Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
Were you a current or former student in the last few decades? Or a parent? Or an educator?
If so, your sensitive data — like Social Security numbers and medical records — may have fallen into the hands of cybercriminals. Their target was education technology behemoth PowerSchool, which provides a centralized system for reams of student data to damn near every school in America.
Given the cyberattack’s high stakes and its potential to harm millions of current and former students, I teamed up Wednesday with Doug Levin of the K12 Security Information eXchange to moderate a timely webinar about what happened, who was affected — and the steps school districts must take to keep their communities safe.
Sign-up for the School (in)Security newsletter.
Get the most critical news and information about students’ rights, safety and well-being delivered straight to your inbox.
Concern about the PowerSchool breach is clearly high: Some 600 people tuned into the live event at one point and pummeled Levin and panelists Wesley Lombardo, technology director at Tennessee’s Maryville City Schools; Mark Racine, co-founder of RootED Solutions; and Amelia Vance, president of the Public Interest Privacy Center, with questions.
PowerSchool declined our invitation to participate but sent a statement, saying it is “working to complete our investigation of the incident and [is] coordinating with districts and schools to provide more information and resources (including credit monitoring or identity protection services if applicable) as it becomes available.”
The individual or group who hacked the ed tech giant has yet to be publicly identified.
Asked and answered: Why has the company’s security safeguards faced widespread scrutiny? What steps should parents take to keep their kids’ data secure? Will anyone be held accountable?

In the news
Oklahoma schools Superintendent Ryan Walters, who says undocumented immigrants have placed “severe financial and operational strain” on schools in his state, proposed rules requiring parents to show proof of citizenship or legal immigration status when enrolling their kids — a proposal that not only violates federal law, but is likely to keep some parents from sending their children to school. | The 74
- Not playing along: Leaders of the state’s two largest school districts — Oklahoma City and Tulsa — rebuked the proposal and said they would not collect students’ immigration information. Educators nationwide fear the incoming Trump administration could carry out arrests on campuses. | Oklahoma Watch
- Walters filed a $474 million federal lawsuit this week alleging immigration enforcement officials mismanaged the U.S.-Mexico border, leading to “skyrocketing costs” for Oklahoma schools required “to accommodate an influx of non-citizen students.” | The Oklahoman
- Timely resource guide: With ramped-up immigration enforcement on the horizon — and with many schools already sharing student information with ICE — here are the steps school administrators must take to comply with longstanding privacy and civil rights laws. | Center for Democracy & Technology
A federal judge in Kentucky struck down the Biden administration’s Title IX rules that enshrined civil rights protections for LGBTQ+ students in schools, siding with several conservative state attorneys general who argued that harassment of transgender students based on their gender identity doesn’t constitute sex discrimination. Mother Jones
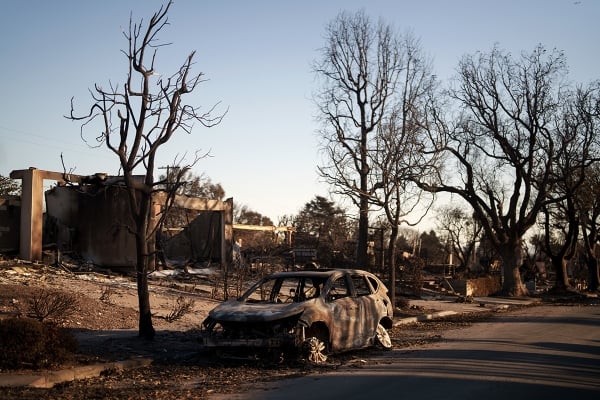
Fires throw L.A. schools into chaos: As fatal wildfires rage in California, the students and families of America’s second-largest school district have had their lives thrown into disarray. Schools serving thousands of students were badly damaged or destroyed. Many children have lost their homes. Hundreds of kids whose schools burned down returned to makeshift classrooms Wednesday after losing “their whole lifestyle in a matter of hours.” | The Washington Post
- At least seven public schools in Los Angeles that were destroyed, damaged or threatened by flames will remain closed, along with campuses in other districts. | The 74
Has TikTok’s time run out? With a national ban looming for the popular social media app, many teens say they’re ready to move on (and have already flocked to a replacement). | Business Insider
Instagram and Facebook parent company Meta restricted LGBTQ+-related content from teens’ accounts for months under its so-called sensitive content policy until the effort was exposed by journalist Taylor Lorenz. | Fast Company

The Federal Communications Commission on Thursday announced the participants in a $200 million pilot program to help schools and libraries bolster their cybersecurity defenses. They include 645 schools and districts and 50 libraries. | FCC
Scholastic falls to “furry” hackers: The education and publishing giant that brought us Harry Potter has fallen victim to a cyberattacker, who reportedly stole the records of some 8 million people. In an added twist, the culprit gave a shout-out to “the puppygirl hacker polycule,” an apparent reference to a hacker dating group interested in human-like animal characters. | Daily Dot
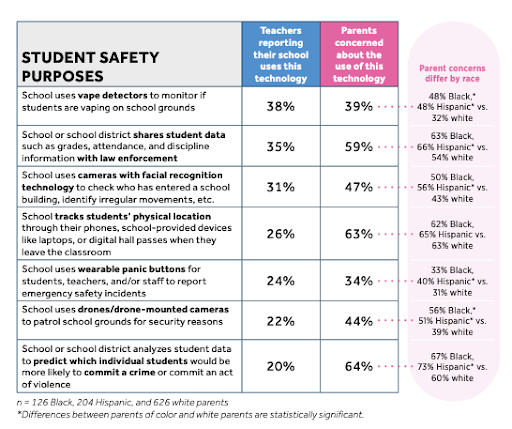
Not just in New Jersey: In a new survey, nearly a quarter of teachers said their schools are patrolled by drones and a third said their schools have surveillance cameras with facial recognition capabilities. | Center for Democracy & Technology
The number of teens abstaining from drugs, alcohol and tobacco use has hit record highs, with experts calling the latest data unprecedented and unexpected. | Ars Technica
ICYMI @The74
Librarians Gain Protections in Some States as Book Bans Soar
RFK Jr. Could Pull Many Levers to Hinder Childhood Immunization as HHS Head
Feds: Philadelphia Schools Failed to Address Antisemitism in School, Online
Emotional Support

New pup just dropped.
Meet Woodford, who, at just 9 weeks, has already aged like a fine bourbon. I’m told that Woody — and the duck, obviously — have come under the good care of 74 reporter Linda Jacobson’s daughter.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter







