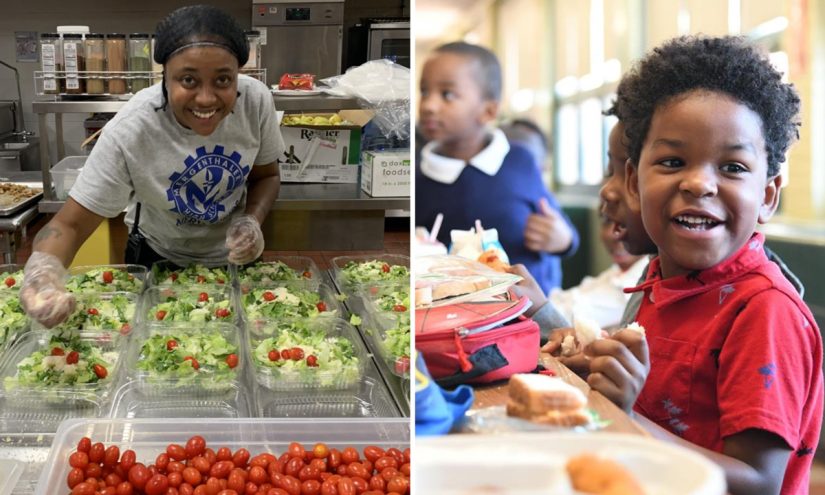
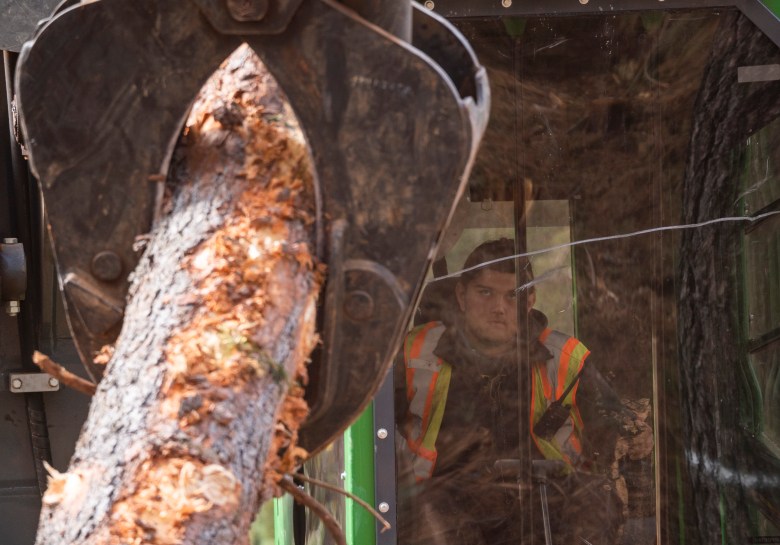
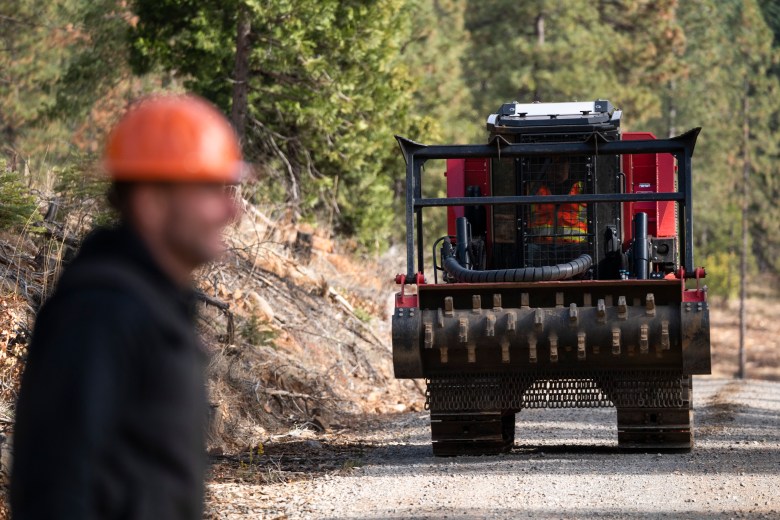
A multi-pronged attack on food aid by Republican lawmakers could mean more of the nation’s children will go hungry — both at home and at school.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture recently cut two federal programs that provided roughly $1 billion in funding for the purchase of food by schools and food banks.
And the Community Eligibility Provision, which reimburses tens of thousands of schools that provide free breakfast and lunch to all students, may tighten its requirements, potentially pushing some 12 million kids out of the program.
These moves come at the same time the House Republican budget plan calls for deep cuts to the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, or SNAP. The program fed more than 42 million low-income people per month nationwide in 2023. In 2022, 40% were younger than 18.
This recent shift reflects a stark reversal of earlier, nationwide efforts to keep families fed during the pandemic. Many districts, such as Baltimore, organized grab-and-go meals sites days after schools were shuttered in March 2020 with no identification or personal information required. Those initiatives led to the nation’s food insecurity rate dropping to a 20-year low when it reached 10.2% in 2021, down from a 14.9% high a decade earlier, according to the USDA.
It has since crept back up to 13.5% and now, five years after schools utilized USDA waivers to deliver meals in innovative ways, they are bracing for what could be massive cuts from the federal government.

