Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
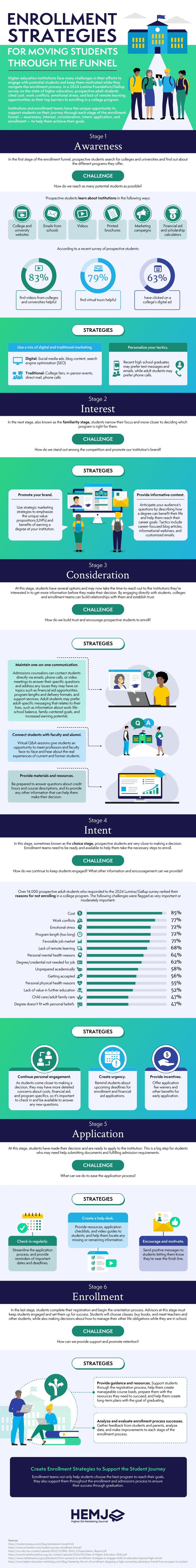
$390,000 to Jaylon Tyson, a former basketball guard at UC Berkeley, from a group of private donors.
$3,000 to Jordan Chiles, a UCLA gymnast and Olympic gold-medal winner, from Grammarly, an AI writing company.
$390 to Mekhi Mays, a former Cal State Long Beach sprinter, from a local barbecue joint.
These payments — derived from data that public universities provided to CalMatters — were part of “name, image and likeness deals” requiring students to create favorable posts on social media.
Such sponsorship deals were unheard of just four years ago. In 2021, California enacted a law allowing athletes to make these kinds of brand deals. It was the first state to pass such a law, prompting similar changes across the country.
This is the first-ever look at what many California athletes have actually made. University records show that money is flowing, but how much college athletes earn depends largely on the popularity of the sport, the gender and star power of its players and the fanbase of the university. While UCLA gymnasts earned over $2 million in the last three school years, university records show that players on the UCLA women’s water polo team earned just $152 during the same time frame, despite winning the national championship last year.
For companies, these name, image and likeness deals are akin to paying any other celebrity or professional athlete to promote a product. University alumni and sports fans can’t give money directly to a student athlete — at least not yet — but they are allowed to make name, image and likeness deals. Many universities have private donor groups, known as collectives or booster clubs, that offer athletes money, sometimes more than $400,000 in a single transaction, in exchange for an autograph or participation in a brief charity event. Often, those deals are a pretext to send money to top-tier players and discourage them from seeking better deals at other colleges.
CalMatters reached out to every public and private university in the state with Division 1 teams, where the potential for profit is typically highest, and requested data that shows how much money each of its student athletes have made since 2021. State law requires all student athletes to report to their school any compensation they receive from their name, image and likeness, and public universities are required to disclose certain kinds of data upon request. Private universities, such as Stanford University and the University of Southern California, are not required to disclose any data about their students’ earnings.
All of the public Division 1 universities responded to CalMatters’ inquiry, though they did not all provide the same degree of transparency. San Jose State and Cal State Northridge said they had no records of any deals.
There’s no consequence for students who fail to report what are known as NIL deals, so the data from public institutions may be incomplete. Still, certain trends emerge:
- College athletes at the state’s public universities received millions of dollars from collectives or booster clubs. At four University of California schools, around 70% or more of all compensation came from these collectives, according to university records. That’s just below national trends, according to a report by Opendorse, a tech company that tracks students’ deals.
- Male basketball players earned the most. While football is more popular and lucrative, nationally, many public Division 1 schools in California lack a football team. The football data may also be incomplete. For instance, all football players at UC Berkeley reported making a total of just over $113,000 since 2021 — less than what all San Diego State players made — even though Berkeley is in a more prominent conference.
- For high-profile football or basketball players in particular, it’s becoming more common for students to transfer multiple times, often in search of better name, image and likeness deals. Some California institutions, such as UC Davis and Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, have seen top athletes transfer colleges or threaten to transfer in order to attain better compensation elsewhere.
- Except for a few star players, such as Chiles, most female college athletes made very little, according to the data provided to CalMatters.
