We’re rounding up last week’s news, from the government shutdown’s impact on schools to differentiated teacher compensation.
Tag: Expansion
-

Advanced manufacturing expansion opens CTE opportunities for rural schools
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.Dive Brief:
- Through strong industry partnerships and career and technical education, rural schools can equip their students for growing workforce needs in advanced manufacturing.
- Advanced manufacturing in the U.S. is undergoing a period of rapid expansion, with an anticipated $1 trillion investment in projects, 63% of which is expected to be allocated to facilities near rural communities, according to an analysis from the McKinsey Institute for Economic Mobility.
- The McKinsey Institute also surveyed nearly 1,500 rural high school students and recent graduates, finding that 8 in 10 would like career-connected learning and apprenticeship opportunities. However, only 5 in 10 reported having access to career-connected learning in high school, and only 3 in 10 had access to apprenticeships.
Dive Insight:
The report highlights that as advanced manufacturers expand into rural America, they play a crucial role in fostering strong relationships with local school systems.
Advanced manufacturing industry experts and companies are seeking workers with foundational, technical and durable skills, the report found. However, there seems to be a short supply of these skill sets across the manufacturing labor pool.
One cause of this shortage, the report argues, is a lack of strong, established collaborations between the industry and K-12 schools. The industry’s need for well-equipped future workers could also meet the needs of K-12 schools to expand students’ career opportunities.
Research has found that taking CTE courses can lead to higher graduation rates and greater employment opportunities, which is why industry and rural schools can work together to provide K-12 students with the necessary education and technical skills to enter the incoming workforce, the report noted.
To ensure that students are learning these high-demand skills, employers and industry associations should provide apprenticeships and other workplace learning opportunities for rural schools, as well as help create industry-relevant curricula, the report explained. A strong collaboration benefits not just schools and students, but companies that are also securing a pipeline of prepared workers.
The report recommends that school systems work with local governments and organizations to build connections with employers. Through strong partnerships with industry professionals, schools can develop more effective, career-connected and evidence-based models, the report said.
CTE courses provide students with hands-on, real-world skills for a defined set of careers, and an effective course focuses on skills in demand in the local market. As manufacturing investments grow in rural communities, the report said, schools could offer CTE courses that prepare students with technical and other STEM-based skills necessary in the advanced manufacturing field.
The report also emphasized that industry partners should have regular interaction with students and touch base with them at regularly scheduled intervals. This ensures students are consistently aware of the different career pathways available to them. These interactions can evolve as students advance through different grades, shifting from informational to more tangible resources like apprenticeships, summer jobs and postsecondary scholarships later in high school.
Beyond industry partnerships, state legislatures can also offer incentives for CTE programming through policies and funding, the report recommends. States are already providing these types of incentives, with 40 states collectively approving more than 150 policies focused on boosting CTE programming in 2024.
-

Shortage of Rural Private Schools Complicates Indiana’s Voucher Expansion – The 74
Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
Sitting on the Kentucky border, the Christian Academy of Indiana draws students from 56 different ZIP codes in southern Indiana. Some come from as far as 30 miles away and live in counties without private schools.
Families in those distant communities make the drive every day — sometimes carpooling — because they’re drawn to the school’s environment and extracurriculars, and especially its Christian teaching, said Lorrie Baechtel, director of admissions for the school, which is part of a three-school network in Indiana and Kentucky.
“There are lots of good public school options in Indiana. Families come to our Indiana campus more for that mission,” Baechtel said.
The school’s enrollment has boomed in the last four years, driven in part by the expansion of the Choice Scholarship, Indiana’s signature voucher program. That’s made tuition more affordable, Baechtel said. More than 1,200 students attended in 2024-2025, up from around 700 in 2021-22.
That reflects a statewide trend: Voucher use has surged in recent years as Indiana lawmakers loosened eligibility requirements. In 2026, the program will open to all families, regardless of income.
But the Christian Academy’s ability to attract students from far away tells another story too. Even as vouchers have become more accessible, Indiana’s rural students aren’t using them at the same rate as their urban and suburban peers. That’s in part because one-third of counties don’t have a private school that accepts vouchers within their borders, and distance is a factor in parents’ decisions on school choice.
The result is that students who live closer to an urban center — which typically have one or more voucher-accepting private schools — may use vouchers at rates up to 30 percentage points higher than those for students who live in a neighboring district.
That also means rural families may be at a significant disadvantage when the state opens the Choice Scholarship to all, and when private school scholarships funded by new federal tax credits also begin to roll out in 2027.
