Join HEPI for a webinar on Thursday 11 December 2025 from 10am to 11am to discuss how universities can strengthen the student voice in governance to mark the launch of our upcoming report, Rethinking the Student Voice. Sign up now to hear our speakers explore the key questions.
This guest blog was kindly authored by Imran Mir, Campus Head and Programme Lead at Apex College Leicester.
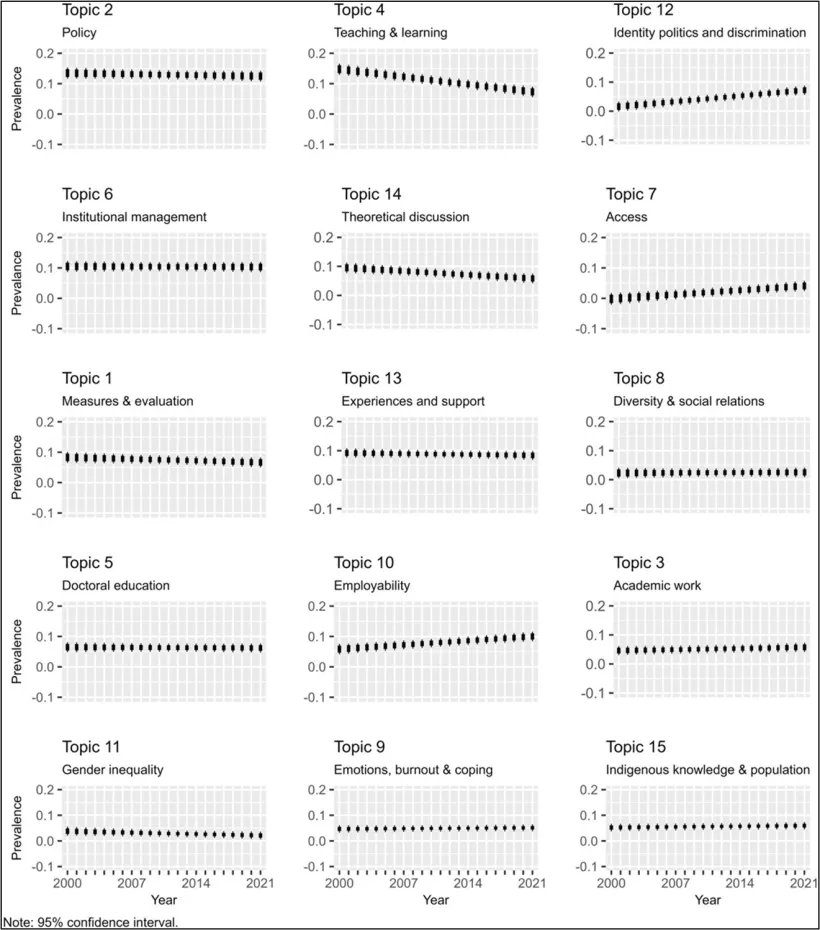
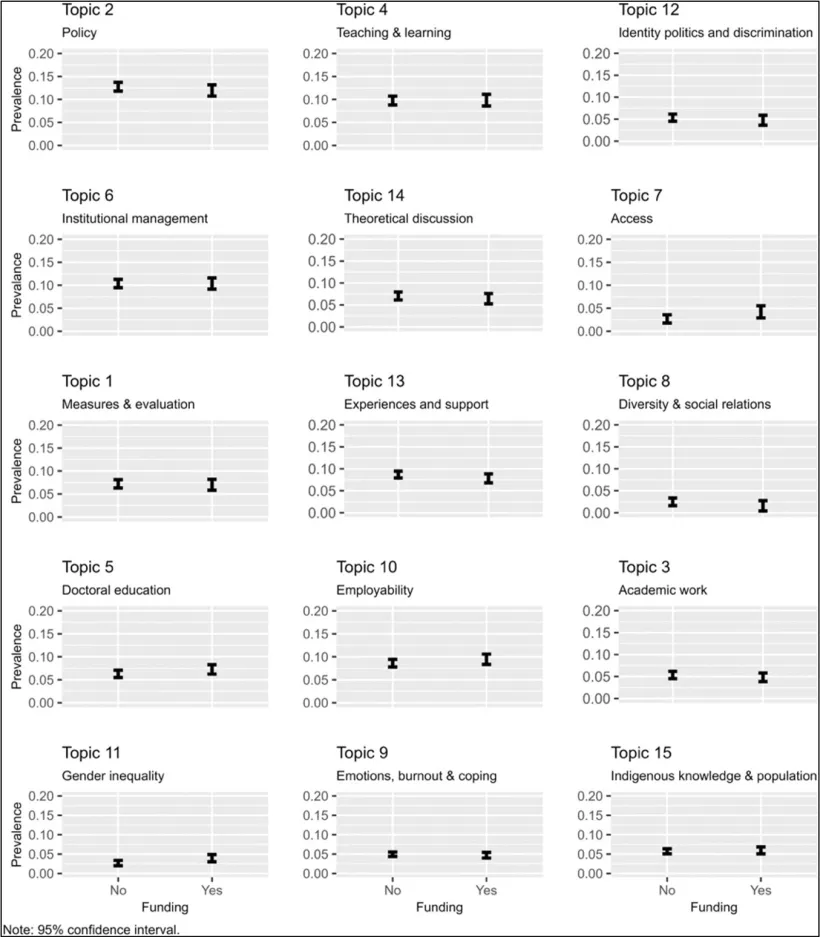
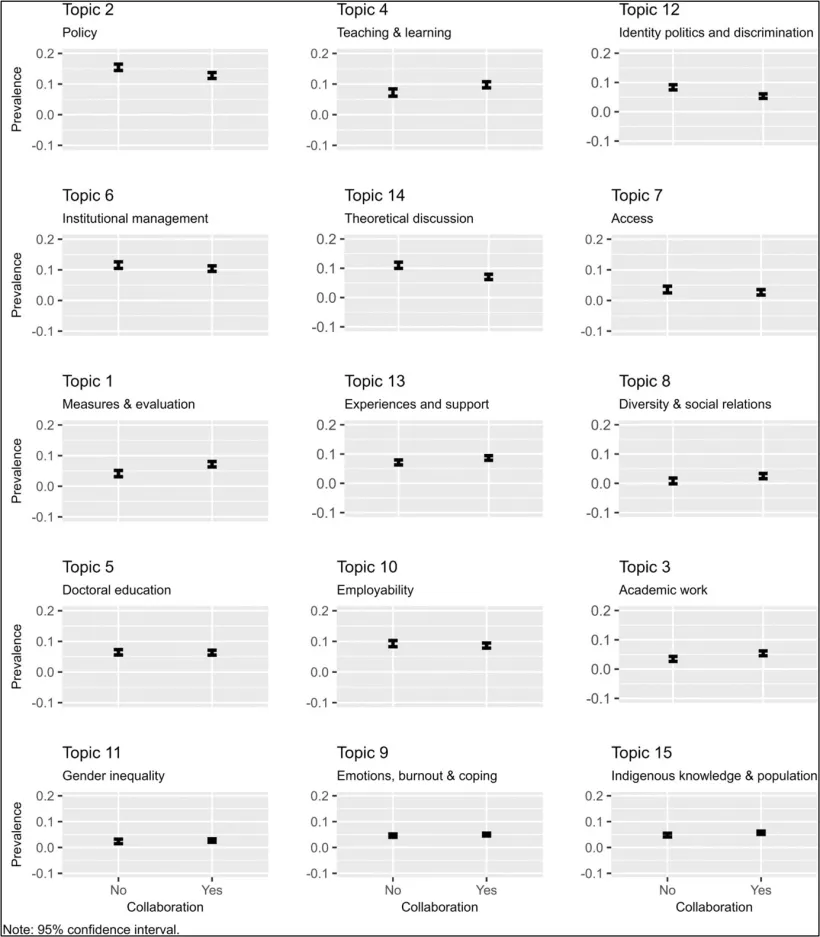
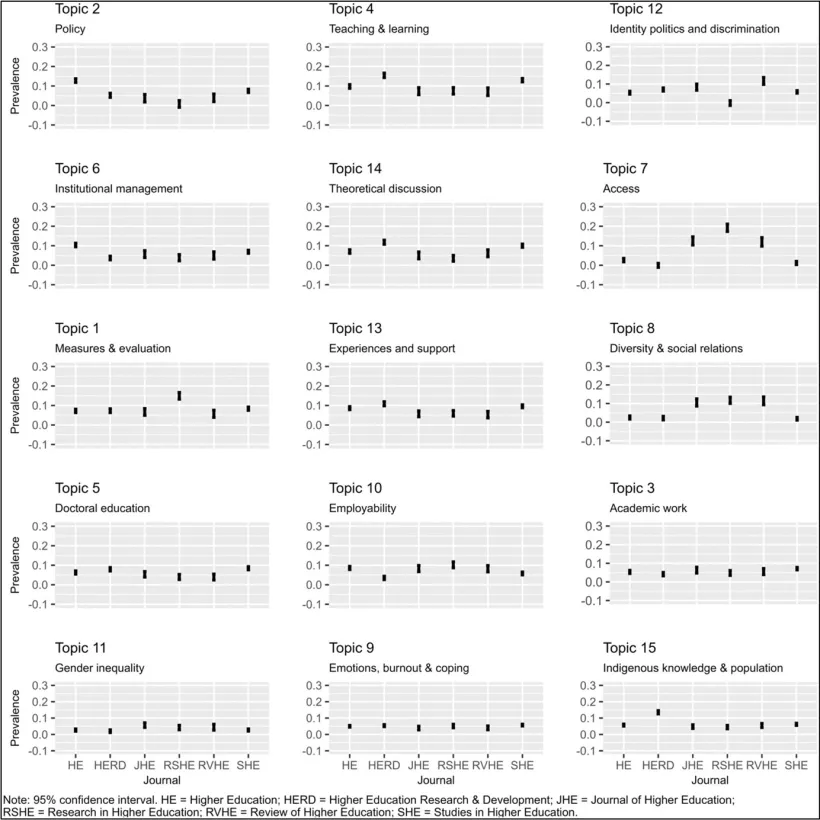
The embedding of the further education and higher education sectors has been a longstanding policy goal, but recent reforms have caused an urgent need than ever. The UK government has set the ambitious goal of having at least two-thirds of young people go on to higher-level learning by age 25, with at least 10% of them pursuing higher technical education or apprenticeships. While such targets can be seen as overly ambitious, they will only come to fruition if the gap between further education and higher education is efficiently bridged. Without this, there is a risk of losing students during the transition from one educational stage to the next. These government ambitions highlight why bridging further education and higher education is so important. Aligning both sectors is essential to turning these national policy goals into real progress for learners.