- Collectively, athletes at UCLA and UC Berkeley earned more than double what those attending other UC and California State University campuses made. Some donors, such as those supporting Sacramento State and UC San Diego, have rapidly raised money to compete, while at other schools, athletic directors say they’ll never be able to guarantee such high-dollar deals.
Schools often removed any information that could identify an individual student. While UCLA generally did not provide the individual names of its athletes, the school was more transparent than most and shared the date of each transaction, the name of the brand or company, the amount of money it gave, and the sport. In February, a UCLA gymnast reported receiving $250,000 from the beverage company Bubbl’r. Since then, Chiles has promoted that brand, repeatedly. In May, a UCLA gymnast reported receiving $210,000 from the cosmetic brand Milani for “social media” — just a few months before Chiles posted a video on Instagram, promoting its makeup. One or more members of the UCLA gymnastics team have also reported deals with the food company Danone for $300,000 and with the health care company Sanofi for $285,000.
Fresno State shared less information. In the 2021-22 academic year, the Fresno State women’s basketball team raked in over $1.1 million from multiple name, image and likeness deals, but the university did not disclose which players were involved or how many were paid. After influencers and former basketball players Haley and Hanna Cavinder transferred to the University of Miami in April 2022, the number and dollar amount of deals for the Fresno team diminished. In the 2023-24 academic year, the team made just over $1,000 from 10 different deals.
Money from boosters or collectives is the hardest to trace. In May, for example, a group of UCLA donors gave an undisclosed football player $450,000 for “social media.”
While private universities are not required to disclose students’ earnings, market estimates from On3, a media and technology company focused on college sports, say the highest-earning Stanford University athlete, basketball player Maxime Raynaud, could collect $1.5 million in the next 12 months. The top USC athlete, football player Jayden Maiava, could make $603,000 in the next year, according to the same estimates. These numbers are based on an algorithm that uses aggregate deals from college athletes across the country. Nationwide, the Opendorse report estimates that college athletes will earn $1.65 billion in the 2024-25 academic year.
Soon, college athletes may make even more. A high-profile class-action lawsuit will likely allow schools to pay athletes directly, while still classifying them as students, not employees. If the proposed settlement agreement goes into effect, students could see payouts as early as this fall.
If a school pays a student directly, the money should be divided roughly proportional to the number of male and female athletes, the Biden administration said in a U.S. Department of Education fact sheet issued in January. The page no longer exists.
In the last few months, attorneys have rescinded federal labor petitions asking that USC and Dartmouth College student athletes be reclassified as employees, but new cases are likely on the horizon, said Mit Winter, an attorney who specializes in name, image and likeness law: “I do think at some point — two years, five years, whatever it is — at least some college athletes will be employees.”
A Times Square billboard reads: NIL has begun
For decades, college sports have been a big business, though most of the money flowed to universities, not students. Nationally, Division 1 universities reported $17.5 billion in athletic revenue in 2022, according to the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). That’s more than the gross domestic product of 83 countries. For schools with top-performing football programs, such as UCLA and Berkeley, broadcast deals and other kinds of marketing represent over a third of total revenue.
Before California’s law went into effect, college athletes weren’t allowed to profit off their sport, though they frequently received scholarships equal to the cost of college tuition. On July 1, 2021 the new law took effect, and Haley and Hanna Cavinder were the first to benefit, signing deals with Boost Mobile, a cell phone company, and Sixstar, a nutrition company, just after the stroke of midnight. A Times Square billboard proclaimed they were the first such deals in the country.
Over the past four years, other California college athletes have signed advertising deals with clothing brands such as Crocs, Heelys and Aeropostale and food brands such as Liquid I.V. and Jack in the Box. FTX, the now-bankrupt cryptocurrency exchange, signed contracts with at least six players on the UCLA women’s basketball team in 2021. In 2022, the Biden campaign gave a UCLA gymnast $7,000, but public records did not disclose the purpose of the transaction. No other politicians appeared in any university’s data.
Last year, Visit Fresno County, a nonprofit that promotes tourism, paid former Fresno State football players Dean Clark and Kosi Agina just under $10,000 to post Instagram videos about a local farmer’s market and a minor league baseball team, according to President and CEO Lisa Oliveira. She said the posts were so successful that she asked Agina to make another video, promoting a hiking trail in the Sierra National Forest.
But much of the money for students’ name, image and likeness doesn’t come from brands at all — it’s from private donors. Philanthropist and entertainment lawyer Mark Kalmansohn has given nearly $150,000 in 12 different transactions to athletes on UCLA’s volleyball, softball and women’s basketball teams since 2022, according to the data, which runs through May of last year. In an interview with CalMatters, Kalmansohn said he’s given more than $175,000 since May. “Women’s sports were almost always treated in a second-hand nature and given inferior resources,” he said, adding that his philanthropy is about “women’s rights.”
In exchange for money, he asks each recipient to issue a free license of their name, image and likeness to a nonprofit organization that’s relevant to the athlete’s sport. But he said that’s not the norm. “In men’s football and men’s basketball, it’s pretty obvious that money is not for an ‘appearance’.” Instead, he explained that it’s a way to support the player and keep the team competitive.
Most donors give money to specific athletes through a collective, where the donors’ identities are largely hidden. At UCLA, public data through the 2023-24 academic year shows that a collective known as the Men of Westwood channeled nearly $2 million in private donations to the football, basketball and baseball teams. At Berkeley, collectives gave over $1.3 million to athletes since the 2022-23 academic year — the vast majority of which went to the men’s basketball team.
Supporting ‘elite talent’ at UC and Cal State
For years, NCAA rules made it difficult for college athletes to transfer schools, but in 2021, right around the time that California started to allow name, image and likeness deals, the NCAA eased those rules. The number of students who transfer suddenly jumped in 2021 and has ticked up each year since, according to NCAA data. In practice, the new rules means that a well-endowed collective can lure athletes who want to make more money.
This year, over 11% of all Division 1 football players have tried to transfer colleges, an increase from the previous year, said Matt Kraemer, whose organization, The Portal Report, uses social media posts and tips from insiders to gauge college athletes’ transfer activity. Quarterbacks are even more likely to try to transfer, Kraemer said.
For institutions like UC Davis, the threat of losing a top athlete can be costly. Late in the 2023-24 academic year, donors from other universities promised top athletes lucrative deals if they agreed to transfer, so UC Davis formed a collective, Aggie Edge, to make counter-offers, said Athletic Director Rocko DeLuca. “It’s a means to retain elite talent here at Davis.”
DeLuca said the collective gave men’s basketball guard TY Johnson $50,000 and UC Davis running back Lan Larison $25,000. Those transactions were for “social media, appearances, autographs,” according to the university’s data.
So far, all other UC Davis athletes — more than 700 students over 25 sports — have reported just under $19,000 in deals since 2021. A few other athletes received products, such as a free cryotherapy session or a commission based on sales.
In December, former UC Berkeley quarterback Fernando Mendoza transferred to Indiana University, where he later signed a name, image and likeness deal with a collective for an undisclosed amount. UC Berkeley then recruited former Ohio State quarterback Devin Brown the day after he won a national championship. It’s not clear if the Berkeley collective offered Brown a deal, since the university’s data doesn’t name Brown.
Justin DiTolla, Berkeley’s associate athletic director, said the university is “not affiliated with the collective” and that the university provides “equal support to all student athletes.” “We recognize that there is a difference in NIL support,” he said, “But it isn’t under our scope or umbrella.” The Berkeley collective, California Legends, declined to comment.
At Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, some football players sought more money through a name, image and likeness deal by transferring to another school, but they didn’t all succeed, said Don Oberhelman, the university’s athletic director. “That’s the dirty little secret of all of this: the number of kids who blow an opportunity.”
This fall, nine football players at Cal Poly San Luis Obispo announced their intention to transfer, he said. Six of them found a new university, he said, including University of Texas El Paso, San Diego State, Stanford, and Washington State — but three of them never received an offer from another school.
Oberhelman said that his football coach begins recruiting a replacement the moment a player announces his intention to transfer. If that student doesn’t end up transferring, he may lose his spot on the football team and the entirety of his athletic scholarship, which can be up to $30,000 a year.
“There’s raw emotion involved in these kinds of decisions,” he said. “I don’t think that’s how we would operate, but I can see a lot of people say, ‘You broke up with us.’”
Oberhelman said he doesn’t know what happened to the three players from the football team who failed to transfer. “For me, it would boil down to: Did we promise that money to someone else? Did we find another transfer or a high school person to replace you? If we did, that would put your future financial aid with us in jeopardy.”
Small-town name, image and likeness deals
Outside of top football and men’s basketball programs, many of California’s college athletes vie for smaller name, image and likeness deals, often with local businesses, lesser-known clothing or athletic brands, or anything else they can find.
Former Berkeley softball player Randi Roelling got $50 from one woman to give a pitching lesson to her daughter. In July 2023, chiropractor Lance Casazza started giving out free sessions to at least one Sacramento State football player in exchange for social media posts.
Annika Shah, a basketball player at Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, got her first deal through a local restaurant, Jewel of India, which occasionally has a pop-up tent outside the college gym. “I just said, ‘Hey I can market you. Let’s think of a cool slogan to put out.’” Customers who ask to “swish with Shah” at the checkout counter get a discount on their meal, she said. Shah doesn’t get any money, she said, but she does get free food whenever she visits.
“It was just a cool relationship and connection that I made with this family and the owners of Jewel of India, where they just want to help me out and I want to help them.”
Walking around campus, friends jokingly refer to Shah as their own “Jewel of India” and she likes it. “It’s such a marketable slogan now, and it kind of identifies who I am.”
Many Division 1 schools have their own websites where customers can buy gear with an athlete’s name on it, but last fall, no such platform existed at Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, said Shah, so she created her own. She partnered with a company, Cloud 9 Sports, and launched her own apparel brand. It’s brought in about $2,000 in sales so far, but after the university and Cloud 9 Sports take a cut, Shah said she’s left with about $800.
Shah said she was never told to report any of her monetary or in-kind contributions. After CalMatters asked, Oberhelman, the athletic director, said the school is now requiring it. “We haven’t done a great job following up because we’re just not going to have student athletes that are getting even five-figure deals,” he said.
Oberhelman said he only knew of eight deals, each for $2,000, all to the men’s football team from a group of private donors.
Fresno State provided more data than Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, but it did not designate which deals came from its collective, known as Bulldog Bread. On its website the collective says it has raised more than $690,000 in corporate donations for Fresno State. At the top tier, that includes money from former Fresno State quarterbacks David and Derek Carr, property developer Lance Kashian, and construction company Tarlton and Son, Inc. The collective recently launched a vodka brand in partnership with a distillery, where a portion of all proceeds support students’ name, image and likeness deals.
Athletes at UC Santa Barbara have reported $1,800 from their collective, Gold & Blue, but many other transactions reported by the school provide few details. According to the school’s data, an unnamed person or group made 15 deals with one or more members of the UC Santa Barbara men’s basketball team, totaling over $50,000 in “appearance fees” for an event last August associated with Heal the Ocean, a local environmental nonprofit.
The organization’s executive director, Hillary Hauser, said the nonprofit made no such contribution and had no events in August. University spokesperson Kiki Reyes said it’s “possible” that a collective made those payments, but she refused to respond to CalMatters’ questions regarding Hauser’s statement the event never occurred.
From August 2023 to August 2024, male basketball and baseball athletes at UC Santa Barbara reported roughly $500,000 in compensation for appearance fees related to various charities. Over the same time frame, all other athletes reported receiving free products, sales referrals, and cash payments totaling about $1,000.
At UCLA, the CEO of the Men of Westwood collective, Ken Graiwer, is listed in university records as the “point of contact” for a $450,000 contribution, distributed over six transactions in the 2023-24 academic year, to the men’s basketball team for “public appearances.” For each of those transactions, the university’s data lists the Team First Foundation, a sports nonprofit, as the vendor. Neither UCLA nor the Team First Foundation responded to questions about who made the payment.
A few months before those transactions, the Men of Westwood posted a few photos on its Instagram account, showing UCLA men’s basketball players on the court with smiling children from the Team First Foundation programs. In the post, the Men of Westwood said it was “NIL outreach.”