“If there are no schools there for you to attend it’s unlikely it’s going to be all that useful for you,” said Jon Valant, director of the Brown Center on Education Policy at the Brookings Institution.
More than that, public education advocates say splitting state school funding with vouchers leaves less for the rural public schools these students do attend.
“We’re making the policy choice to fund a lot more choices than we used to,” said Chris Lagoni, executive director of the Indiana Small and Rural Schools Association, which represents public schools. “We’re inviting more and more folks to Sunday dinner. It’s a little bit of a bigger meal, but a lot more guests.”
But the state’s Republican lawmakers have dismissed the fears of a hit to public rural schools as a result of vouchers, saying that rural voters support choice and parents want educational options — whether that’s private, charter, or traditional public schools.
Meanwhile, school choice advocates say the latest expansion of the Choice Scholarship, along with a growing preference for smaller learning environments and the rise of voucher-accepting online schools, could mean more private school access for rural areas in the near future.
“I think we’re best when we have a robust ecosystem of private and public options,” said Eric Oglesbee of the Drexel Fund, a nonprofit venture philanthropy organization that funds new private schools in Indiana and throughout the U.S.
Location matters in accessing a private school
Across the state, around 76,000 students received vouchers for the 2024-25 school year — an increase of about 6,000 students from the year before. The program cost the state $497 million last year, and the average voucher recipient came from a household with just over $100,000 in income.
But around one-third of Indiana counties don’t have voucher-accepting private schools within their borders, according to a Chalkbeat analysis of state data, which also shows that voucher use is lower in rural areas than urban ones.
Voucher use can shift dramatically even between nearby areas. For example, around 16% of students who reside in the Madison school district in southern Indiana use vouchers, but that rate drops to as low as 1% in nearby districts that are more rural. Similar trends hold in other areas of the state, like Indianapolis, Evansville, Fort Wayne, and South Bend.
Location matters because driving distance has been shown to be a factor in how parents choose a school.
In a 2024 survey of parent preferences by EdChoice, an Indianapolis-based group that supports vouchers, around half of parents said they would drive a max of 15 minutes for their children “to attend a better school.” Just over a quarter said they would drive no more than 20 minutes, and the final quarter said 30 minutes would be their max.
Concerns about this issue have persisted in the state for years. Alli Aldis of the advocacy group EdChoice pointed to a 2018 report from her organization that called areas of rural Indiana as “schooling deserts.” It estimated that in the 2017-18 school year, around 3% of Indiana students, many in rural counties, lived more than 30 minutes from a charter, magnet, or voucher-accepting private school.
Starting a new school anywhere, but particularly in a rural area, comes with challenges like finding a building, said Oglesbee of the Drexel Fund.
A 2023 Drexel Fund report found that facilities in the state are “inadequate to meet the needs of new entrants to the market.” Though the report notes that real estate is both affordable and available, there are no public sources of facilities funding, and surplus facilities are not available to private schools.
But new laws in Indiana have the potential to change that. House Enrolled Act 1515 established voluntary school facility pilot programs open to both public and private schools to “allow for additional flexibility and creativity in terms of what is considered a school facility,” like colocating with schools, government entities, and community organizations.
Oglesbee said the organization is fielding an explosion of interest from potential new private schools in Indiana, possibly as a latent result of the 2023 expansion to voucher eligibility, which made the program nearly universal.
School succeeds ‘if the community asks for it’
Other challenges to opening a private school include hiring staff and recruiting students, which can be a particular issue in rural areas with both fewer children and licensed teachers, advocates said.
Opening a school also requires a team of people with both education and business experience, Oglesbee said. And they’re more likely to succeed if they have roots in the community they hope to serve.
“I see less of the ‘if you build it, they will come’ idea,” Oglesbee said. “A school is successful if the community asks for it.”
At a recent conservative policy conference, Indiana House Speaker Todd Huston said rural Indiana communities were “super excited” for school choice, and noted that no Republican lawmaker had been beaten in a primary for supporting the policy.
But Indiana voters haven’t voted on school vouchers, and don’t have a legal avenue to overturn the policy, said Chris Lubienski of the Center for Evaluation and Education Policy at Indiana University. Last year, voters in Kentucky and Colorado rejected ballot measures in favor of school choice, while Nebraska voters partially repealed a state-funded scholarship program.
“There’s resistance: ‘Why do I want to have my taxes fund a program I can’t use?’” Lubienski said.
In rural areas, support for school choice may actually mean support for transfers between public school districts, said Lagoni.
Ultimately, the Rural Schools Association believes any school receiving state dollars should be subject to the same expectations of transparency and accountability, Lagoni said.
Asked about concerns that rural students often have difficulty using vouchers, Huston said he expects voucher usage to continue to grow once the program becomes universal in 2026-27.
“We want to make sure our policies align with what works best for families,” Huston said.
Vouchers add to financial stress for rural schools
With more school options in Indiana, downward pressure on local tax revenue, and declining population, rural public schools feel pressure to compete. Sometimes that means closing and consolidating schools.
Vigo County schools recently announced plans to close two rural elementary schools as part of a plan to renovate facilities and offer more programming. The school corporation’s enrollment has declined slightly, due in part to an overall decline in the county’s total population, said spokesperson Katie Shane.
More students who reside in the district are using vouchers, although they’re not the biggest reason for the district’s falling enrollment. While 429 students used vouchers to attend private schools last school year, an increase from 252 the year before, around 870 Vigo students transferred to another public school district in the fall of the 2024-25 school year. That reflects a statewide trend.
Without their nearest public elementary schools, students may have to travel by bus for half an hour or more to the nearest school, according to community members who have started a petition to save one of the two schools marked for closure, Hoosier Prairie Elementary School.
“Hoosier Prairie isn’t just about going to school,” said Shyann Koziatek, an educational assistant at the school who also signed the petition to stop its closure. “Kids love to learn and love the routine we have.”
Rural schools also often function as large area employers and drivers of the economy.
“Schools are often the center and identity of the community, how people view who they are,” Lubienski said. “You go and cheer on your football team, it’s where you put on your school play.”
But private schools can serve the same role, choice advocates say.
“If people have stronger educational options, more choices, that only strengthens the community,” said Aldis of EdChoice.
Chalkbeat is a nonprofit news site covering educational change in public schools. This story was originally published by Chalkbeat. Sign up for their newsletters at ckbe.at/newsletters.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
-

7 Trends to Inform Online Program Expansion in 2025
As I reviewed the new IPEDS data release last week, I was looking for the data and intelligence that would be most helpful for online enrollment leaders to have in hand to underpin and inform this year’s success. These points, in combination with key trends that became clear in other sources I reviewed late last year will enable online leaders to succeed this year as well as plan for the future.
Note that I am not discussing changes that may emerge after January 20, but I will be doing so after a long talk I have scheduled with Cheryl Dowd from WCET who tracks online regulations and with whom I will be co-presenting at the RNL National Conference this summer.
So, what do you need to know?
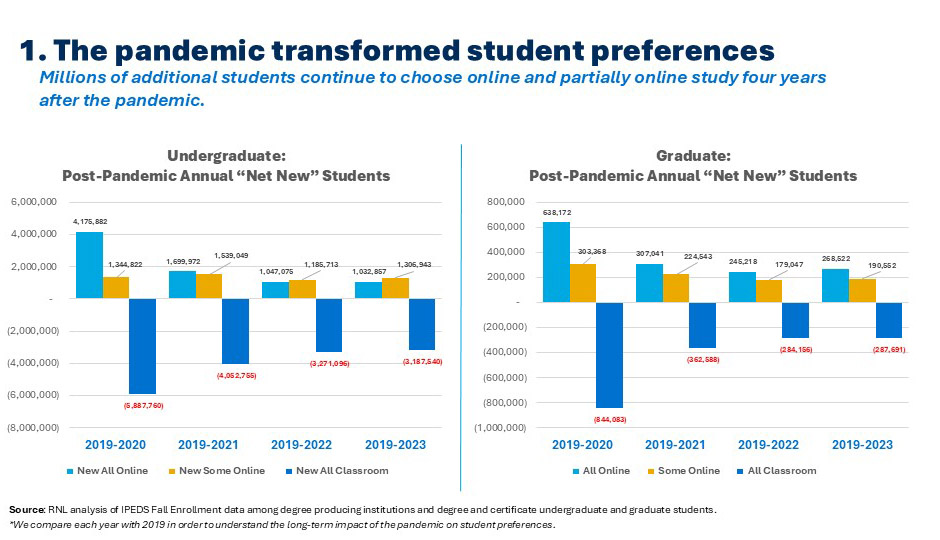
1. Online and partially online enrollment continue to dominate growth.
Four years after the pandemic, more students each year are continuing to decide to enroll in either fully or partially online study. While year-over-year change in every post-pandemic year has seen some “return to the classroom,” when compared with pre-pandemic enrollment (2019), 2.3 million more undergraduates and 450k more graduate students are choosing fully or partially online study. Perhaps more important, 3.2 million fewer undergraduates and 288k fewer graduate students are choosing classroom-only programs. Institutions seeking to grow enrollment must develop processes to quickly determine the best online programs to offer and get them “to market” within 12 months.
