by CUPA-HR | January 11, 2023
As previous research from CUPA-HR has shown, America’s colleges and universities are in the midst of a talent crisis, as many employees are considering other employment opportunities due to a number of factors. As a follow-up to the initial findings of CUPA-HR’s 2022 Higher Education Employee Retention Survey, CUPA-HR has released new findings focused specifically on those in supervisory roles, and the data show that many supervisors are overwhelmed, under-resourced, and struggling to fill positions and maintain morale.
The newly published report, The CUPA-HR 2022 Higher Education Employee Retention Survey: Focus on Supervisors, explores supervisors’ likelihood of looking for new employment, their current challenges and working environments, and which job aspects specific to supervisors are associated with their retention. The report analyzes data from the 3,815 higher ed administrators, professionals and non-exempt staff, most (57 percent) of whom were supervisors, who responded to CUPA-HR’s 2022 Higher Education Employee Retention Survey.
Findings
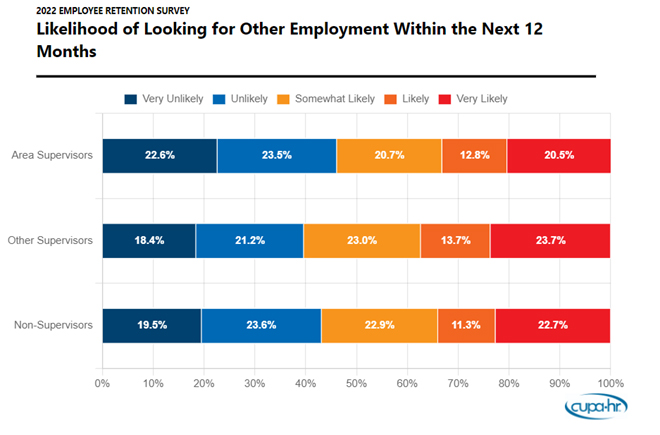
Higher ed supervisors are looking for other employment opportunities, and less than half would seek new opportunities at their current institution. Nearly two in five (36 percent) supervisors indicate they are likely to look for other employment in the next 12 months, and only 40 percent say they would seek job opportunities at their current institution. The most common cited reason for seeking other employment is pay.
 Most higher ed supervisors work long hours and have absorbed more duties since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Data show that supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to work additional hours. Fewer than half (47 percent) of non-supervisors work more hours than what is considered full-time. However, 89 percent of area supervisors and 76 percent of other supervisors work more hours per week than what is considered full-time at their institution. Additionally, supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to agree that they have absorbed additional responsibilities of other staff who have left the institution since the onset of COVID-19. Supervisors are also more likely than non-supervisors to report that they experienced an increase in job expectations since the start of the pandemic.
Most higher ed supervisors work long hours and have absorbed more duties since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Data show that supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to work additional hours. Fewer than half (47 percent) of non-supervisors work more hours than what is considered full-time. However, 89 percent of area supervisors and 76 percent of other supervisors work more hours per week than what is considered full-time at their institution. Additionally, supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to agree that they have absorbed additional responsibilities of other staff who have left the institution since the onset of COVID-19. Supervisors are also more likely than non-supervisors to report that they experienced an increase in job expectations since the start of the pandemic.
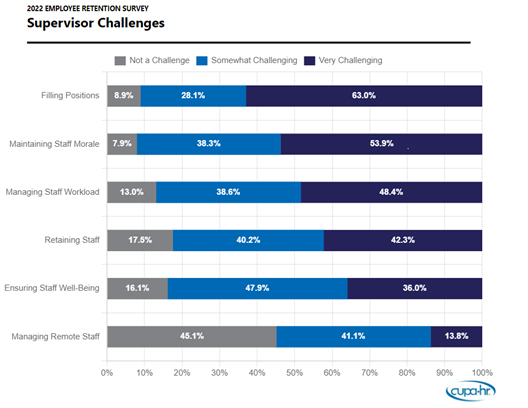
Filling positions and maintaining morale are supervisors’ top challenges. As shown in the figure below, almost two-thirds (63 percent) of supervisors indicated they find filling positions very challenging and over half (54 percent) found maintaining staff morale very challenging.
Higher ed supervisors report a lack of adequate training and support. Only three in five supervisors agree that they have resources and support in their supervisory role. Less than half (46 percent) agree that they have been provided with adequate management training for their supervisory role. However, when supervisors have more resources and support in their supervisory roles, more power to advocate for their staff, more power to allow flexible schedules, and more power to allow their staff to work remotely, they are less likely to seek other employment.
Implications of Supervisor Turnover and How to Combat It
Turnover in any role can impact an institution due to loss of talent, institutional knowledge and team or interdepartmental rapport. However, turnover in a supervisor role has more far-reaching implications. Supervisor turnover also impacts direct reports, who must adjust to a new supervisor and may need to adapt to new team priorities and vision. Loss of supervisors also equates to a loss of leaders who are key to succession plans.
In light of what the data show, there are several actions higher ed institutions can take to keep their supervisors:
- Provide supervisors with resources and support in their capacity as supervisors, particularly around filling empty positions and managing staff morale.
- Ensure supervisors have the ability, knowledge and resources to advocate for their staff.
- Give supervisors more autonomy to determine their staff’s working arrangements, as the data show that supervisors who have more power to allow their staff to work remotely and have flexible schedules are less likely to seek other employment.
- Commit to reducing supervisor workload.
- If possible, raise salaries for supervisors (but not at the expense of non-supervisors).
For a deeper look into the data, read the full report.
Note: In the findings, “area supervisors” refer to those supervisors who are the top-most leaders in their department, units or areas (self-identified in the survey; 26 percent of respondents). “Other supervisors” are those who self-identified as having at least one direct report but were not the top-most leader in their department (31 percent of respondents). “Non-supervisors” are those employees who have no direct reports (43 percent of respondents).
CUPA-HR Research
CUPA-HR is the recognized authority on compensation surveys for higher education, with its workforce surveys designed by higher ed HR professionals for higher ed HR professionals and other campus leaders. CUPA-HR has been collecting data on the higher ed workforce for more than 50 years, and we maintain one of the largest workforce databases in existence. CUPA-HR also publishes numerous research publications and interactive graphics highlighting trends and issues around higher ed workforce planning, pay equity, representation of women and racial/ethnic minorities and more. Learn more about CUPA-HR research.
Share This Article:





 Most higher ed supervisors work long hours and have absorbed more duties since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Data show that supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to work additional hours. Fewer than half (47 percent) of non-supervisors work more hours than what is considered full-time. However, 89 percent of area supervisors and 76 percent of other supervisors work more hours per week than what is considered full-time at their institution. Additionally, supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to agree that they have absorbed additional responsibilities of other staff who have left the institution since the onset of COVID-19. Supervisors are also more likely than non-supervisors to report that they experienced an increase in job expectations since the start of the pandemic.
Most higher ed supervisors work long hours and have absorbed more duties since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Data show that supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to work additional hours. Fewer than half (47 percent) of non-supervisors work more hours than what is considered full-time. However, 89 percent of area supervisors and 76 percent of other supervisors work more hours per week than what is considered full-time at their institution. Additionally, supervisors are more likely than non-supervisors to agree that they have absorbed additional responsibilities of other staff who have left the institution since the onset of COVID-19. Supervisors are also more likely than non-supervisors to report that they experienced an increase in job expectations since the start of the pandemic.