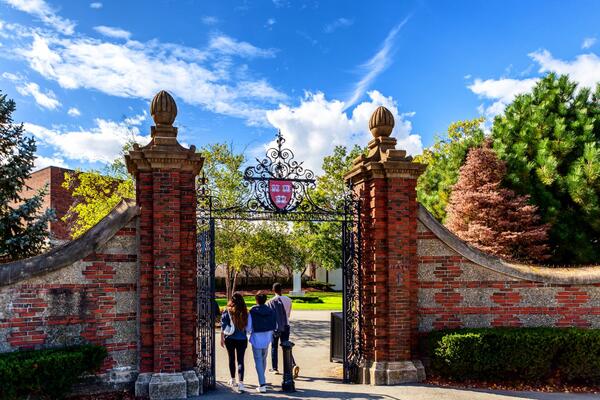
International students make up more than one-quarter of Harvard’s student body.
APCortizasJr/iStock Unreleased/Getty Images
Less than a day after having its ability to host international students revoked by the federal government, Harvard University successfully sued the Trump administration to block the move. A judge granted a temporary restraining order late Friday morning.
Department of Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem announced Thursday afternoon that the Trump administration had stripped Harvard’s Student and Exchange Visitor Program certification in a letter that vaguely accused Harvard of a “failure to adhere to the law.”
However, the letter did not name any specific violations of the law by Harvard.
On Friday morning, Harvard threw a legal counterpunch, filing a lawsuit challenging the revocation of SEVP certification and seeking a temporary restraining order to halt the action, which could cost Harvard to suddenly lose more than 6,000 students if they are unable to enroll. (International enrollment typically makes up about a quarter of Harvard’s head count.) Beyond blocking new enrollments, the revocation would require current international students to transfer.
Harvard president Alan Garber blasted the SEVP revocation as “unlawful and unwarranted” and said it was a punitive effort by the Trump administration in response to Harvard’s rejection of demands to reform governance, admissions, hiring processes and more following allegations of antisemitism and harassment that stemmed from pro-Palestinian protests last year. (Harvard filed a separate lawsuit pushing back on those demands last month, prompting the Trump administration to retaliate by freezing $2.7 billion in grants and contracts, or about a third of its federal research funding.)
“It imperils the futures of thousands of students and scholars across Harvard and serves as a warning to countless others at colleges and universities throughout the country who have come to America to pursue their education and fulfill their dreams,” Garber wrote in a message to campus.
He added, “We will do everything in our power to support our students and scholars.”
Harvard’s lawsuit echoed Garber’s points in an even sharper tone, accusing the federal government of blatantly violating the First Amendment and Harvard’s due process rights.
“With the stroke of a pen, the government has sought to erase a quarter of Harvard’s student body, international students who contribute significantly to the University and its mission,” lawyers representing Harvard argued in Friday’s early-morning legal filing.
Harvard’s lawsuit named DHS, Noem and other officials within the department as defendants, as well as the U.S. Departments of Justice and State and agency leaders.
Assistant DHS secretary Tricia McLaughlin fired back at Harvard in a response to Inside Higher Ed.
“This lawsuit seeks to kneecap the President’s constitutionally vested powers under Article II. It is a privilege, not a right, for universities to enroll foreign students and benefit from their higher tuition payments to help pad their multibillion-dollar endowments. The Trump administration is committed to restoring common sense to our student visa system; no lawsuit, this or any other, is going to change that. We have the law, the facts, and common sense on our side,” she wrote.
Another Legal Setback
A judge swiftly agreed with Harvard’s argument, signing off on the temporary restraining order to prevent revocation of the university’s SEVP certification within hours of the lawsuit being filed.
In a brief opinion, a district court judge in Massachusetts wrote in response to Harvard’s legal filing that the temporary restraining order was “justified to preserve the status quo.” The judge blocked DHS from stripping SEVP certification, at least temporarily, and granted a hearing.
A date for the hearing was not specified in court documents.
The temporary restraining order is one of multiple legal setbacks the Trump administration has faced recently as it has sought to pull student visas over minor infractions (and for constitutionally protected speech), cap federal research funding reimbursement rates, and slash staff at the Department of Education and other agencies. Many of those efforts face ongoing challenges.
On Thursday, for example, a federal judge barred the Trump administration from firing thousands of Department of Education employees as part of a sweeping reduction of force.
The federal government has already appealed that decision.
‘Do This Everywhere’
The Trump administration’s latest action against Harvard prompted broad condemnation from academics and free speech groups, who argued that the federal government did not follow legal processes for stripping SEVP certification and had ignored the university’s due process rights.
“The administration has clearly targeted Harvard in recent months. In doing so, it has violated not only Harvard’s First Amendment rights, but also the rights of the university’s students and faculty,” the free speech group Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression wrote in a Friday social media post. “We commend Harvard for standing up for itself. Free speech and academic freedom are essential to higher education. They are values worth fighting for.”
Despite widespread concerns from academics and lawyers that stripping Harvard’s SEVP certification is not legal, multiple Republican officials have endorsed Noem’s actions.
Rep. Randy Fine, a Republican who represents Florida and a member of the House Education and the Workforce Committee, cheered on the move in a Friday appearance on FOX Business. Fine, a two-time Harvard graduate, said the Trump administration should “do this everywhere” amid concerns about antisemitic behavior and harassment on college campuses.
Fine also took a dim view of international students exercising their First Amendment rights.
“We should not be bringing people into America to get an education who hate us. They should be coming here to get an education, and frankly they should keep their mouths shut beyond that. I don’t go into someone else’s house and complain about it when I’m there,” Fine said.