The persistent progression problem
Although there has been some growth in participation in higher education, disparities remain. Students who come from disadvantaged backgrounds are four times less likely to have access to high-tariff universities. Whilst UCAS data for 2024 has shown growth in learner acceptances, this is largely down to an increase in the number of 18-year-olds, rather than a reduction in gaps between the most and least advantaged students. Further education is vital for social mobility; however, too many learners face major barriers when trying to transition into the higher education institutions of their choice.
Five key levers to improve bridging
- Align curriculum and assessment
When transitioning from further education to higher education, students will face a contrast in learning expectations. In the former, through A-Levels and vocational qualifications, assessments are exam-focused and often high-stakes. In comparison, higher education has a variety of assessment types, including coursework, presentations, and exams. These assessments are often less frequent, and a student’s grade is not as reliant on a single, high-stakes exam. To make this transition process smoother, higher education providers and further education providers should collaborate to co-design first-year assessments that look to integrate a blend of authentic tasks, ranging from portfolios to presentations. This would allow better preparation for students to progress into higher education while aligning expectations between further and higher education. This approach is supported by the Foundation Year Fee Cap Guidance, which explains the importance of curricula that support progression into higher-level study while avoiding the repetition of Level 3 content. - Use admissions to recognise potential
A large number of further education students, particularly those without access to enrichment activities, find it difficult to reach their potential, something which is not always recognised in higher education admissions. Many of these learners focus on technical or applied qualifications such as T Levels and Higher Technical Qualifications (HTQs), which develop valuable practical and professional skills. However, because these programmes may not include the same kinds of enrichment activities often valued in traditional academic routes, their achievements are sometimes overlooked in admissions decisions. Universities should value T Levels, Higher Technical Qualifications (HTQs), and other applied learning pathways. These routes must be recognised by universities. They must provide clear pathways showing how credits earned in further education can be transferred to the Lifelong Learning Entitlement (LLE). This would result in the system being more inclusive for students who come from non-traditional routes into higher education.. - Share data and pastoral insight
The lack of continued student support is another barrier. Colleges and universities must work together in creating a standardised set of transition data that includes information on curriculum, assessment types, and available support measures. For example, shared data could help universities identify where incoming students may need additional academic or well-being support. To enable a smooth transition, both sectors need to agree on how to share this information. The OfS Regulatory Framework promotes transparency in data sharing to ensure positive student outcomes. - Co-deliver first-year teaching
In certain subjects, co-delivering first-year content between FE and HE providers could help students with transitioning from further education. Modules on study skills, digital literacy, and professional competencies could be delivered jointly; this approach would particularly benefit students who work or commute. This method aligns with the OfS Strategy 2025–2030 Guide, which clearly stresses student success and sector resilience as a major priority. - Make the LLE a ladder, not a maze
The LLE offers an opportunity for modular, credit-bearing study across a lifetime. For this vision to come to fruition, higher education institutions must look to implement clear credit transfer rules, transparent pricing, and clear pathways for learners to progress from Level 4 to full degrees. By having routes which are clearly mapped out, students will be better able to understand how to continue their education without getting lost in a complex system. The House of Commons Library LLE Briefing outlines how this could be achieved.
Reflecting on the recent Post-16 Education and Skills White Paper (DfE, 2025), there is clear intent to have a more connected tertiary system through plans such as the Lifelong Learning Entitlement and stronger employer-education partnerships. The proposal clearly acknowledges many of the issues outlined above, especially the need for smoother progression routes and credit transfer between further and higher education. However, questions will remain on how effectively these ambitions are going to be implemented. Without unified collaboration from both sides, clear accountability, and investment in teaching capacity and resources across both sectors, the reforms risk reinforcing the existing divides rather than bridging the gap.
The prize
For the government to achieve its goal of equity, further education students must not just enter higher education but also succeed once there. The reforms present an opportunity; they must be matched with the practical changes in how we align assessment, recognise technical routes in admissions, share data, work together where possible, and make the LLE more navigable. By taking these actions, policy ambitions can be translated into real-world success for students.