Hamish Coates, Ellen Hazelkorn, Hans de Wit, Tessa Delaquil, and Angel Calderon




Hans de Wit, Ellen Hazelkorn and Hamish Coates are editors and Tessa DeLaquil is associate editor of Policy Reviews in Higher Education. Angel Calderon is a member of the PRiHE Editorial Board. This blog is based on their editorial for issue 2, 2025.
It often feels like there is lots more ranting and moaning than imagining and evidencing around higher education these days. With excellent policy research, it does not have to be this way.
The immediate post-millennium era was arguably a golden age for universities, with huge interest in massification, investment, especially in research, and institutional autonomy. But the global financial crisis followed a decade later by global pandemic shocked higher education into different worlds. Most countries still promulgate objectives for a sustainable and cost-efficient, equitable and accessible, high quality education system as the basis for growth. In OECD countries, however, assumptions that massification would on its own provide opportunities for everyone with mechanisms for social inclusion and social mobility are being heavily questioned. In developing and emerging economies, the challenge is meeting demand and being able to absorb graduates. Yet, too many countries and research-focused universities keep chasing ‘quick prestige’, leaving others to put up with disproportionately lower funding, as well as poorer facilities, resources and opportunities.
Wealth and opportunity inequalities are increasingly greater within rather than between countries. At the same time, questions about educational outcomes such as employability, skills gaps and skills mismatches and over-qualification which have been long ignored by academic communities as irrelevant, are gaining public and policy traction. Governments and industries document the shift away from credentials towards greater focus on competencies – what people can do with what they know – and alternative accreditation processes.
A few large countries are in the foothills of a demographic cliff, while others are (currently) privileged by demand. Traditional public systems in many countries face an identity crisis and appear too sluggish to grasp new opportunities. Parts of the private subsector are progressively active and more responsive to the needs of diverse and older learners and to competency-based learning, micro-credentials and other forms of just-in-time learning. Accordingly, the private sector is the fastest growing segment of postsecondary education worldwide.
Countries vary considerably in their ability to cover costs associated with policy objectives due to revenue challenges and competitive demands elsewhere within society and the economy, alongside student and public unease about cost. Certain systems promote a laissez-faire or marketised approach whereby individual colleges and institutions (public and private) pursue their own agendas, while others grasp at opportunities for a more strategic state-led approach. Countries are beginning to examine the opportunities of a more joined-up post-secondary tertiary system (Hazelkorn, 2025). As Piketty has written, “it is access to skills and diffusion of knowledge that allow inequality to be reduced both within countries and at the international level” (2020: 534). But funding a mass system is very different from one catering to a small minority especially at a time when geopolitical/geoeconomic power shifts reshape the global landscape.
Deglobalisation and populist nationalism are shaking these issues out differently around the world. In many countries, these tensions are contributing to a growing sense of people and communities being left behind, and to social unrest. The dominance of information technology over universities, challenging the value of graduates for entry-level work and of faculty, will spur heightened questioning of the value of higher education (Coates, 2017; The Guardian, 2025; Roose, 2025). While others look on in disbelief, there is a sense that this may not be a problem for higher education today, though it is likely to be so one day.
It is too easy to blame governments and other external stakeholders. What role has higher education played itself, and what role can it play into the future? Is the sector, especially the public side, sufficiently strategic, forward-looking and adaptable? What are the implications for the governance of the system and of its many institutions? Or is it wandering unchained in the global wilds? Universities praise themselves as being one of the world’s oldest and most enduring institution, but as Darwin said: “It is not the strongest of the species that survives, nor the most intelligent that survives. It is the one that is the most adaptable to change.”
Once, such questions may have been ludicrous to provoke at the outset of a Policy Reviews in Higher Education (PRIHE) editorial. Not anymore. Accordingly, in the balance of this editorial we sketch frontier topics which higher education can embrace to drive positive reform, then current journal contributions (Figure 1). We conclude with a call to engage and transform.
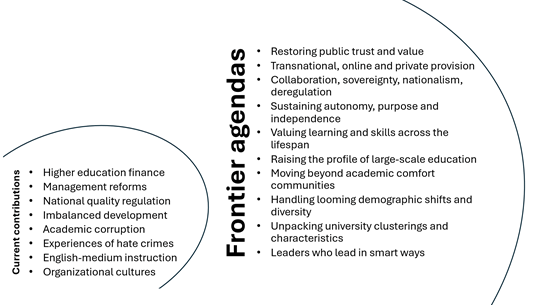
Figure 1: Current and frontier contributions
Any higher education policy zealot who has read Arnold Lobel’s brilliant treatise on Owl’s strange bumps in the bed (in which the Owl is afraid to go to sleep because of two strange bumps at the bottom of his bed, which are, in fact, his feet) (Lobel, 1982) understands that fear is created by running scared and can be tackled by uncovering and addressing matters in ways that unlock innovation and progress.
Policy Reviews in Higher Education plays this important role, though to date with fewer endearing drawings. Springing from inspiring intellectual dialogue with a member of the PRIHE Editorial Board and consequently guest author, Angel Calderon, we mark out a handful of narratives to carry forward policy research over the coming decades:
- Moving beyond academic comfort communities
- Handling looming demographic shifts and diversity
- Addressing concerns about academic value
- Creatively unpacking university clusterings and characteristics
- Leaders who lead in smart ways.
Higher education researchers must explore how universities and the academics who comprise them can move beyond comfort communities. This means finding ways to move beyond conservative research literatures and straightjacketing bibliometrics, beyond discipline and collegial communities, beyond the academic treadmill, beyond the subsector itself, and beyond naval-gazing research. A doctorate followed by decades toiling in the same institution is no prudent recipe for forging broader cognitive or tangible engagement with enterprise and industry (public and private) and the broader world. How can career trajectories be redefined to evoke and even provoke experimentation, fertilisation, and broader contribution?
Policy researchers must find productive ways for helping universities handle looming demographic shifts. The Asian investment in higher education which has fuelled the last thirty years will plateau and in major instances decline. Smart countries and universities are already looking beyond increasingly risky ‘foreign and school-leaver markets’ at reconfigured alignments with career-inspiring work and adult life. As yet, however, few if any countries have policy and associated regulation or funding to spur new ventures and directions. Beyond the sensible need for regional or perhaps global ‘harmonisation’, what is the scope for more imaginative forward-thinking about the sort of institutional reconfigurations needed to deliver for societies in 2050? Also, universities continue to see international students as an alternative for demographic declines as well as for income generation, adopting imperialist approaches to new markets rather than anticipating global and local shifts. Internationalisation is still seen as an income source based on mobility flows, instead of as a possible change agent for innovation in education, research and service to society.
Genuine political concerns about academic quality and value are unlikely to be assuaged by fluffing up the fame of elite researchers who typically have little to do with students or voting communities. Graduate outcomes and relevance are some of the most pressing challenges for all governments pushing people to question the value of higher education and ensure it translates into good jobs. Broadening rankings to include topics like sustainability, while useful, misses the more substantial need to focus on local engagement rather than global striving. It is folly to think that all the ~88,000 higher education institutions (UNESCO, 2022: 12) should aspire to look the same. Pursuit of ‘world-class’ sameness is no substitute for critical research and delivery of more robust and compelling public information on value, quality of educational delivery and outcomes, and at the same time nuanced differentiation of the difference each and every institution can make. And arguably rankings bear increasing responsibility for distorting funding allocations and institutional/government priorities across many post-secondary systems.
Higher education sector growth in recent decades has spawned exciting, misunderstood and very important institutional and national configurations. There is an urgent need to creatively unpack university clusterings. Far too much time and money has been invested in studying groups characterised by bibliometric performance. More interestingly, there are university-defined groups, ranging from ‘presidents’ dinner clubs’ to disciplinary groups of nationally aligned associations. There are broader political, cultural and religious associations. There are groups connected through graduate or professional diasporas, or research connections. There is an emergent clustering of associations shaped by geopolitical/geoeconomic and national security imperatives. Ownership and tax-status has long been a means of shuffling universities into groups. What novel patterns and projections can be revealed?
Leading universities and the sector in smart ways will be imperative to ensuring the sector’s promise does not demise. Finding effective leaders is an obvious necessary step, which surprisingly little research has clarified. Cultivating and developing leaders is an obvious next step, though it is tackled in so many perplexing ways. Diversity is important, of course, including in intellectual as well as manifest characteristics. Assuring value and delivery is paramount, with increasing suspicions but to date far too little warrant is given to importing governance techniques from other sectors. Strengthening institutional governance and management is required to ensure that the right leaders are appointed and that they have the capacity and capability to deal with more frequent and overlapping crises and conflicting externalities in uncertain circumstances. There should be willingness to find new ways to govern tertiary education sectors more robustly considering turbulence and increased uncertainty and the level of emergent discord between the public and universities. No doubt policy governance can be tricky, but it needs to be more strategic and forward thinking, willing to take innovative steps to ensure the education system meets the needs of all learners and society. Governance systems were designed based on periods of relative stability and the occasional minor disturbance. What can be done, for instance, to build more resilient leadership for public and private vocational and higher education, encouraging active engagement with each other and their communities beyond the campus? Is there renewed scope to refresh ‘old public management’?
With the intent of curating even more purposeful contributions, PRIHErecently launched a call for experts around the world to curate cognate collections on a high-impact policy contributions. These contributions which relate to hot topics in higher education policy seek to engage a group of scholars around important themes, and work with the journal and related networks to convene hybrid global seminars and deliver substantial insights on consequential frontier issues. PRIHE’s Editorial Board and Editors have spotlighted six shaping themes which raise questions, insights and issues to be addressed by policy, drawing on experiences from around the world. These include:
- Proving contributions: Restoring public trust in higher education and universities
- Emerging formations: Transnational, online and private higher education, regulation, ethics
- Geopolitical upheavals: Collaboration, sovereignty, nationalism, deregulation
- Global challenges: Sustaining autonomy, academic freedom, purposeful research, independence
- Lifelong learning: Valuing higher learning and skills across the lifespan, and
- Valuing education: Raising the profile of large-scale teaching and learning.
Higher education in many if not most countries is confronting strong headwinds and needs strident thinking and reform rather than rent-seeking complacency. Carving out intellectual architectures to stimulate dialogue from disorder creates tailwinds for the tough work then required to create and promulgate the evidence which may sway policy and reform practice. In this editorial we have advanced a handful of non-ignorable developments as a guide for authorship, deliberation, and reforming practice.
Reference: Hazelkorn, E (2025) ‘Building a Unified Tertiary Education System. Trends and Propositions to Provoke Discussion, Trending Topics’ New Directions for Community Colleges Forthcoming.
Professor Ellen Hazelkorn is Joint Managing Partner, BH Associates. She is Professor Emeritus, Technological University Dublin.
Hamish Coates is professor of public policy, director of the Higher Education Futures Lab, and global tertiary education expert.
Hans de Wit is Professor Emeritus and Distinguished Fellow of the Boston College Center for International Higher Education, Senior Fellow of the international Association of Universities.
Tessa DeLaquil is postdoctoral research fellow at the School of Education at University College Dublin.
Angel Calderon is Director of Strategic Insights at RMIT University and expert on global tertiary education.








