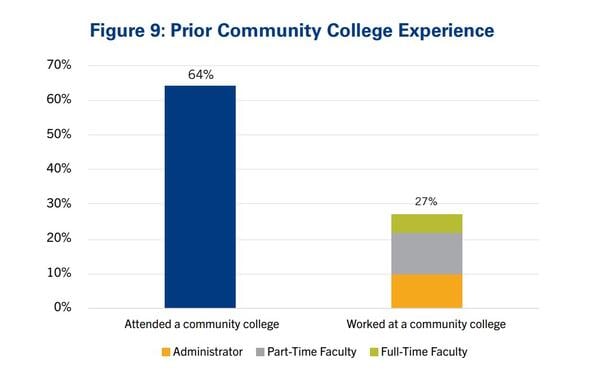
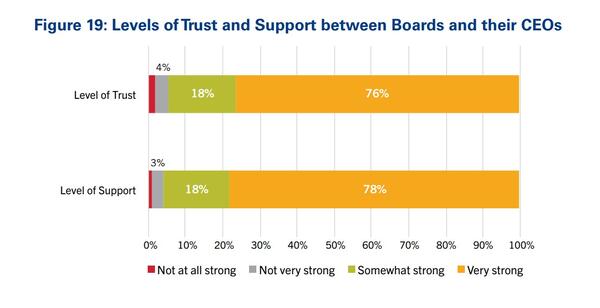
In late 2023, Robin Baker made the career pivot from assistant professor at OHSU-PSU School of Public Health to learning designer at Dartmouth College. I asked if Robin would be willing to share some thoughts about her career path, and she graciously agreed.
Q: What motivated you to shift from a traditional faculty position into a learning designer role? What preparation and background did you bring to the work of a learning designer, and what advantages and challenges have been posed by coming from a faculty role?
A: I decided to transition from a traditional faculty role to a learning designer position after considerable reflection on what I wanted my work and life to look like. I was in a soft money–funded position, where success often felt tied to research output and securing grants. But in practice, most of my energy went into teaching and supporting students, the parts of the job that truly mattered to me. Over time, I began to realize that the pace and structure of that kind of academic role were not sustainable for me in the long run. As I thought more deeply about what aspects of my work I found most rewarding, I realized that, in addition to teaching and mentoring, I found immense satisfaction in designing learning experiences that were inclusive, authentic and relevant. I often spent significant time redesigning assignments and activities to make them more engaging and meaningful for my students. Learning design offered a way to stay connected to the core of what I value: teaching, learning and student success.
I brought to this role a strong foundation in pedagogy, assessment and curriculum design, developed through years of intentionally reflecting on my teaching. Whenever I noticed a strategy fell flat, I dug into the literature and experimented with new approaches, refining my practice based on evidence and observation. Another advantage that my previous life as a faculty member has provided me is that I have developed empathy and practical insight into the challenges that faculty face when trying to create robust learning experiences, provide meaningful feedback and maintain a work-life balance. I have found that acknowledging those realities and engaging in open, honest dialogue helps build trust and leads to more creative and effective solutions. Coming from a faculty background has allowed me to serve as a bridge between teaching practice and design strategy.
At the same time, that transition has come with some challenges. In my faculty role, I was accustomed to being the sole decision-maker for my courses, so adapting to a highly collaborative environment, where I needed to influence others without formal authority, was a major shift. In this context, I had to develop strong project-management skills, work within structured timelines and production workflows, and communicate clearly across teams. Learning to navigate these processes and contribute meaningfully without directing every decision was initially difficult, but it strengthened my ability to work strategically, build consensus and support high-quality learning experiences in partnership with others.
Q: Having now experienced life as both a full-time professor and full-time learning designer, how do the two roles compare and contrast? For someone trained for research and employed mostly in teaching (as most Ph.D.s are), what recommendations might you have for anyone else contemplating a similar career path?
A: Having experienced life as both a full-time professor and now as a full-time learning designer, I see both roles as connected by a shared commitment to improving student learning, though they differ in scope and kind of impact. As a faculty member, I had a very immediate connection with students: teaching, mentoring and witnessing their growth in real time. That direct engagement was deeply rewarding and energizing, but it also came with heavy workloads, administrative pressures and blurred boundaries. Over time, I found that level of intensity difficult to sustain, which prompted me to reflect on the kind of work-life balance and long-term impact I wanted.
As a learning designer, the work feels broader and more strategic. Instead of focusing on one group of students, I now collaborate with faculty across disciplines to design courses and learning environments that enhance teaching and learning for many more students. The impact is less direct but often greater in scale, as it shapes the systems and supports that enable effective teaching.
At the same time, I think it is important to acknowledge that the loss of direct connection with students can be a real adjustment. There is something uniquely special about witnessing students’ aha moments and seeing the immediate results of your teaching. As a learning designer, that feedback loop is more indirect. Faculty are often very appreciative of our collaboration, but it does not carry quite the same emotional resonance as seeing students thrive firsthand. For anyone considering this transition, it is worth reflecting on how central that kind of direct engagement is to their sense of purpose and whether there are other ways, such as mentoring colleagues, engaging in professional development or contributing to the broader learning community, to fill that gap.
Another concern I often hear from faculty considering this path is the fear of losing autonomy, particularly the flexibility to structure their own days or pursue creative ideas. In my experience, that depends heavily on the team and institutional culture. In my current role, which is largely remote and hybrid, there is a genuine appreciation for the whole person. We are trusted to manage our time and energy, and that autonomy is still very much present.
The difference is that I now have a healthier kind of control. I set realistic goals for what I can achieve in a given day, while being careful not to let work bleed into personal or family time. That structure allows me to work efficiently and intentionally and it has given me space to reconnect with family, friends, community and nature. For anyone thinking about making this transition, it’s worth having open conversations about team expectations, workflows and culture. Understanding these aspects up front can help you gauge whether the role is a good fit and set you up for long-term satisfaction.
Q: Recently, you took on an additional role as course co-director of the Capstone for the Dartmouth M.H.A. program. How does that work integrate with your learning design role, and how have you been able to balance both responsibilities?
A: In many ways, my role as course co-director is a meaningful complement to my work as a learning designer. In this role, I serve as one of the faculty for the capstone course, guiding students as they pull together what they’ve learned across the program and apply it to complex, real-world challenges. It’s been incredibly rewarding to reconnect directly with students, something I’d missed since stepping away from a full-time faculty role.
What makes this role even more meaningful is that I was one of the learning designers who helped faculty develop many of the courses in the M.H.A. program. Now, I get to see that work come full circle. It provides me with a unique perspective on how our strategies are implemented in practice and highlights opportunities to further refine the learning experience.
I also appreciate how this teaching role complements, rather than competes with, my work in learning design. My design experience informs how I approach the capstone, helping me think carefully about scaffolding, alignment and authentic assessment. At the same time, teaching keeps me connected to the student perspective, giving me a firsthand understanding of how learners experience our courses. That insight flows directly back into my design work and strengthens my collaborations with faculty.
Balancing both roles does require intentional structure and realistic expectations. I’ve learned to be clear about what I can reasonably accomplish each week and to protect time for rest, family and personal commitments. I rely on block scheduling to focus on design projects, faculty consultations and capstone mentoring, while making sure these blocks don’t spill into evenings or weekends. Maintaining these boundaries has been essential for sustaining both quality and balance.
I’m also fortunate to have supportive leadership in both the learning design team and the M.H.A. program, who recognize the value of these complementary roles. That culture of trust and flexibility makes it possible to do both well.
In many ways, this dual role gives me the best of both worlds: the broader, systemic perspective of learning design and the direct, human connection of teaching. Together, they keep me grounded in why this work matters and allow me to contribute to both faculty and student success in meaningful, sustainable ways.