Elizabeth A. Marchetta, executive director of food and nutrition services for Baltimore City Public Schools, said 31 campuses — serving 19,000 children — would lose out on free breakfast and lunch if the Community Eligibility Provision changes go through. They are among 393 schools and 251,318 children statewide who would be shut out.
“It would be devastating,” Marchetta said. “These are critical funds. If we are not being reimbursed for all of the meals we’re serving … the money has to come from somewhere else in the school district, so that is really not great.”

Nearly 48,000 schools in more than 7,700 districts benefited from the Community Eligibility Provision in the 2023-24 school year. The program reimburses schools that provide universal free meals based on the percentage of their students who automatically qualify for free and reduced-price lunch because their families receive other types of assistance, like SNAP.
In 2023, after the COVID-era policy ended where any student could receive a free school meal regardless of income, President Biden lowered the percentage of high-need students required for a school to qualify from 40% to 25%, greatly expanding participation.
House GOP Budget Committee Chairman Jodey Arrington now seeks to raise the rate to 60%. The budget proposal would also require all students applying for free and reduced-price meals to submit documentation verifying their family income.
School meal debt, a barometer of food insecurity among students, is already on the rise. It will almost certainly increase if universal school meals disappear for students whose families make too much to qualify for free and reduced-price lunch but too little to afford to buy meals at school. At the same time, kids who are eligible for free and reduced-price meals could lose that benefit if the required paperwork becomes harder.
In the fall of 2023, across 808 school districts, the median amount of school meal debt was $5,495. By the fall of 2024, that amount reached $6,900 across 766 districts, a 25% increase, according to the School Nutrition Association.
It was just $2,000 a decade earlier. A trio of Democratic senators is pushing to erase the $262 million annual debt total, with Pennsylvania Sen. John Fetterman saying in 2023, “‘School lunch debt’ is a term so absurd that it shouldn’t even exist. That’s why I’m proud to introduce this bill to cancel the nation’s student meal debt and stop humiliating kids and penalizing hunger.”
Research shows students benefit mightily from free meals: those who attend schools that adopted the Community Eligibility Provision saw lower rates of obesity compared to those who did not. Free in-school meals are also credited for boosting attendance among low-income children, improving classroom behavior and lowering suspensions.

Joel Berg, the CEO of Hunger Free America, said further cuts will greatly harm the poorest students.
“Over the last few years, things have gone from bad to worse,” he said. “We were all raised seeing Frank Capra movies, where, in the end everything works out. But that’s not how the real world works. In the real world, when the economy gets a cold, poor people get cancer.”
Hunger Free America found the number of Americans who didn’t have enough to eat over two one-week periods increased by 55.2% between August-September 2021 and August-September 2024. The states with the highest rates of food insecure children were Texas at 23.8%, Oklahoma at 23.2% and Nebraska at 22.6%. Georgia and Arkansas both came in at 22.4%.
The USDA slashed the $660 million Local Food for Schools Cooperative Agreement Program for 2025 — it allowed states to purchase local foods, including fresh fruits and vegetables, for distribution to schools and child care institutions — and $500 million from the Local Food Purchase Assistance Cooperative Agreement Program, which supported food banks nationwide.
Diane Pratt-Heavner, director of media relations for the School Nutrition Association, said that as families struggle with the high cost of groceries, the government should be doing more — not less — to bolster school meals and other food aid programs.
“We’re urging Congress not only to protect the federal Community Eligibility Provision, but to expand it,” Pratt-Heavner said. “Ideally, all students should have access to free school breakfast and lunch as part of their education.”
SNAP benefits stood at $4.80 per person per day through 2020 before jumping to more than $6 per person per day after they were adjusted for rising food and other costs. Even then, the higher amount was not enough to cover the cost of a moderately priced meal in most locations.
Republicans in Congress seek to cut the program by $230 billion over the next nine years, possibly by returning to the pre-pandemic allotment of $4.80 and/or expanding work-related requirements, said Salaam Bhatti, SNAP director at the Food Research & Action Center.
Another possibility, he said, is that SNAP costs could be pushed onto states — including those that can’t afford them.
“This would be an unfunded mandate,” Bhatti said. “States would have to take away from their discretionary spending to offset the cost and if it is not a mandate, then states in rural America and in the South that don’t have the budgets just won’t do it.”
Food-related funding decreases come as the child tax credit, created to help parents offset the cost of raising children, is also facing uncertainty, said Megan Curran, the director of policy at the Center on Poverty and Social Policy at Columbia University.
The American Rescue Plan increased the amount of the child tax credit from $2,000 to $3,600 for qualifying children under age 6, and $3,000 for those under age 18. Many taxpayers received monthly advance payments in the second half of 2021, instead of waiting until tax filing season to receive the full benefits. The move cut child poverty nearly in half. The expanded child tax credit was allowed to lapse post-pandemic and now even the $2,000 credit could revert back to just $1,000.
All food-related and tax benefit cuts — plus the unknowns of Trump-era tariffs — will leave some Americans particularly vulnerable, Curran said.
“It’s shaping up to be a very precarious time for families,” she said, “especially families with children.”
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter