by Gail Cornwall, The Hechinger Report
December 9, 2025
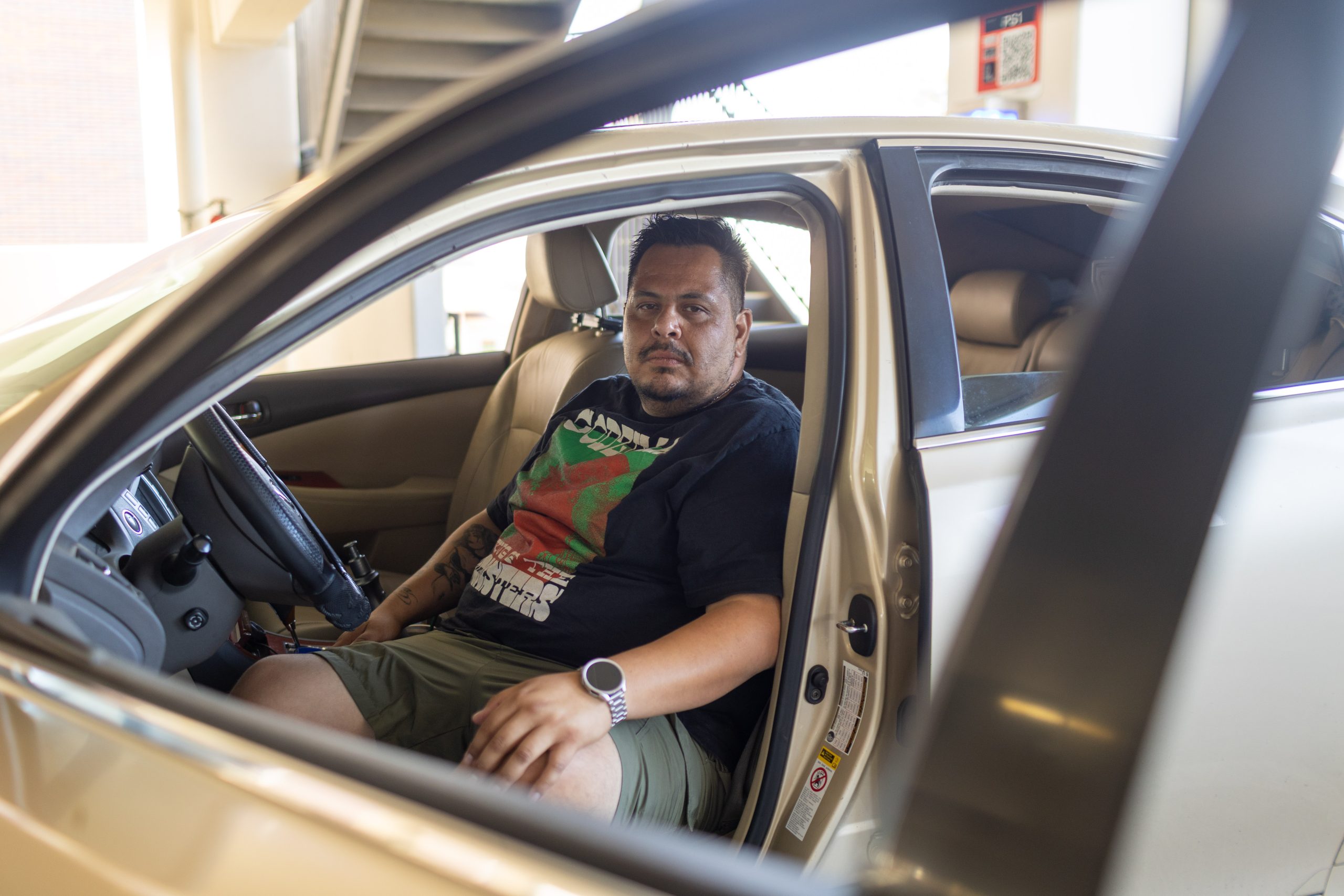
LONG BEACH, Calif. — When Edgar Rosales Jr. uses the word “home,” the second-year college student with a linebacker’s build isn’t referring to the house he plans to buy after becoming a nurse or getting a job in public health. Rather, the Long Beach City College student is talking about the parking lot he slept in every night for more than a year. With Oprah-esque enthusiasm, Rosales calls the other students who use LBCC’s Safe Parking Program his “roommates” or “neighbors.”
Between 8 and 10:30 p.m., those neighbors drive onto the lot, where staff park during the day. Nearby showers open at 6 a.m. Sleeping in a car may not sound like a step up, but for Rosales — who dropped out of a Compton high school more than 20 years ago to become a truck driver — being handed a key fob to a bathroom stocked with toilet paper and hand soap was life-altering. He kept the plastic tab on his key ring, even though he was supposed to place it in a drop box each morning, because the sight of it brought comfort; the sense of it between his fingers, hard and slick, felt like peace.
When Rosales and his son’s mother called it off again in the fall of 2024, just after he’d finished a GED program and enrolled at LBCC, he stayed with his brother for a week or so. But he didn’t want to be a burden. So one day after work at the trucking company — he’d gone part-time since enrolling, though he’d still regularly clock 40 hours a week — he circled the block in his beat-up sedan and parked on the side of the road, near some RVs and an encampment. The scariest part of sleeping in his car was the noises, Rosales said: “I heard a dog barking or I heard somebody running around or you see cop lights going down the street. You see people looking in your car.” He couldn’t sleep, let alone focus. Without the ability to bathe regularly, he began to avoid people to spare them the smell. The car became his sanctuary, but also, a prison. As he put it, “It starts messing with your mental health.”
First, Rosales dropped a class. A few weeks later, he told his LBCC peer navigator he couldn’t do it anymore and needed her help to withdraw. Instead, she got Rosales signed up for the college’s Safe Parking Program, and everything flipped on its head. With the LBCC lot’s outlets and WiFi, the back seat of his car morphed into a study carrel. Campus security was there to watch over him, not threaten him like the police had, telling him to move along or issuing a citation that cost him a day’s pay. For the first time in a month, Rosales said, “I could just sleep with my eyes closed the whole night.”
Related: Interested in more news about colleges and universities? Subscribe to our free biweekly higher education newsletter.
Forty-eight percent of college students experience housing insecurity, meaning “challenges that prevent them from having a safe, affordable, and consistent place to live,” suggests the most recent Student Basic Needs Survey Report from the Hope Center at Temple University. That number rises to 60 percent for Black students, 67 percent for students who are parenting and 72 percent for former foster youth. The problem also tends to be worse for veterans and those who identify as LGBTQ+ or have been labeled undocumented, said Sara Abelson, an assistant professor and the Hope Center’s senior director of education and training. Fourteen percent of the nearly 75,000 students surveyed experienced homelessness, the most severe form of housing insecurity. Other analyses produce similar estimates.
Of course, rates differ by institution. The Hope Center found that housing insecurity at two-year schools, like LBCC, was about 10 points higher than at their four-year counterparts. A similar gap divided institutions that serve high proportions of students classified as racial and ethnic minorities from those that don’t. Geography also matters: It’s much easier to find a rental unit in Wilmington, North Carolina, for example, than in Portland, Oregon. And yet, the problem is a national one, said Jillian Sitjar, director of higher education for the nonprofit SchoolHouse Connection, affecting both rural and urban areas and “not just a California thing.” That’s partly because of a national housing supply shortage and the fact that eligibility rules for affordable housing programs often exclude students; and it’s partly because the cost of college has risen nationwide as both government investment in higher education and the purchasing power of financial aid have fallen over the decades. The second Trump administration’s threatened and actual changes to Pell Grants, the largest federal student aid program, haven’t helped, nor have its cuts to the social safety net generally and erosion of laws meant to ensure equitable access to housing.