California universities try to ‘stay competitive’
Since becoming legal in 2021, the market for name, image and likeness compensation has exploded. Sports commentators, attorneys, and athletic directors say the landscape is a kind of “wild West” or “gold rush”: The money is pouring in, but the regulations are sparse or evolving.
CalMatters has partial data from the 2024-25 academic year, but early indicators suggest that even more cash will soon flow to players. In September, a group of Sacramento State alumni, including some state lawmakers, said they raised over $35 million in one day for name, image and likeness deals. Cal State Bakersfield and UC San Diego recently formed their own collectives too.
Last year, former Democratic Sen. Nancy Skinner of Berkeley — one of the co-authors of the watershed name, image and likeness law — proposed a new bill to gather more data about spending by collectives and its impact on women’s sports. Newsom vetoed the bill, saying “Further changes to this dynamic should be done nationally.”
Initially, the NCAA tried to prevent colleges from directly assisting athletes with deals, but the association has eased those regulations recently, blurring the lines between universities and the private collectives that support them. Many states have passed laws explicitly allowing universities to make deals directly with students. In October, Skinner and former Democratic Sen. Steven Bradford wrote a letter to California universities, encouraging them to do the same.
“I strongly urge California schools to make full use of (the watershed law) to stay competitive in college sports, especially now that other states are copying California and allowing their schools to make direct NIL deals with their student athletes,” said Skinner in a press release about the letter.
This spring, California District Judge Claudia Wilken is expected to approve a settlement between athletes and the NCAA that would further expand the ways universities can pay their players. In the proposed settlement, a college could directly spend up to a combined $20.5 million per year on payments to all of its athletes. The spending limit would grow over time.
Regardless of the settlement, athletic directors at many of California’s public institutions, such as Cal Poly San Luis Obispo and Cal State Bakersfield, said they don’t plan on giving any more money directly to students because their athletic programs lack the cash. “They’re already on full scholarship, so there aren’t any more existing dollars we can really offer that person,” said Oberhelman, with Cal Poly San Luis Obispo. Even if the university did have the money, he said he’s concerned about the legal implications of paying students directly. “Are they going to get a W-2 now? Are we paying workers comp? Nobody seems to have answered a lot of these questions.”
DiTolla, at Berkeley, said the university will start paying its athletes once the settlement is finalized. UC San Diego joined Division 1 sports last year, and Athletic Director Earl Edwards said it is “seriously considering” paying its athletes too “if that’s what we need to do to be competitive.” UCLA refused to comment on the proposed settlement.
USC Senior Associate Athletic Director Cody Worsham said the university will “invest the full permissible $20.5 million in 2025-26.” Stanford refused to answer any questions.
While no Division 1 school in California has shared details about how it plans to pay its athletes, experts, such as attorney Mit Winter, say the proposed settlement is unlikely to change the current disparities in college sports, especially within the four most lucrative and dominant athletic conferences, known as the Power Four. Stanford, USC, UC Berkeley and UCLA are all in the Power Four.
For female rowers like Anaiya Singer, a freshman at UCLA, the disparities among men’s and women’s sports — and between football, basketball and everyone else — are no surprise. “Those big sports do bring in the most revenue, and they’re the most watched,” she said, while acknowledging that other athletes, such as fellow rowers, “deserve much more than we’re getting.”
Singer said she’s been working on building her social media brand and has nearly 3,000 followers on TikTok and just over 1,300 on Instagram. A few “very small companies” reached out to her through TikTok about promoting beauty products, but none of the brands felt like a good fit, she said. She has yet to agree to any deals or receive any funding from a collective.
Neither have most of her peers. The UCLA women’s rowing team has reported less than $500 in name, image and likeness compensation since 2021.
In the proposed settlement, each school will each be able to independently determine how to distribute their funds, but Winter said universities will likely follow their peers. “If you’re in UCLA, Berkeley….you’re in the Power Four and you’re going to have to stay competitive in recruiting,” he said.
“Most of the Power Four schools have all sort of landed on a similar way they’re going to pay that money out,” he added: 75% to the football team, 15% to the basketball team, around 5% to women’s basketball, and 5% to all other sports.
This article was originally published on CalMatters and was republished under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives license.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter