have a lot of money to spend on financial aid, they’re trying to increase access in a very direct way. It is good for them to enroll more lower-income students from a public relations perspective. And I think every school wants to do the right thing. But as you stray from the very top of the spectrum, there’s also an interest in simply increasing enrollment, where they don’t want to be turning away students because they think they can’t afford it when they can. They’re just looking for more students, especially because there’s fewer kids. So the ability to open the door to as many kids as possible at this moment has appeal.