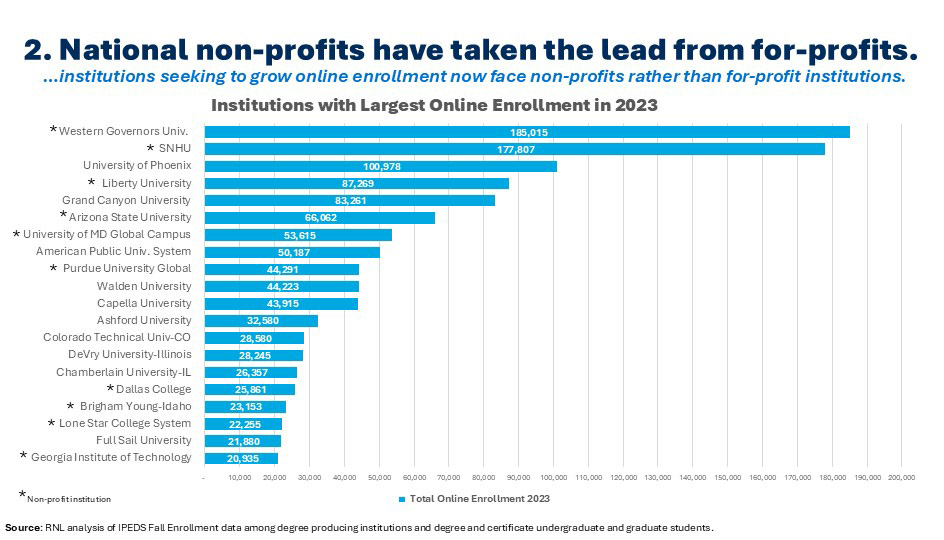
2. Institutions seeking to grow online enrollment are now competing with non-profit institutions.
As recently as five years ago, your strongest competition came from for-profit institutions. In some ways, these institutions were easy to beat (excepting their huge marketing budgets). They had taken a beating in the press to the extent that students knew about it, and they were far away and unknown. Today, institutions face no less of a competitive environment, but the institutions dominating the scene – and most likely a students’ search results – are national non-profits. These institutions are, of course, not local so they aren’t well known, but they have not been through the scrutiny which eroded interest in the for-profits. Student search engine results are also now filled with ambitious public and private institutions seeking to “diversity their revenue streams.” As such, institutional marketers need to adjust their strategies focused on successfully positioning their programs in a crowded market, knowing that they can “win” the student over the national online providers if they ensure that they rise to the top of search results.
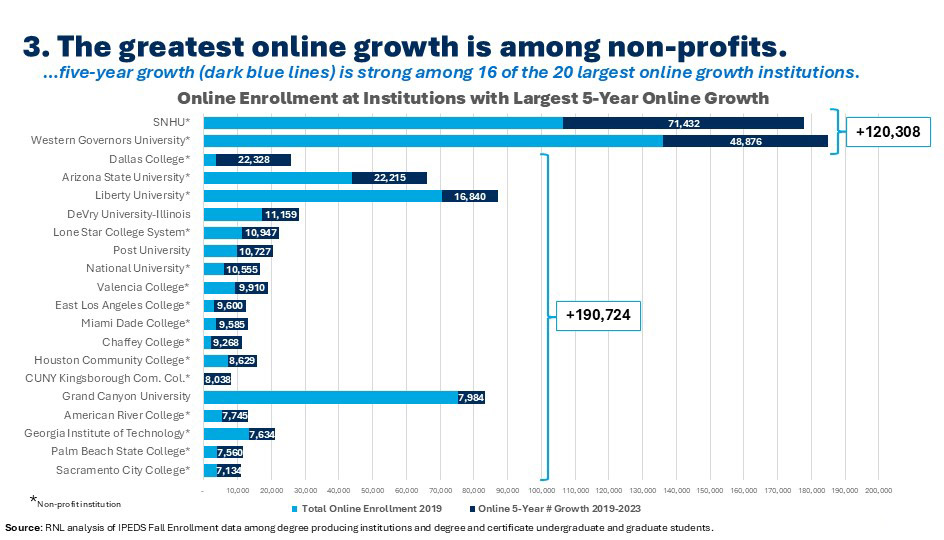
3. Online enrollment growth is being led by non-profit institutions.
Seventeen of the 20 institutions reporting the greatest growth in online enrollment over the last five years are nonprofit institutions—a mix of ambitious public and private institutions and national non-profits. What is more, the total growth among institutions after the two behemoths far exceeds Southern New Hampshire University and Western Governors University. These nimble and dynamic institutions include a variety of institution types (with community colleges well represented) across the higher education sector. Institutions seeking to grow online enrollment should research what these institutions are offering and how they are positioning their programs in the market and emulate some of their best practices.
4. New graduate program growth is dominated by online/partially online offerings.
In 2024, a research study by Robert Kelchen documented growth in the number of available master’s programs in the U.S. over the last 15 years. Not only did Kelchen document a massive expansion in availability (over the 15-year period, institutions launched nearly 14,000 new master’s programs on a base of about 20,000), but also that the pace of launching online or hybrid programs dramatically outpaces classroom programs. This rise in available offerings far outpaces the rate of growth of the online student market, resulting in significantly higher levels of competition for each online student. Institutions seeking to grow their online footprint must ensure that they fully understand both the specific demand dynamics for each of their programs and the specifics of what online students want in their program. A mismatch on either factor will inhibit growth.
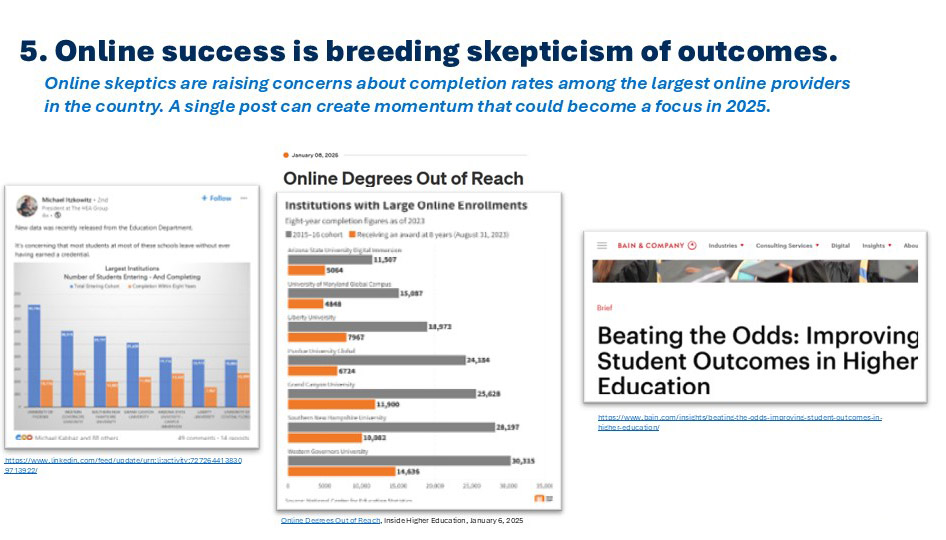
5. Online success is breeding scrutiny of outcomes.
We all know something of the power of social media today. This was reinforced for me recently by an Inside Higher Education story which focused on the 8-year rates of degree completion among the biggest online providers. The story was triggered by a widely read Linked IN post and followed up by numerous other stories and posts and comments across the platform. This is just the kind of exposure that is most likely to generate real scrutiny of the outcomes of online learning – which were already taking shape over the last year or more. In fact, this focus on outcomes ended up as one of the unfulfilled priorities of the Biden Education Department. I have long said that institutions seeking to enter the online space have an opportunity to tackle some of the quality issues that first plagued the for-profits, now challenge the national online non-profits, and will confront others if not addressed soon.
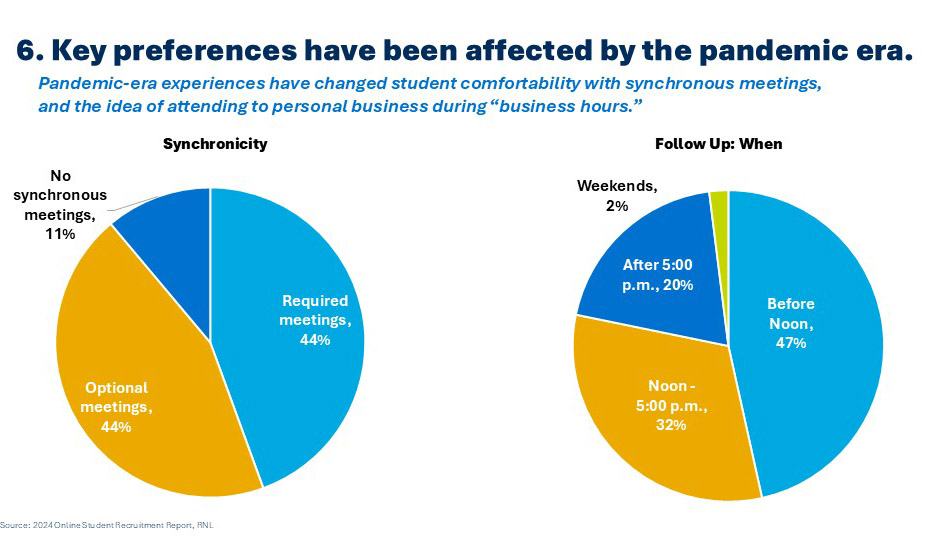
6. Key preferences for online study have been changed by the pandemic.
RNL’s own 2024 online student survey surfaced dozens of important findings that online leaders should consider as they chart their course. Two findings stand out as reflecting profound changes in online student preferences, and both are likely the result of pandemic-era experiences. First, all but 11 percent of online students told us that they are open to at least some synchronous activities in their program, likely the result of hundreds of online meetings during the pandemic. Similarly, they told us that the ideal time to communicate with recruiters/counselors from online programs is now during business hours. This is also likely to be related to the pandemic period, in which millions of people working from home began to regularly contend with some personal business during their day. Institutions should assess both of these factors as they think through student engagement (to address point #5), and the intense competition of the online space (to address point #3).
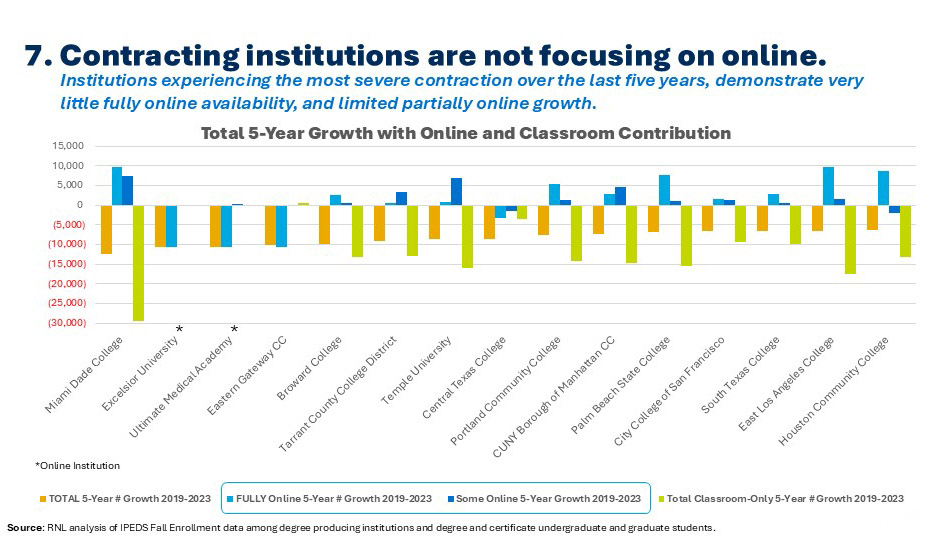
7. Contracting institutions are not focusing on online enrollment.
Finally, we return to the new IPEDS data to see that institutions that have experienced the greatest enrollment contraction over the last five years demonstrate almost no access to fully online study (dark blue lines in the chart below), and only limited access to programs in which students can enroll in both online and classroom courses (light blue lines). Even where there has been some online or partially online growth, these efforts have not been given adequate attention to counterbalance contraction among students enrolled in classroom-only programs (green lines). These data again make it clear (as stated in point #1) that institutions facing classroom-only contraction must either amend their goals to account for reduced enrollment or determine which online or hybrid programs would be most attractive to students in their region and then ensure that such offerings are visible in a highly competitive higher education market.

Explore more at our webinar
Join us for a deeper dive into trends during our webinar, 5 Enrollment Trends You Need to Know for 2025. This discussion with me and a number of my RNL expert colleagues will look at research and trends that should shape strategic and tactical planning over the next 12 months. Particularly, as we enter what has been identified as the first year of the “demographic cliff,” data-informed decision-making will be more important to enrollment health than ever before. Register now.


