Former Western New Mexico University president Joseph Shepard received an exit package that included severance pay of $1.9 million, and a tenured faculty job, with perks adding up to an estimated $3.5 million.
Photo illustration by Justin Morrison/Inside Higher Ed | skodonnell/iStock/Getty Images | rawpixel
The controversial exit package for former Western New Mexico University president Joseph Shepard could have funded multiple scholarships, according to one analysis, while the state’s governor says that the money could have helped feed hungry students at the university for a year.
Judith Wilde, a research professor at George Mason University who studies presidential compensation and contracts, previously told Inside Higher Ed that Shepard’s exit package could have funded 90 scholarships for undergraduate students at Western New Mexico.
To Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham, a Democrat, the decision to green-light a $1.9 million severance payment to the departing president “demonstrated an appalling disconnect from the needs of our state, where the median income of a family of four is just $61,000.”
“The amount of money contained in Dr. Shepard’s separation agreement could have addressed food insecurity across the entire WNMU student body for a full year,” Lujan Grisham said in a news release last week.
The estimated $3.5 million package—including benefits—for a president accused of improperly spending taxpayer dollars has infuriated state lawmakers and led to the resignations of several regents. More fallout is expected as the state attorney general seeks to claw back the severance payment.
Shepard’s last day as president was Wednesday.
Shepard, who led the university for 13 years, made a base salary of $365,000 a year. He’s not the only college president to get a generous severance on his way out the door, but compared to deals at other institutions, the agreement is unusually lucrative and will cost the university more than multiple line items in its budget. For example, when Ben Sasse stepped down as president of the University of Florida, he struck a deal to keep his $1 million annual salary through 2028 despite exiting the top job. But UF’s annual budget is just over $5 billion, meaning Sasse’s exit package comprises a tiny fraction of university expenses.
Comparatively, Shepard’s exit package far exceeds those of other former presidents in his state. Former New Mexico State University system chancellor Dan Arvizu received an exit package valued at between $500,000 and $650,000 when he announced his early departure in 2023, a move both parties referred to as a “mutual separation” amid tensions. In 2016, Bob Frank left the University of New Mexico presidency early amid allegations of bullying, striking a deal for a $190,000-a-year tenured faculty job—down from the $350,000 annual salary initially considered.
At WNMU, a university that enrolled 3,570 students in fall 2023, Shepard’s total exit package adds up to almost 5 percent of its $74.2 million fiscal year 2024 budget, an Inside Higher Ed analysis found.
In one of the poorest states in the union, more than half of WNMU’s students receive Pell Grants. A 2023 survey also found nearly 60 percent of college students in New Mexico were food insecure, prompting efforts at Western New Mexico and other colleges to address the issue.
Shepard’s exit package has roiled lawmakers, particularly in light of the economic challenges in the state and a state investigation that found the outgoing president improperly spent $360,000 in taxpayer money on international travel, splashy resorts and expensive furniture. Had the board elected to fire Shepard without cause, it could have spent roughly $600,000 to cut ties with him. Or the board could have waited for the conclusion of another state investigation, which might have given them cause to fire him without spending any additional money, depending on the findings.
Instead, regents cut him a $1.9 million check and gave him a tenured faculty job teaching two courses a year with a remote option. Altogether those perks add up to a $3.5 million, Wilde estimated. (WNMU officials said the money was paid for out of reserves.)
Four out of five WNMU regents have since resigned under scrutiny from lawmakers, including the governor. Attorney General Raúl Torrez also demanded an investigation into Shepard’s “golden parachute” and sought a restraining order to prevent him from accessing the $1.9 million severance payment as the state challenges the contract. However, a judge shot down the request to place a hold on those funds Monday. A legal challenge to the contract is pending.
ButJohn C. Anderson, an attorney for Shepard, defended the payment as “appropriate” and said that the former president had “worked tirelessly on behalf of Western New Mexico University for nearly 14 years to increase graduation rates, modernize the campus through major renovations and the construction of new facilities, and expand the school’s programs,” among other accomplishments. (Shepard’s legal team also disputed the estimate of $3.5 million but did not provide their own figure.)
As the legal wrangling continues, Inside Higher Ed took a look at WNMU’s budget to determine how Shepard’s controversial exit package stacks up to spending on athletics, academic support, faculty salaries and other line items in the fiscal year 2024 budget, which was last updated in December. While Shepard has already received a nearly $2 million severance payment, the remainder of his deal will be paid out to him as a tenured faculty member where he’ll initially make $200,000 a year. His salary will be paid for by the business school.
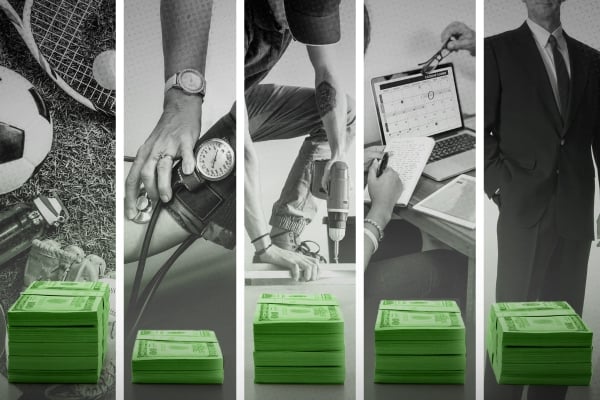
- WNMU athletics teams—known as the Mustangs—compete on the NCAA Division II level. Western New Mexico University sponsors 13 sports with an athletics budget of $5.4 million.
- The student services budget at WNMU is $4.5 million. That money is spread across a range of offerings from disability services to funding for special events and student health and well-being.
- WNMU budgeted $4.4 million for the operation and maintenance of campus.
- WNMU budgeted $3.9 million in academic support.
- The student financial aid budget at WNMU was $1.2 million.
- Shepard’s exit package also surpasses the total faculty salaries for any department at WNMU. The nursing department has 19 full-time faculty members, earning a combined salary of $1.4 million, according to budget documents. Nursing appears to be the largest program at WNMU based on the number of full-time employees listed. Social work is also among the university’s largest programs, with 17.2 full-time faculty members listed earning just over $1 million.