For years, colleges have primarily referred homeless students to shelters, nonprofits and other external organizations, but “there’s kind of a shift that’s happening,” Sitjar said: “Institutions are starting to look internally, being like, ‘OK, we need to do more.’” LBCC’s Safe Parking Program is one of the most visible of a new crop of programs addressing student housing insecurity by giving students unorthodox places to sleep: cars, hotels, napping pods, homes of alumni and even an assisted living facility. What sets these stopgap efforts apart from longer-term strategies — such as initiatives to reduce rents, build housing (including out of shipping containers), rapidly rehouse students, cover housing gaps (like summer and holidays) and provide students with more financial aid — is that they’re designed to be flawed. College administrators know full well that Band-Aid programs are insufficient, that they’re catching blood rather than addressing the source of the bleeding. And yet, while long-term projects are underway, what’s woefully inadequate can be quite a bit better than nothing.
An oversize sink sure was for Mike Muñoz. Decades before earning his doctorate and becoming the president of LBCC, Muñoz was a community college student who worked in a mall as the assistant manager of a portrait studio. After coming out as gay, he couldn’t go home, and then the family lost their house to foreclosure so “there wasn’t a home to go back to,” he said. Many nights, he’d crash on friends’ couches, but in the week leading up to payday, he couldn’t afford the gas to get there from work. Feeling hopeless, Muñoz would find a parking spot near the mall and spend the night in his car, dealing with the exact same stressors Rosales would endure years later. In the morning, he’d take a sponge bath in the oversize sink that the studio used to develop film. His No. 1 concern, after survival, he says, was keeping anyone from finding out about his homelessness, especially on campus.
President Muñoz — who is warm like Rosales yet more self-contained, often listening so intently as to become motionless — said the Safe Parking Program is about more than providing physical safety for students who sleep in their vehicles. Muñoz wants these students to feel safe bringing their full selves to college, in a way he didn’t until transferring to a four-year school and moving into student housing. “The mental load that I was carrying, I was able to set that down,” he said, “and I was able to then really focus that energy” — on classes, on who he wanted to be. That’s Muñoz’s answer to those who say emergency housing is a distraction, ancillary to the mission of a college.
Indeed, research suggests that asking a student to thrive in college without a reliable place to sleep is no more reasonable than asking them to ace a test without access to books or lectures. Multiple studies find that housing insecurity is associated with significantly lower grades and well-being. Lacking a stable housing arrangement has also been shown to negatively affect class attendance, full-time enrollment and the odds of getting a degree. What’s more, a 2024 survey found that housing-insecure students rely more on risky credit services like payday loans and auto-title loans. This Gordian knot of need and peril, which often also includes child care obligations and food insecurity, makes it hard to prove that emergency housing alone will improve students’ lives. But Rashida Crutchfield, a professor of social work and executive director of the Center for Equitable Higher Education at California State University, Long Beach, said, “It’s one of those ‘obviously’ moments that if you house students, they do better.”
Related: Housing insecurity derails foster kids’ college dreams
When a pandemic-era survey revealed at least 70 LBCC students living in their cars, Muñoz asked the college’s board to support him in implementing a safe parking program. They agreed something had to be done, but issues like legal liability concerned some LBCC staff. Additional worries included the cost and that it would mean less money for longer-term solutions, the risk of sending a message that it’s OK for students to have to sleep in their cars, and “the sky is falling kind of stuff” — visions of drugs, sex, trash, urine. But Muñoz pressed, and in 2021 the school piloted a program with 13 students and a startup budget of $200,000 from pandemic relief funds. That money covered private overnight security and paid for the nonprofit Safe Parking LA to train LBCC staff and help develop an application, liability waiver and more. The school’s facilities team installed security cameras, scheduled more cleaning and figured out how best to handle the extra opening and closing of the lot’s gates.
Similar efforts sprang up during the pandemic but later shuttered. For example, a collaboration in Oakland between Laney College and West Side Missionary Baptist Church wound down as did the safe lot program near the University of Washington’s Seattle campus. “The funding isn’t there anymore,” explained Marguerita Lightfoot, a professor at OHSU-PSU School of Public Health. Yet still to this day, she said of sleeping in cars, “There are students who are doing that at every institution.”
Knowing that, LBCC was determined to keep the Safe Parking Program running even after the federal tap ran dry. The school moved the program from its original location to the lot Rosales would call home, which has a clear line of sight from the campus security office. One extra campus security position replaced the private company, cutting LBCC’s overall spend in half. In other words, Muñoz made it work.
Other schools have swung different hammers at the same nail. Some colleges and universities with dorms maintain “in-and-out rooms,” beds set aside for short-term, emergency use, the way Roosevelt University in Chicago and Fort Lewis College in Colorado do. But Sitjar says a lot of red tape and considerable expense make in-and-out rooms uncommon. For specific student populations, some schools offer year-round housing, like West Chester University’s Promise Program for former foster youth and qualifying homeless students and a similar program at San Diego State University. But “during the summer, it’s really, really, really hard for institutions to try to keep those rooms set aside,” Sitjar said, since they otherwise generate revenue via summer camps, reunions and more, and during the academic year mean room-and-board money.
And community colleges — which educate the majority of American college students — mostly don’t have dorms that allow for this option. A few have teamed up with four-year institutions to house students at a discounted rate. In New Jersey, Rider University hosts students from Mercer County Community College. Through a pilot program launched in 2019, Massachusetts reimburses four-year campuses for the cost of keeping dorm beds available for community college students experiencing homelessness. A review of the program, through which eight colleges and universities have hosted students, found that 72 percent of participants showed academic improvement and even more experienced improved mental health.
Other types of partnerships also put roofs over students’ heads in short order. Cape Cod Community College works with a local health center to get students into hotel rooms on days the temperature falls below 32 degrees. And Norco College in Southern California is just one of dozens that contracts directly with a hotel. Religious organizations help too, such as Depaul USA in Philadelphia, which houses homeless college students in a converted convent. Around 400 miles south, in Wake County, North Carolina, HOST is a nonprofit that began with members of the NC State University community inviting students to move into their homes. And New York City’s LaGuardia Community College partners with Airbnb to house students short term, with the company reimbursing hosts.
Related: From Pony Soldier Inn to student housing: How an old hotel shows one solution to community college housing problems
A particularly unusual partnership resulted when Winona Health, a health care system in Minnesota, acquired a nursing home that had a mansion sitting on the same parcel of land. The century-old building, Watkins Manor, wasn’t ideal for assisted living, so in 2021 Winona invited students from nearby colleges to move in for a very low monthly rent plus volunteer hours. Students help senior citizens do things like troubleshoot tech, go shopping and participate in therapeutic recreation programs. “The residents love it, the students love it,” said Linda Atkinson, the administrator who oversees the program. While students don’t need to experience housing insecurity to apply, the program has provided emergency housing for those who have been kicked out of a parent’s home, experienced domestic violence and more.
Some schools combine these solutions, inching toward more comprehensive support. At California State University, Sacramento, the CARES program maintains four beds in on-campus dorms for immediate use. It also partners with the Hampton Inn and offers rent subsidies, eviction-avoidance grants (a utility bill here, a late fee there) and move-in support grants (think security deposits), among others. Additionally, the program has helped connect students with members of local churches willing to open their homes. Understanding that some students don’t have cars, LBCC too offers much more than the Safe Parking Program. As Crutchfield put it, “Different people have lots of different needs, and we have to have a buffet of options.”
At Howard Community College in Maryland, one smörgåsbord item is a place to nap. President Daria Willis doesn’t have anywhere to put a shelter for housing-insecure students, as Harvard, UCLA and the University of Southern California have done. “We are pretty much landlocked,” she explained, “I’ve got a hospital on my left side, and I’ve got neighborhoods on the right, back, and front side of the campus.” But she wanted to do something to help the exhausted students she walked by on the way to her office morning after morning. Students who worked night shifts, parented young kids or didn’t have a place to sleep at night were curled into chairs and draped over benches. In a pilot program, the school bought five chairs, known as sleeping pods, designed for rest. After Willis posted a picture on social media of herself relaxing in one, “it exploded,” she said: “Students were in them every single moment of the day,” often needing to be asked to leave when buildings closed at 11:30 p.m. So the school bought more sleeping pods. And more again.
No one, though, believes napping facilities and parking lots are really the answer.
Rosales has leg issues and a bad back. “I’m a big guy,” he said as he folded himself into the back seat of his car in an origami-like series of steps in early September. The WiFi on the lot is spotty, one bathroom for more than a dozen people often means a line, there’s no fridge to store leftovers or microwave to reheat them, and Safe Parking Program users aren’t able to sleep in or get to bed early. Last semester, when he took a class that didn’t get out until 10 p.m., Rosales had to move as fast as his busted knees would carry him to make the cutoff at 10:30. And he was still homeless. He’d go to a restaurant, spending dollars he couldn’t spare and eating too much just “to feel like a normal person,” Rosales said. He’d say hello to everybody and strike up a conversation with his server, to try to “be normal for a minute.”
Yet despite its limitations, the Safe Parking Program let Rosales “breathe, relax, continue on,” he said. And the lot offered a chance to build community. He began encouraging new arrivals to connect: “Trust me, we’ll help you,” Rosales would say. And they do often require help like that. Even when campus resources exist, two-thirds of students in need lack awareness about available supports, the Hope Center researchers concluded. Stigma is part of the problem. As Rosales put it, “We’re scared that we’re going to get judged or someone’s going to give us pity or give us a look … like, ‘Oh, there goes the homeless one.’” He didn’t even tell his family about his homelessness. In fact, Rosales’ peer navigator was the first to know — and he only had one of those to turn to because of LBCC’s surveys and targeted outreach.
Recently, Rosales organized a free breakfast to connect his “roommates and neighbors” with campus resources and each other. He felt terrible that he still couldn’t do much for the son he’d barely seen since moving out, especially after being laid off by the trucking company on Christmas Eve. But gathering participants in the Safe Parking Program, helping them — now he could add value to someone. And he felt valued by LBCC, having been given comprehensive support and case management meant to find an on-ramp to stable housing, as well as money for car repairs. (Each year, between $23,000 and $115,000 from the LBCC Foundation — which swelled after a $30 million gift from MacKenzie Scott, the philanthropist formerly married to Jeff Bezos — goes to students for vehicle registration, insurance, repairs and daytime parking permits.) Rosales felt like he mattered at LBCC, even after bringing his whole self to campus, just as Muñoz had hoped.
Related: Overdue tuition and fees — as little as $41 — derail hundreds of thousands of California community college students
At some point in the nation’s history, homelessness on college campuses was nonexistent, a rounding error when it did occur, because students had to have wealth behind them to access higher education. As efforts to democratize admissions and attendance (like the GI Bill) have borne fruit, “more of those who are facing these issues are getting to institutions,” said Abelson, the Hope Center’s senior director of education and training, combining with housing and funding shortages to create need that “has largely gone under the radar and unrecognized.” Efforts to equalize opportunity have been insufficient, and yet, they’ve made it possible for someone like Muñoz to graduate and then rise through the ranks. They’ve made it possible for his days of rationing gas and sink-bathing to open an institution’s eyes to the need for a net to catch students who are slipping off its ivory tower, and for Muñoz to push to create one, even if it must be stitched together from imperfect materials.
But the reality is that the majority of schools have massive holes in their nets, or to return to Crutchfield’s metaphor, they don’t offer any of these emergency housing dishes, let alone the whole spread. For the most part, colleges and universities still just create a list of resources and refer students out, suggesting they try their luck with local shelters and Craigslist. It’s inadequate. “Our shelter systems are overtaxed,” Crutchfield said, “there’s just not enough capacity.” And even when there is, “students don’t see shelter systems as for them,” she said. In some ways, they’re right: Shelter rules, including the need to queue up and turn lights off when there’s homework still to be done, often clash with students’ needs.
“If I fall down and I’m bleeding, definitely get me medical attention, get me a Band-Aid,” Crutchfield said. “But if the road is broken, and that’s why people keep falling down, you have to deal with the road.” So yes to safe parking, she said, but also, “What are we going to do next?”
In addition to building housing, participating in rapid rehousing models and advocating for financial aid that covers the true cost of college, some schools have hired homeless liaisons, staff members dedicated to assisting students experiencing homelessness. According to SchoolHouse Connection, California, Florida, Illinois, Louisiana, Maryland and Tennessee require schools to establish these roles. Maine encourages doing so, and California, Minnesota and Washington even set aside funds that can be used to pay for them. The impact appears to be significant. In Washington, 22 out of 25 community colleges surveyed said they provide some sort of emergency housing. Sitjar said, “For institutions and states that have these individuals, that have these roles, we’re then seeing those colleges make the really unique solutions of addressing housing.”
She pointed to bipartisan federal legislation, two bills that are expected to be reintroduced this session, that would require homeless liaisons as well as force colleges to develop plans for housing during academic breaks, do a better job of identifying students struggling with homelessness and more. One of the bills would update the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit program to allow full-time students to live in LIHTC housing if they’ve experienced homelessness within the last seven years. Abelson said the Hope Center and others support this reform as well as similar efforts aimed at “reducing the many barriers that students face to accessing [government] benefits.”
These days, Rosales still eats his feelings sometimes, he said, but “it’s slowly getting better because I see a therapist every two weeks through the school.” When LBCC told him in September that he’d been offered housing through a rapid rehousing program called Jovenes — a two-bedroom, two-bath to be shared with three roommates — Rosales began to cry, from relief but also from fear. “I never thought I was going to get out of here,” he said of the Safe Parking Program. “This is my home, this is where I live, this is where I’ve been — holidays, weekends, a birthday.” He finds comfort in knowing that the lot is always an option, as it is for the dozens of LBCC students living on the brink who have signed up for the program just in case. But he doesn’t sleep there anymore. “I’m not going back,” Rosales said, and for the first time, he believes in his ability to make that happen. He can feel in his truck-weary bones that he’ll graduate, that he’ll get that house he’s been dreaming about: “I’m moving ahead.”
Contact editor Caroline Preston at 212-870-8965, via Signal at CarolineP.83 or on email at [email protected].
This story about emergency housing was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.
This <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org/a-new-solution-to-student-homelessness-a-parking-lot-where-students-can-sleep-safely-in-their-cars/”>article</a> first appeared on <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org”>The Hechinger Report</a> and is republished here under a <a target=”_blank” href=”https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/”>Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License</a>.<img src=”https://i0.wp.com/hechingerreport.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/cropped-favicon.jpg?fit=150%2C150&ssl=1″ style=”width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;”>
<img id=”republication-tracker-tool-source” src=”https://hechingerreport.org/?republication-pixel=true&post=113649&ga4=G-03KPHXDF3H” style=”width:1px;height:1px;”><script> PARSELY = { autotrack: false, onload: function() { PARSELY.beacon.trackPageView({ url: “https://hechingerreport.org/a-new-solution-to-student-homelessness-a-parking-lot-where-students-can-sleep-safely-in-their-cars/”, urlref: window.location.href }); } } </script> <script id=”parsely-cfg” src=”//cdn.parsely.com/keys/hechingerreport.org/p.js”></script>