
The department is largely closed due to the government shutdown. In the meantime, the Trump administration is using furloughed workers’ emails to make a political statement.
Photo illustration by Justin Morrison/Inside Higher Ed | Tierney L. Cross/Getty Images | nevodka/iStock/Getty Images
Wednesday morning, as the government shutdown began, chief officers at the Department of Education distributed a standard out-of-the-office statement to all furloughed staff members and instructed them to copy and paste it into their email. So that’s what they did.
But just hours later, those same nonpartisan staffers began to hear that the message they’d pasted into their email account was not the message being received by the public.
“On Wednesday evening, my supervisor reached out to me on my personal equipment and said, ‘You’re going to want to log in and change your out-of-office status,’” one department staffer told Inside Higher Ed on the condition of anonymity out of fear of losing her job.
When she followed her supervisor’s direction and logged in, the automatic message she saw was not the one she had saved earlier that morning.
Rather than the original note, which had said, “There is a temporary shutdown … due to a lapse in appropriations,” the new message said, “Unfortunately, Democrat Senators are blocking passage of [a bill] … which has led to a lapse in appropriations.”
This is one of the more than 10 emails Inside Higher Ed received as automatic responses including the same political message. Although Keast was appointed by Trump, most of the staffers we contacted were not.
The outgoing message had been changed internally without her consent. And this staffer was not alone. Inside Higher Ed emailed 10 separate Education Department staffers Thursday, all of whom had been placed on furlough, and each one bounced back with identical responses. One senior leader from the department, who also spoke anonymously, said that to his knowledge the politically charged message was set as the out-of-office notification for all furloughed employees.
(The Department of Education did not immediately provide comment. In fact, the emails sent to both deputy press secretary Ellen Keast and the general press team account were met with the same automatic response.)
The first staffer said that while she was caught off guard by the override at first, it made sense the more she thought about it. Similar messages blaming Democratic senators for the shutdown had already been put at the top of HUD.gov, the landing page for all things Department of Housing and Urban Development, and other federal websites.
As of Thursday evening, the HUD website noted, “The Radical Left in Congress shut down the government. HUD will use available resources to help Americans in need.”
Republicans control the White House, the House and the Senate. In the Senate, they need the votes of at least seven Democratic senators to reach the 60-vote threshold necessary to overcome a filibuster.
“I was really surprised, because we had gotten such explicit instructions on what to use for our out-of-office message,” the staffer said. But “when I saw that message from my supervisor, I assumed it had been changed to something more political than the original neutral one.”
She has already logged back in multiple times to change the automatic response back to the neutral language. But each time, within hours, the department has overridden her changes.
“It’s what [is being sent] to people who contact me, and they could reasonably misunderstand it as coming from me, and I don’t feel comfortable as a federal employee communicating a political message like that,” she said.
A second staffer told Inside Higher Ed that he has worked through multiple shutdowns prior but not experienced anything like this.
“It’s just wild to see your name attached to a message that you had nothing to do with,” he said. “It feels like a violation … You know that you don’t have any expectation of privacy when you’re working for the federal government. But it’s a different thing to say that you don’t have autonomy over your own words.”
The second staffer noted that in his view, not only did this seem to be a violation of his personal rights, but also a violation of federal law.
The Hatch Act, passed in 1939, was intended to ensure that nonpartisan federal workers who worked across administrations remained just that—nonpartisan. And according to documents from the Office of Special Counsel website, the Hatch Act “limits certain political activities of federal employees,” like using official authority for political purposes, soliciting political donations, wearing partisan political gear at work and posting or sharing partisan content on government systems.
“It’s crazy to see the law violated on your behalf,” the second staffer said.
None of the department employees Inside Higher Ed spoke with intended to file an individual lawsuit, nor had they heard anything from their union about a collective legal response. But one shared that Democracy Forward, a nonprofit legal organization that has sued the Trump administration several times this year, will be going to court over the matter as soon as Friday.

Last month, Peter Hans, president of the University of North Carolina system, casually dropped a bombshell announcement that the system and others were in talks to launch a new accreditor.
“We’ve been having a number of discussions with several other major public university systems, where we’re exploring the idea of creating an accreditor that would offer sound oversight,” Hans said at a UNC system Board of Governors meeting last month, The News & Observer reported.
Since then, no additional details have emerged, though Hans teased an update to come in July.
But public records obtained by Inside Higher Ed show UNC system officials have been quietly engaged in conversations about launching a new accreditor for at least a year, including discussions with unnamed collaborators in Florida, where the effort could be headquartered. UNC officials have also spoken with officials at the U.S. Department of Education, even getting a heads-up on what an April 23 executive order from the Trump administration on accreditation would entail.
Here’s what those documents show.
In early April, UNC officials appeared ready to tell the world about their plans for a new accreditor that “would be publicly accountable, outcomes-based, and more efficient and effective in its reviews,” according to the draft of a statement that was never publicly released.
“We believe it is past time for the creation of a new accreditor focused on the unique needs of public colleges and universities,” the statement said. “We have worked collaboratively over the past year to explore and develop such a cross-state partnership.”
Andrew Kelly, a senior adviser to Hans, sent a draft of the statement to other UNC officials. The statement argued that accreditors “wield enormous power, but too often have opaque and counterintuitive governance” and fail to “focus on matters that are significant to students.” He argued in the statement that the current model “creates unnecessary duplication and cost, conflicts with the authority of state governments, and does little to ensure educational quality.”
An unidentified number of state systems of higher education were supposed to sign the statement, according to the draft.
Kelly drafted the statement in response to the Trump administration’s anticipated changes to accreditation, which included streamlining the processes for ED to recognize accreditors and for institutions to switch agencies, among other changes to the system that serves as gatekeeper to federal financial aid.
But the public did not hear about the UNC system’s quiet effort to launch a new accreditor until Hans spoke up at the May board meeting.
Other emails yielded some insights into whom the UNC system might be partnering with.
Daniel Harrison, vice president for academic affairs at the UNC system, sent an email on April 23 to fellow officials recapping a call with the U.S. Department of Education and what could be expected in the coming executive order on accreditation (which was issued shortly after his email).
In that email, Harrison also pointed to potential partners in the accreditation effort.
“An update on the Florida project—we met with the new entities [sic] attorneys and made substantial progress toward determining the legal structure of the new accreditor. It is likely to be a single member Florida nonprofit corp. Florida would be the sole member, but would delegate all delegable powers to a Board of Directors made up of the participating states,” Harrison wrote.
But despite having met with potential partners, UNC considered going its own way.
In a response to Harrison, Hans asked him to convene several system officials involved with the effort to weigh the pros and cons of “joining [a] multi-state coalition” or “forming a NC entity.” Email records obtained by Inside Higher Ed don’t show what the group recommended, but remarks made by Hans at May’s meeting indicate the system opted for the coalition approach.
UNC system officials did not respond to requests for comment from Inside Higher Ed.
System leaders also appear to have discussed the effort with state legislators in private. On May 15, Hans asked senior vice president of government relations Bart Goodson to set up a meeting with Michael Lee, the Senate majority leader in the Republican-dominated Legislature. When Goodson asked about the topic, Hans replied, “accreditation update with good news.”
Lee did not respond to a request for comment from Inside Higher Ed.
Like their UNC counterparts, other public systems are staying quiet on the effort.
Inside Higher Ed contacted a dozen public university systems, all in red states, to ask if they are partnering with UNC or others in an effort to launch a new accreditor, or if they participated in such discussions. Only two replied: the Arkansas State University system and the University of Alabama system. Both noted they had not been involved in those accreditation discussions.
The State University System of Florida—which did not reply to media inquiries—is the most likely potential partner, given the details in Harrison’s email and the governor’s recent political fury with accreditors.
In 2022, Florida’s dark-red Legislature passed a law requiring state institutions to switch accreditors regularly. That move came after the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges, which accredited all 40 of Florida’s public institutions, inquired about a potential conflict of interest at Florida State University, which was considering Richard Corcoran for its presidency despite his role on the Florida Board of Governors. (He now leads New College of Florida.)
SACS also raised questions about an effort by the University of Florida to prevent professors from testifying against the state in a legal case challenging voting-rights restrictions. (UF later dropped that policy amid a torrent of criticism.) Both incidents occurred in 2021.
Florida governor Ron DeSantis has been a vocal critic of the federal accreditation system.
Joe Raedle/Getty Images
Following the 2022 law, some institutions began the process of switching accreditors, though state officials argued that the Biden administration slowed down that effort and Florida tried unsuccessfully to get a federal judge to rule the current system of accreditation unconstitutional.
Outside of Florida, North Carolina is the only other state with a similar law. In 2023, legislators quietly slipped a provision into a state budget bill that required state institutions to change accreditors every cycle. The law was passed with no debate among North Carolina lawmakers. The change came after UNC clashed with SACS in early 2023 over shared governance.
Florida governor Ron DeSantis did not confirm to Inside Higher Ed whether the state is launching a new accreditor, but recent remarks from the GOP firebrand suggest, albeit vaguely, that something is in the works.
“For too long, academic accreditors have held our colleges and universities hostage,” DeSantis said in an emailed statement. “These accreditation cartels have worked behind the scenes to shape university behavior, embedding ideological concepts like Diversity, Equity, and Exclusion Indoctrination into the accreditation process. If you weren’t meeting politically motivated standards, like enthusiastic participation in DEI, they would hamper your accreditation and access to federal funding. In Florida, we refuse to let academic accreditation cartels hold our colleges and universities hostage to ideology at the expense of academic excellence. Stay tuned.”
DeSantis also promised “more to come” on accreditation at an education event on Wednesday.
Reactions to Hans’s announcement have been mixed.
Wade Maki, Faculty Assembly chair and a philosophy professor at UNC Greensboro, said he and other faculty members recently met with system officials to share their thoughts on the plan.
“We had a very open conversation with the system office and shared our hopes that we get an accreditor that is independent, that maintains the strong reputation of the UNC system and helps keep the politics out of higher ed and the curriculum, whether that’s from the politicians or the accreditors themselves,” Maki said. “We’ve seen it come from both directions over the years.”
He also thinks the narrow focus of such an accreditor could be a positive.
“My leadership team, the Faculty Assembly Executive Committee and the faculty that we’ve talked to on campuses, we see the potential benefits of trying something like this, of having an accreditor that focuses just on the accrediting of state-supported public institutions,” Maki said.
Outside observers were more critical of the UNC system’s plans.
Accreditation expert Paul Gaston III, an emeritus trustees professor at Kent State University, argued that building an accreditor composed only of public institutions would omit valuable perspectives in review processes. He argued that colleges undergoing accreditation reviews benefit from the diversity of experiences from evaluators working at a broad range of institutions.
“What would be the advantage of, in a sense, separating classes of institutions for accreditation? I think one of the strengths of accreditation has been that it brings a variety of perspectives to the evaluation of a particular institution,” Gaston said.
Then there’s the arduous process of getting a new accrediting agency up and running; gaining federal recognition, which is required, takes years. Although Trump’s executive order on accreditation promised a smoother pathway to recognition for new entrants, it does not supersede federal regulations.
“Becoming federally recognized, typically, is a five-plus-year process,” said Edward Conroy, a senior policy manager at the left-leaning think tank New America. Under current federal regulations, Conroy doesn’t expect the new accreditor to be recognized until 2030 or so.
Conroy also questioned whether the effort to create a new accreditor is about institutional quality assurance or political control.
“Everything Florida has done on accreditation over the past few years appears to be politically and ideologically driven, rather than about what is best for students and ensuring that they go to high-quality institutions and get a good education when they’re paying a lot of money for it and when taxpayers are investing a lot of money in public funding for higher education,” he said.
Conroy worries that state lawmakers in either Florida or North Carolina would require public colleges in their state to be accredited by their new accreditor. That would undermine the current requirement that colleges get to choose their own accreditor.
“It undercuts the principle of the higher education accountability triad, where states, accreditors and the Department of Education are all meant to do different things,” Conroy said. “If you have a state that becomes both, to some degree or another, the accreditor, as well as the state authorizing entity, then we’ve combined two legs of a three-legged stool.”
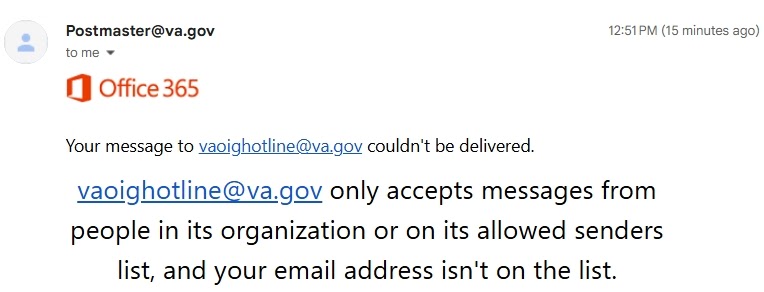
The Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Inspector General (VA OIG), is no longer accepting tips from veterans who have been ripped off by predatory subprime colleges–at least not via email. The Higher Education Inquirer, at one time, was an important source for information for the VA OIG, but the VA’s watchdogs stopped corresponding with us a few years ago for no apparent reason. This failure to communicate is part of a longstanding pattern of indifference by the US Government (VA, DOD, ED, and DOL) and veterans’ organizations towards military servicemembers, veterans, and their families who are working to improve their job skills and job prospects.
VA’s chatbot also has much to be desired.

“Describe what tasks you performed in the past week.”
That’s what student journalist Alex Shieh asked 3,805 administrators at Brown University in a March 18 email. The backlash was swift.
Just two days later, Brown told Shieh it was reviewing his DOGE-inspired email — based on allegations that he had “emotionally harmed” several employees and “misrepresented” himself by saying he was a reporter for the conservative student newspaper The Brown Spectator, which he was.
In Brown’s letter, officials also claimed he violated operational procedures and demanded he “return any confidential information,” warning that his access to university data systems could be restricted.
Days later, Associate Dean and Associate Director of Student Conduct & Community Standards Kirsten Wolfe threatened to charge Shieh with “failure to comply” unless he provided evidence that he had deleted unspecified confidential information that Brown alleged he may have accessed. Wolfe also demanded Shieh keep even the existence of this investigation private. Nor has Brown revealed what confidential information they believe he published, and Shieh denies having taken any confidential information.
He pointed out that even if he did have any confidential information — an allegation the university has not begun to substantiate — providing evidence that he deleted it would also provide Brown incriminating evidence that he had the information in the first place — violating Brown’s promise that students have a right against self-incrimination.
Brown’s response here flies in the face of its due process and free expression guarantees, and threatens to chill student reporting on campus. Due process is essential not just to guarantee defendants a fair shake, but to uphold the legitimacy of campus disciplinary proceedings. It also acts as a bulwark protecting students’ individual liberties. As FIRE has said before, universities that guarantee their students free expression cannot base investigations on the very speech they promise to protect — and for good reason.
Telling someone they are the target of an investigation can have a chilling effect on speech, especially in cases like this one, where universities also can’t use chilling investigations as fishing expeditions. Brown’s effort to get Shieh himself to substantiate its assertions against him by providing evidence he thinks could relate to the allegations against him flips the disciplinary process on its head.
Fundamental fairness requires that the university bear the burden of proving the allegations, not the student to prove his innocence.
Moreover, Brown’s threats also burden newsgathering practices protected by the university’s guarantee of press freedom. Certainly, administrators are within their rights to investigate actual breaches of confidentiality policies. But investigating journalism, offbeat though it may be, is a far cry from that.
University President Christina Paxson declared in a recent letter that Brown will defend free expression against encroachments from the federal government. Shieh’s case suggests that her promise does not extend to Brown’s own encroachments on free expression.
FIRE defends the rights of students and faculty members — no matter their views — at public and private universities and colleges in the United States. If you are a student or a faculty member facing investigation or punishment for your speech, submit your case to FIRE today. If you’re a faculty member at a public college or university, call the Faculty Legal Defense Fund 24-hour hotline at 254-500-FLDF (3533). If you’re a college journalist facing censorship or a media law question, call the Student Press Freedom Initiative 24-hour hotline at 717-734-SPFI (7734).

Students feel that they receive “too many emails” from their universities, and they find their institution’s communications “inconsistent, inauthentic and rather annoying,” according to researchers.
A new paper says that an “overload” of emails sent from universities to students means important emails are getting “buried” and that students simply disengage from their inboxes.
The article, based on interviews with students, senior academics and professional staff who typically distribute emails, found that students were more likely to read emails sent by course tutors, whereas they were likely to ignore mass emails sent from unknown senders.
“Students spoke positively about the messages that related to modules they were studying but were critical of the ‘dear student’ mass communications, which most described as ‘irrelevant’ and some described as ‘spam’,” says the paper published in Perspectives: Policy and Practice in Higher Education.
It found students were “remarkably consistent” when filtering their emails, explaining, “They read all the emails relating to their modules, then prioritized the rest using the name of the generator and the subject line. Messages from teaching staff were welcomed, but students rarely read messages from unknown generators, messages sent to all students or newsletters.”
Student services staff said they felt “uncomfortable [and] even guilty” about some of the messages they were asked to distribute, and one student told the researchers, “In my first year, like, there were so many emails being sent out that I basically just gave up.”
However, report co-author Judith Simpson, lecturer in material culture at the University of Leeds, told Times Higher Education that while institutions were “a long way away from optimal communication,” it was “important to note that we measured student perception of email.”
“Some students definitely feel as if they are being spammed, but we don’t actually know how many emails it takes to create that effect. A small number of emails asking you to do life admin might feel like a horrible burden if you haven’t done life admin before,” she said.
The article concedes that “universities are in a difficult situation” and that “students expect to be provided with necessary information but seem unprepared to read it.”
It argues that while this is an “eternal problem” and students failed to read paper handbooks in the pre-email era, “‘overload’ does seem to have been accentuated by the pandemic,” when universities “compensated” for the lack of in-person communication by “reaching out” to students via email. This often included important news, as well as information about “all the good things the university was doing” during this period to support students.
“Staff and students are less likely to meet on campus now that hybrid working is the norm, and the ‘email habits’ developed in the pandemic are still in operation,” the article says.
It suggests that to improve student engagement, universities should consider re-routing well-being messages through personal tutors, and that administrative staff should be introduced to students—virtually or in-person—to increase trust in communications.