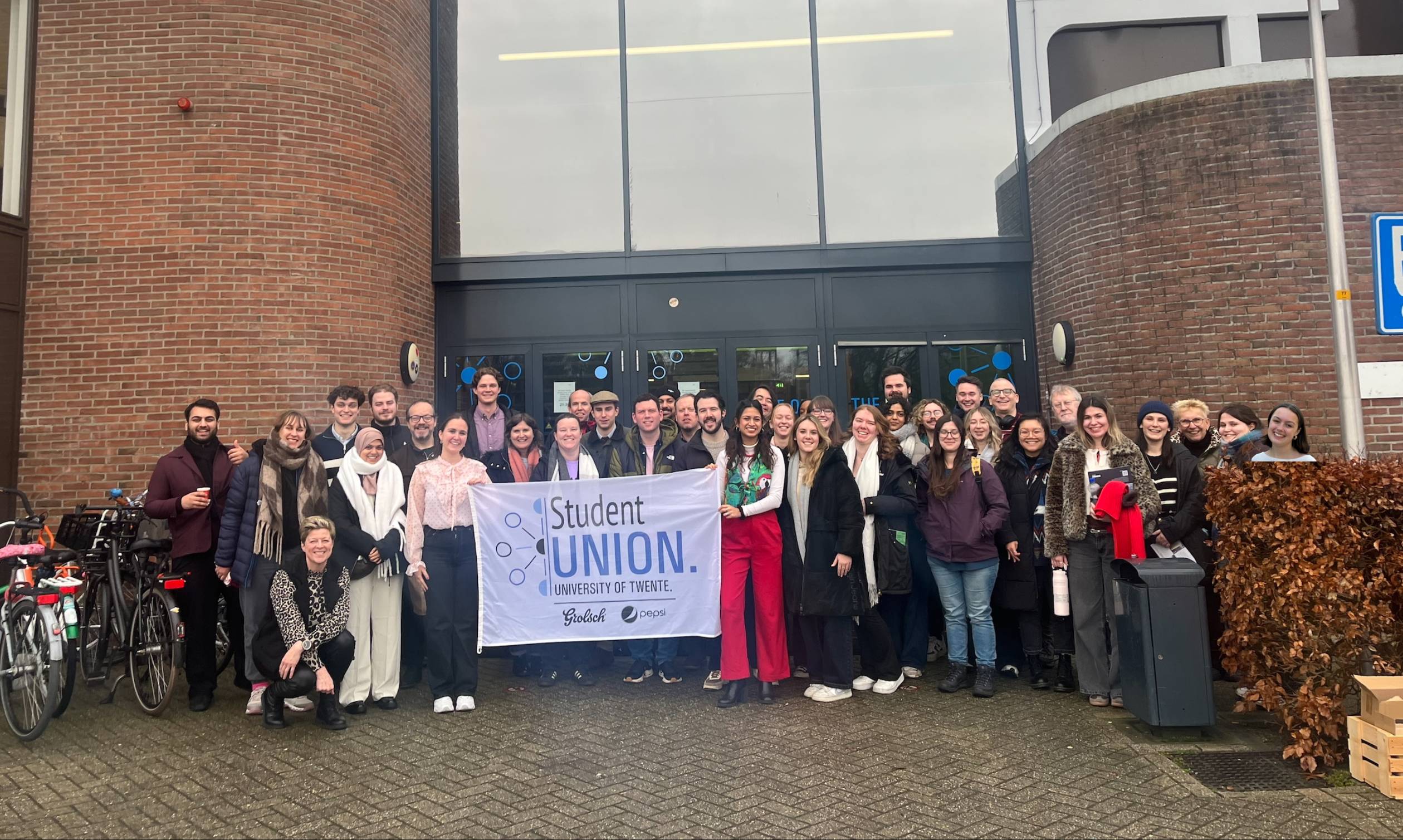
When people look at the apparently frenetic itineraries for our SUs study tours, we’re often met with confusion about why we would even attempt to visit so many cities in so few days.
This year we managed to fit in fifteen university cities in five days across Germany, Switzerland, France, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and both halves of Belgium – avoiding low bridges and Belgian traffic, and re-routing around the worst of Storm Goretti on a chartered bus whose toilet had frozen up.
In total we probably spent about 24 hours on the road with our driver Rene, which on first sight looks like an agenda full of dead time which could have been better spent immersing more deeply with our numerous hosts.
Sometimes the journeys are a good opportunity for a nap, or to sneak a look at emails, or to catch up on the gossip or just to stare out of the window at pretty houses in Spreitenbach.
But that time on the bus can also be a great time to look at and reflect on what we don’t see, the things we’re not told, the things that don’t make it onto the slide deck or into the tours and talks that we’re treated to by our largely student hosts.
Some of us started the week in Munich, which provided the excuse to while away at least one journey looking at the Technical University of Munich (TUM)’s Agenda 2030 strategy and teaching model.
On most programmes students choose from a bunch of “Plug-In Modules” – short courses designed to give students from one discipline a window into another – and one of the most popular ones is called “Politics for Rocket Scientists”, an introduction to political science for people who aren’t political scientists.
It’s a three contact hours a week, 6 ECTS (12 UK CATS) “lecture” module, an hour of which is chalk and talk by research-active political scientists, while students from later semesters in politics run “exercise” sessions.
Assessment takes the form of a ninety-minute closed-book exam – mainly a multiple choice quiz with a couple of open-ended questions – and it’s graded on the German system of 1.0, 1.3, 1.7, 2.0, 2.3, 2.7, 3.0, 3.3, 3.7, or 4.0. And you can retake that exam unlimited times until you pass.
Every year that it runs, a joke which we reckon is funnier in German is used to open the first module:
Welcome to Politics for Rocket Scientists. We also run Rocket Science for Politicians, but that one is less popular.
TUM has won awards for its teaching, where the academic model reflects its guiding principle of human-centered engineering – aimed at providing students with sufficient “integrative valency and educational capacity” to benefit the natural, engineering, life and economic sciences as well as society more generally.
The structure – which sees bachelor’s students only studying for about half of their credits in their “major” – also sees students separately acquire credit in “soft” skills, academic induction, out-duction to the labour market and electives in related subjects.
Students who are earning while learning on the peer teaching team are trained in the latest pedagogical techniques and take part in the university’s annual teaching innovation competition, all of which is both great for their development and for improving outcomes.
The structure ensures that some of the research active academics can continue their work without having to sustain entire degree programmes or departments framed around their own specialism. And the university’s student-staff ratio? 40.7.
Students need some context
There were plenty more like that. At our first official stop – Universität St. Gallen in Switzerland – every student, regardless of their main subject, has to complete 24 ECTS of “Contextual Studies” chosen from areas like Creativity, Technologies, Cultures and Responsibility. Neither the SU President nor his huge team of elected student officers and “teamies” were paid – but had the time to undertake their roles because the learning from them counts in the structure.
At the University of Twente in the Netherlands, the final third of the bachelor’s programme is genuinely elective – minors, free choices, preparation for different master’s routes. Students also get real control over how they learn – which projects to pursue, which workshops to attend, and when to study. Much of the scaffolding is labelled “Student-Driven Learning”, and almost always involves problem-oriented group project work that students enjoy rather than resent.
In France in 2017 the government launched Nouveaux Cursus à l’Université – New University Curricula – with funding distributed through competitive bids to fund undergraduate curriculum transformation. The core concept is “progressive specialisation”, where students specialise gradually rather than choosing narrow tracks at eighteen, with built-in gateways between different qualification routes, and flexible routes that can combine higher technical and academic tracks.
At KU Leuven in Belgium, the final four weeks of each semester are reserved for “lab courses” where students integrate knowledge across subjects and connect it to society. At the University of Maastricht, students don’t spend hours in lectures – they meet twice a week in tutorial groups of ten to fifteen, working through cases where assessment might be participation, presentations, essays, or exams, but where the emphasis is on whether students can use what they’ve learned.
Bits of all of this exist in the UK, of course, and there’s plenty to be proud of when we compare some of the facilities, support systems and services that we have built in the name of “student experience” back home. But while all of these systems are under financial pressure (everyone in Europe, it seems, wants a better education population but taxpayers are reluctant to fund it), what we didn’t find was a hurtle towards “do it all” 15 ECTS (30 CATS) modules to fit a forthcoming funding system and a rapid erosion of student choice.
More often, we found ways of delivering efficiency that were about giving students educational and social responsibility.
Maybe their Bologna-addled minds have been warped into collaborative conformity while the UK forges ahead alone by bolstering its reputation for excellence by overloading academics. But it was hard not to feel the impacts of isolation as visit after visit casually mentioned pan-European university alliances, compulsory mobility semesters, degrees that can be built from credit from multiple universities in multiple countries and systems that sustain student leaders whose English was often better than ours.
At various points, we were asked what they might learn from us. What not to do was the theme of our answers.
Money honey
Sometimes on the trips, there’s things to steal. The pot of honey we were all given on arrival in Mulhouse was created by a project aimed at causing academic and vocational students from multiple universities to interact with craft and small industry experts in the region, with a beehive in the garden of the regionally-run halls. Maybe there’s a way to get something similar going back home.
The international student spaces we saw in Wageningen and Leuven combined space for associations, facilities for cooking and seating for studying – as a set of (comparatively) skeleton set of staff to facilitate student-run study sessions, cultural nights and interaction both between international students and with those from the home countries. We’d face questions about risk assessments and students’ willingness to get involved – but there’s a pilot in there somewhere.
The posters up in Strasbourg asking students if they thought all the hours they were having to work were “normal”, the student (and staff) arts centre in the middle of an ostensibly STEM-oriented university, the student-run city-centre study spaces projects we saw in different forms, the lighting and the furniture and the St Gallen symposium – they’re all worthy of a try, if we can find the time.
Sometimes those long journeys between stops allow us to wallow not in possibility but its opposite – it’s the culture of the country, it’s a hundred years of history, it’s the funding system or the governance of student services away from the academic endeavour that produces the Truman show of magic in the powerpoints and presentations that must mask worse mental health problems and higher attrition than we enjoy in the UK.
But sometimes the projects – like the one at the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich – were the antidote to such moments of pessimism.
Easier and more enjoyable
In the autumn of 2021, Sarah Hofer – a researcher who had previously documented how teaching methods rather than student ability explained vast gender gaps in physics performance – returned to ETH as a professor.
She quickly got to know the student board at VMP – the maths and physics student association – which has been making studying easier and more enjoyable for its members for 80 years.
Somewhere between an academic society and a set of course reps, it’s a bit of associative scaffolding that runs its own little welcome week, offers group social mentoring on arrival, provides old exams and organizes assessment preparation courses, and puts on poker and chess tournaments, fondue nights, parties and barbecues. And the VMP offers its members one free coffee a day at its lounge on campus.
It also stages its own careers fair, holds formal representation on departmental governance structures including the Departement conference (the highest departmental body), teaching committees, and grading conferences where exam standards are set.
It has working groups on sustainability and conduct, it has a project that focuses on equal opportunities through coffee lectures with professors, organises company excursions and social gatherings for computational science students, and supports international and master’s students with practical issues like housing and supervision.
Events include weekly talks on theoretical physics, an undergraduate colloquium with student presentations and apéro (think wine, beer, soft drinks, nibbles, and light finger food), as well as social events like ski weekends, fondue nights, and poker tournaments. Its student magazine VAMP publishes twice a semester in print and digital formats. And so on.
Unlike in the UK, where much of what it offers would be delivered for students by professionals in separate centrally-run departments inside student services or the SU, the assumption is that peer delivery backed up by the centre and associatively scaffolded at faculty level is good for the volunteers, good for belonging, good for innovation and good for students. Broadway musicals fail – school plays sell out.
And for Sarah Hofer, it was the perfect partner for operationalising some of her research.
No dumb questions
The idea was simple – create “exercise class” groups aimed at students who self-assessed as having less prior knowledge and/or imposter syndrome, where students facilitating would spend more time on fundamentals and where a “there are no dumb questions” culture was explicit rather than aspirational.
The pilot worked. Participants who might have been expected to underperform passed at higher rates than for the cohort overall, all via an intervention that was part-belonging, part-pedagogical and part-confidence building, changing the composition of the room so that nobody has to perform competence they don’t feel.
Workshops train TAs to think about what stops people asking questions – the group composition means there’s less stopping them. The research had said teaching methods were the barrier, not student ability. The recognition that heterogeneous prior knowledge makes some students fall silent, and that silence compounds, had found an outlet in a student society.
When Hofer left ETH for LMU Munich less than a year later, the initiative didn’t leave with her. VSETH kept running it. The SU now provides significant implementation infrastructure – recruiting student TAs, coordinating with departments, embedding it in their broader educational development work.
A working group – AG Fokusgruppen – sits under VSETH and works through the faculty student associations. Klara Sasse, who became the key student lead, was simultaneously active in VMP (the maths and physics faculty association, established over 80 years ago). Her dual positioning mattered – she could advocate at university level while having credibility and networks within the specific departments where focus groups needed to be implemented.
Departments have adopted it enthusiastically – Physics merged it with their existing Exercise Class Market infrastructure – but ownership remains with the SU. Klara has since become VSETH Vice President, VMP President, and Head of Communications at VSS (the national Swiss student union), and won second place in ETH’s individual Diversity Award 2024. The focus groups themselves won third place in the organisation category the same year.
I could KOKO
We heard so many stories like it during the week. They were rarely about responding to regulation, or delivering on KPIs, or lobbying the university to “provide” more for students. They were more often about students having the associative infrastructure – not so small as a course rep, not so large as a university-wide SU or student services department – to do things for each other.
Sometimes, ECTS credits were on offer. Sometimes students were paid for their work. One system saw students financially supported to pause while serving others for a semester. But almost without fail, when we interrogated why those in front of us had got involved, the money or the time or the academic recognition were always second-order hygiene. The real answer was always that they wanted to be the person that had first helped them.
At student social association KOKO in Maastricht, student chair Japke Zoon directs the board, oversees policy implementation, and maintains contact with Maastricht University, Zuyd University of Applied Sciences, the municipality, and other key partners. Sophie van Oosterhout oversees the bar committee, the club building, and safety during activities and parties.
Both Japke and Sophie were viscerally impressive and eminently employable – but it wasn’t really the things in their job descriptions that mattered the most. In conversation, it was the student who needed support, the first year that was thinking about dropping out, the international student who felt lonely, and the neurodiverse students who found a way to socialise with those who weren’t. Sophie was responsible for changing a barrel, but she was really responsible for other students’ success.
Cecile Kwekeu took the mic next – Secretary and Academic Co-Comissionier of SCOPE, the official study association of the university’s School of Business and Economics. She’s 20, originally from a small city in Germany, and got involved when she went to a Maastricht Business Days event:
As Academic Commissioner, my mission is simple: make sure our events actually help you grow. Whether it’s soft skills like communication and networking or hard skills like analytical thinking, I want to create opportunities that matter – both now and down the road. This year, I’m heading up some exciting projects including the Symposium, Consulting Case Challenge, Business Case Challenges, Career Development Days, and our Brussels Trip.
She also talks of building better systems, streamlining processes, and making sure her team can get the most out of student life. She and over 350 students like her across the university are helped by a bit of scaffolding that allows students to pause their studies to undertake an association board year or semester – and in turn, they support thousands of students to support others through projects, groups, committees and events.
The cold never bothered me anyway
None of it should be a surprise. Plenty of academic theory tells us that whole chunks of our lives have become increasingly hyper-organised, professionalised, and compliance-driven, adopting formal structures, metrics, and professionally-led processes that mirror “good organisation” norms but unintentionally erode amateur-led energy.
Money, measurement, risk management, staffing growth, and symbolic compliance often displace informal, trust-based activity. There’s evidence from wider civic life that shows that declining volunteering, loss of social infrastructure and low institutional trust is part of a broader hollowing-out of associational life, and has deep impacts on mental health, trust in governments and attitudes to others.
Increasingly, what we do in adult life is what students do – taking part in technically excellent but tightly controlled, professionally-run, highly transactional service provision – and in doing so there’s a crowding out of participation, a reduction in social solidarity and a widening of the intention–behaviour gap for those who might otherwise help others.
Letting go is hard. The pressure on UK students’ time is real. The regulation demands safety, the funding follows the metrics, and everyone remembers that time when that thing went wrong before the grown-ups took control. But this is less about letting go, and more about creating the conditions for student success.
Live and kick-in
When Frans van Vught got elected as Rector Magnificus of the University of Twente back in 1997, he inherited a technical university with declining student numbers, fragmented departments, a huge hole in the budget and a culture that had attempted to fix things by doing more centrally:
Campus life was bureaucratically controlled by a campus director. Not much was allowed, there were closing times, and students had to apply for permits for all kinds of things. I found that very unappealing. I felt that as a campus, or rather as a university community, we should be able to do better than that. Let the students organise things themselves.
Many encouraged Van Vught to retain the systems and structures that had been built up, only to operate them more efficiently. Instead, he set about shifting the culture both academically and socially – designing structures and scaffolds that would sustain a collaborative community with benefits both for individuals too.
And after his own study visit with some of his student associations to Queens in Belfast, he returned and set up the SU, giving it (against available advice) a raft of responsibilities previously assumed to be the university’s – all on the condition (agreed in a covenant) that they found student groups to run them.
“Universities have to take care not to become a bundle of non-communicating hyperspecialisms”, he said on the day he retired – bearing the scars on his back from a radical restructure:
[Students] are a very important part of the academic community and I think it’s important that they take their own responsibility… we have increased cohesion in student activism and increased the community feeling for the university as a whole.
Today, the SU hosts a student-led outreach and talent development programme for secondary school pupils, a £0.5m student run “kick in” welcome programme designed to build belonging, study space facilities across the city and hundreds of other student committees that operate everything from student support to PC repairs to the world’s biggest case competition.
The wider academic infrastructure helps. Every department gives space to an an academic student association on the basis that students need a “home” to work together in. On their courses, students work in multiple teams over extended periods, encouraging early peer bonding, a sense of belonging, and shared responsibility, reducing anonymity and social isolation.
There’s an emphasis on collaboration, role negotiation, and joint problem-solving that develops interpersonal skills like communication, empathy, and conflict management, while the coaching role of staff an integrated authentic assessment structure strengthens confidence, creativity, self-efficacy, and emotional resilience by providing an environment where students learn from mistakes and high-stakes pressure is reduced.
On the tours, we often pick up the differences in dual systems between elite universities and their old ideals of education for education’s sake, and newer players in the applied sciences who focus on labour-market prep. On paper, Twente ought to have been the most individualistic, transactional, skills-for-the-CV provider on the trip. But it wasn’t.
The Netherlands has a much higher percentage of students working while studying than the UK. Belgian and French students are just as likely to be struggling with the costs of living. Students in Luxembourg find it difficult to afford their placements, and Bavarian students are attempting to rent the most expensive student bedrooms in Germany. Even Swiss students struggle to maintain the sort of student experience that their parents said was possible.
But while HE and student funding was never far from the top of the lists of problems on the slides, it was also repeatedly obvious that the spaces and structures deliberately designed to create collaboration, engender responsibility and operate autonomously were helping to ensure that students were both transformed by their education, and were helping to transform both their university and their municipality as a result.
Society concerns social relationships and civic participation. Social networks provide support and contribute to quality of life. It is also important that everyone can participate in society, and trust other people, the government and other institutions.
Statistics Netherlands (CBS) reports that in 2024, 49.5 per cent of the population aged 15+ did voluntary work for an organisation or association at least once in the previous year – and it’s much higher for graduates. In the end, both in the university and the country, isn’t HE partly about the community you’re trying to create?