The Albanese government has asked universities, researchers and businesses for feedback on joining the world’s largest research program.
Please login below to view content or subscribe now.
Membership Login

The Albanese government has asked universities, researchers and businesses for feedback on joining the world’s largest research program.
Please login below to view content or subscribe now.

Growing public skepticism in higher education has fueled a number of polls and surveys aimed at understanding how families, students and taxpayers perceive the value of a college degree.
For instance, a majority of Americans believe at least one type of postsecondary credential holds value, according to a 2025 study by Gallup, and most parents want their kids to attend college. But few of those studies have looked at how colleges and universities see themselves improving students’ lives.
A new survey by Tyton Partners released Thursday found three in four college stakeholders strongly believe their institution’s education is worth the cost of tuition. However, two-year institutions were more likely to say this is true, compared to private universities.
Only 28 percent of administrators and support staff working at private four-year institutions strongly agree that their institution’s education is worth the cost, compared to 68 percent of community colleges. The survey, fielded in late June and early July, includes responses from more than 1,600 stakeholders at 825 institutions.
The sector breakdown wasn’t a surprise to Catherine Shaw, Tyton’s managing director, in part because of how the vocational missions of two-year colleges to prepare the local workforce compare to four-year private institutions that focus more on holistic student development.
“That part of it was so squarely within the value proposition of the reasons we have two-year degrees,” Shaw said.
For students, there’s a direct relationship between those who say their college is worth the cost and those who think the college prepares students well for jobs and careers. Among the 792 student respondents who do believe their college is worth the cost, 95 percent believe college is preparing them well for jobs and careers. Inversely, fewer than half (48 percent) of students who don’t see the value of their degree believe college is preparing them well for a career.
“In short, perceptions of value hinge on whether institutions effectively prepare students for the workforce,” the report states. This was true regardless of an institution’s sector, size, selectivity or demographic makeup.
This was the first time Tyton’s survey has asked respondents about perceived value, which Shaw said was in part because of larger national studies gauging perceived value among individuals in the U.S.
“It was interesting that there wasn’t the institutional perspective captured at scale [in previous surveys],” Shaw said. “We wanted to contextualize [the conversation] and see if our institutional stakeholders and our students are asking themselves the same questions and how they feel relevant, because they’ve got skin in the game.”
More than a quarter of all institutions pointed to career readiness as a top college outcome beyond earning a credential, but two-year colleges were most likely to say this was the top outcome (37 percent). In comparison, the most popular outcome among four-year public and private institutions was critical thinking skills (41 percent and 36 percent, respectively).
Faculty members were most likely to say critical thinking skills were a top college outcome, which Shaw said makes sense given their role in higher education. Administrators and advisers were more likely to point to career readiness as a top outcome for students.
Tyton’s survey also asked administrators, support staff and faculty members which support services improve students’ value of education. Academic and career advising rose to the top, with over half of respondents in all roles ranking these services higher than tutoring, financial aid counseling or mental health counseling.
How institutions deliver high-impact career preparation varied based on institution type. Thirty-eight percent of community colleges said apprenticeships were the most meaningful measures to improve student employment metrics, followed by career pathways at 35 percent.
In comparison, embedded career exploration ranked highest among four-year institutions (54 percent of public universities, 50 percent of private) as did guaranteed internships for all students (31 percent of four-year public institutions) and experiential learning coursework (33 percent of four-year privates).
Student awareness of these opportunities is the greatest barrier to career readiness, according to career services professionals (45 percent), followed by limited capacity (17 percent) and a lack of consistent programming throughout the year (13 percent). Fewer than half of surveyed students (42 percent) said they were aware of career services available to them.
“This focus is especially timely as institutions prepare for increased scrutiny under new federal measures, such as the earnings accountability test,” the report states. “Programs that do not result in gainful employment risk losing eligibility for federal aid. Embedding career readiness across offerings isn’t just about boosting ROI: It’s fast becoming essential for institutional viability.”

The latest round of engagement is being undertaken “to gather market insights on newly available and emerging technology in relation to remote testing, and the viability of incorporating this into the HOELT service,” said the Home Office in a notice on July 2.
The notice is the latest update to a government tender to design and maintain a dedicated Secure English Language Test (SELT) owned by the Home Office, holding an initial contract value of £1.13bn, which was since reduced to £680m.
The original tender, launched in August 2024, made no mention of engagement on emerging technologies and digital tests, instead outlining plans for in-person delivery, including invigilators and ID-verification services at physical test centres around the world.
As per the latest update, the developer that wins the tender will still be responsible for “establishing and managing global test centres” – of which there are 268 – though the notice suggests that remote testing will also be incorporated into the model.
While the sector has embraced online delivery and at-home testing, the Home Office will also be taking stock of rising concerns among the public about the use of AI in English proficiency tests.
According to a recent YouGov poll, 40% of the public are worried about AI causing a greater risk of cheating on English language tests, with a similar proportion concerned about the ability of AI to properly assess language skills.
The poll, commissioned by Cambridge University Press & Assessment, asked respondents specifically about tests assessing English language skills for people applying to work and study in the UK.
Additional findings revealed the public’s unease at the prospect of limited human interaction and concerns that AI-led exams would disadvantage those with limited access to technology – both cited by roughly a quarter of respondents.
Meanwhile, only 8% said they had “no concerns” about the use of AI in English language tests for people applying to work or study in the UK.
39% of the public are concerned about AI-based tests enabling cheating
YouGov Poll
Under its initial plans, the Home Office proposed disaggregating the service into two lines; the development and ongoing support of a Home Office branded test to be used globally, and the facilitation of tests around the world, according to the tender.
However, the government’s slashing of the value of the tender led some stakeholders to speculate that the Home Office might turn to a single supplier for both development and delivery.
Despite the additional engagement around emerging technologies and remote testing, the value of the tender remains at £680m (excluding VAT).
Since the government put out the HOELT tender last year, there has been little news about which companies are throwing their hats in the ring or what their proposed model would look like.
Currently, Pearson, LanguageCert, Trinity College London, and IELTS – which is co-owned by IDP, Cambridge English and the British Council – deliver Home Office-approved SELTs in the UK.
The deadline for the latest round of engagement is July 17.

by CUPA-HR | May 20, 2025
How has the higher education faculty workforce changed over the past 20 years? What disciplines have emerged as frontrunners in hiring? What disciplines pay the most? What disciplines pay the least?
In the new research report, Two Decades of Change: Faculty Discipline Trends in Higher Education, CUPA-HR presents findings from an analysis of data from its Faculty in Higher Education Survey from 2003-04 to 2023-24.
Some key findings highlighted in the report:
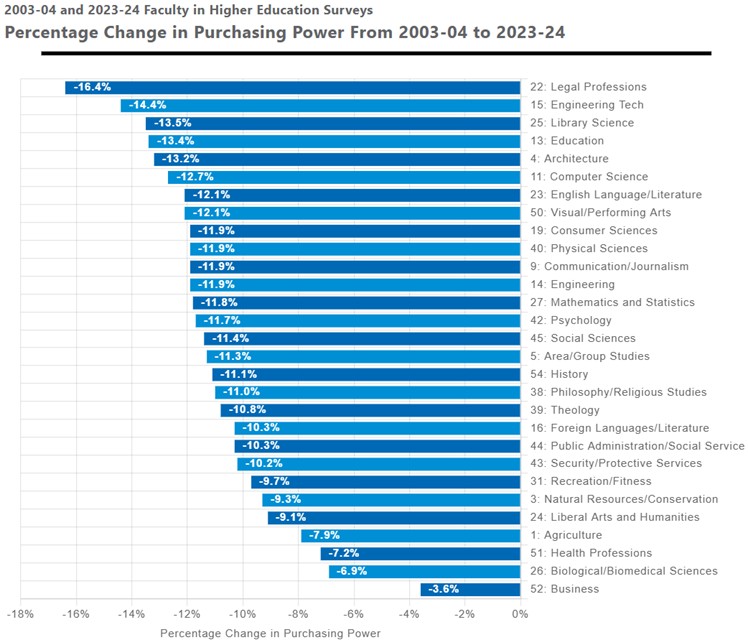
Read the full report and explore the data with interactive graphics.

What can voodoo dolls tell us about the public’s distrust of, and aggression toward, scientists? A new paper has attempted to find out.
Despite a growing fear that global attitudes have hardened toward scientific research, including instances of violence, “virtually nothing is known” about those likely to attack scientists, according to the study, published in Scientific Reports.
The paper, which examined about 750 responses across two different studies, claims to be the first to identify factors associated with an increased likelihood of harassing scientists.
Researchers tested their theories by offering participants a bonus payment of 1 pound ($1.27), which they could gift to themselves or donate to the Union of Concerned Scientists, and by asking them to sign a petition against the harassment of scientists.
Out of the total of £359 ($455) offered, participants opted to donate £69.79 ($88). The study found that political ideology was the best predictor for who would donate, with right-wing individuals contributing less.
The paper also asked those taking part to express their aggression by sticking pins in a digital voodoo doll of a stereotypical scientist—an “old-age male with a lab coat and equipment.”
Participants were asked to “release negative energy” by clicking their mouse, with a higher number of “pins” indicative of more aggressive behavior. It found significant positive correlations with five variables—conspiracy mentality, science cynicism, relative deprivation, threat and attitudes toward harassment.
Lead author Vukašin Gligorić, a Ph.D. researcher in the Department of Psychology at the University of Amsterdam, said across the two studies, distrusting worldviews, political ideology and perception of threat were associated with more approving attitudes toward harassment of scientists.
Notably, the paper found that science cynicism—the belief that scientists are incompetent and corrupt—also drives approval of scientists’ harassment.
In addition, perceiving scientists as threatening, as well as dark personality traits, such as psychopathy and narcissism, contributed to approving harm.
The paper concluded that highlighting reasons why people should trust scientists and not be threatened by them is the most promising way to counter such behavior.
The antiscience movement is a growing trend in some countries, Gligorić told Times Higher Education.
And he said that changing these attitudes will be challenging, because scientists are viewed as part of the “establishment,” which many people around the world are dissatisfied with.
“To address this, I believe scientists should engage more directly with the public … rather than for private or corporate interests, which erode trust.
“Ultimately, people are cynical about the political and economic systems we live in, and they sometimes blame scientists as part of that system. Therefore, scientists should also be critical of and work to improve the system itself.”