Over the past decade, local newsrooms have been disappearing from the U.S., leaving communities without a trusted information source for happenings in their region. But a recently established initiative from the State University of New York aims to deploy student reporters to bolster the state’s independent and public news organizations.
Last year SUNY launched the Institute for Local News, engaging a dozen student reporting programs at colleges across the state—including Stony Brook University, the University at Buffalo and the University at Albany—to produce local news content. Faculty direct and edit content produced by student journalists for local media partners.
This summer, the Institute sent its first cohort of journalism interns out into the field, offering 20 undergraduates paid roles in established newsrooms. After a successful first year, SUNY leaders plan to scale offerings to include even more student interns in 2026.
The background: The Institute for Local News has a few goals, SUNY chancellor John B. King told Inside Higher Ed: to mobilize students to engage in local news reporting in places that otherwise may not be covered, to instill students with a sense of civic service and to provide meaningful experiential learning opportunities.
News deserts, or areas that lack news sources, can impact community members’ ability to stay informed about their region. New York saw a 40 percent decrease in newspaper publications from 2004 to 2019, according to data from the University of North Carolina.
Research from the University of Vermont’s Center for Community News found that over 1,300 colleges and universities are located in or near counties defined as news deserts, but last year nearly 3,000 student journalists in university-led programs helped those communities by publishing tens of thousands of stories in local news outlets.
A 2024 study from the Business–Higher Education Forum found a lack of high-quality internships available for all college students, compared to the number of students who want to partake in these experiences. Research also shows students believe internships are a must-have to launch their careers, but not everyone can participate, often due to competing priorities or financial constraints.
To combat these challenges, SUNY, aided by $14.5 million in support from the New York State budget, is working to expand internship offerings—including in journalism—by providing pay and funds for transportation and housing as needed.
“We think having those hands-on learning opportunities enriches students’ academic experience and better prepares them for postgraduation success,” King said.
The Institute for Local News is backed by funding from the Lumina Foundation and is part of the Press Forward movement.
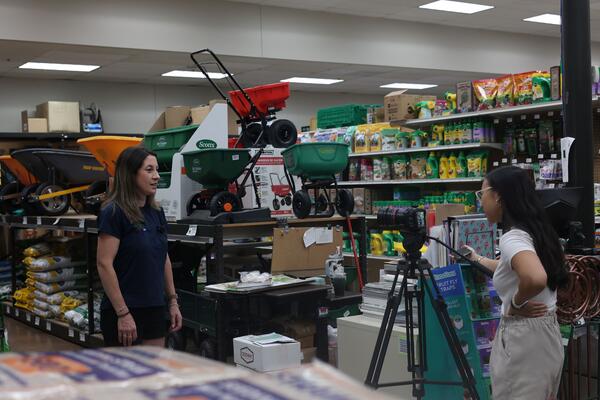
On the ground: Grace Tran, a rising senior at SUNY Oneonta majoring in media studies, was one of the first 20 students selected to participate in an internship with a local news organization this summer.
Tran and her cohort spent three days at Governor’s Island learning about journalism, climate issues and water quality in New York City before starting their assignments for the summer. Tran worked at Capital Region Independent Media in Clifton Park as a video editor and producer, cutting interviews, filming on-site and interviewing news sources.
“I wasn’t a journalism buff but more [focused on] video production,” Tran said. “But having this internship got me into that outlet, and it taught me so much and now I feel like a journalism buff.”
In addition to exploring new parts of the region and digging deeper into news principles, Tran built a professional network and learned how to work alongside career professionals.
“It’s my first-ever media job and there were no other interns there; it was just me with everyone else who’s been in this industry for such a long time,” Tran said. “It built a lot of [my] communication skills—how you should act, professionalism, you know, you can’t go to a site in jeans or with a bad attitude.”
Meeting the other SUNY journalism interns before starting full-time was important, Tran said, because it gave her peers for feedback and support.
What’s next: SUNY hopes to replicate this year’s numbers of 160 students publishing work and 20 summer interns through the Institute for Local News and expand internships in the near future, King said.
The Institute for Local News is just one avenue for students to get hands-on work experience, King said. SUNY is building out partnerships with the Brooklyn and New York Public Library systems for internships, as well as opportunities to place interns with the Department of Environmental Conservation to focus on climate action.
“We have a ways to go to get to our goal for every SUNY undergraduate to have that meaningful internship experience,” King said. “But we really want to make sure every student has that opportunity.”
Do you have a career-focused intervention that might help others promote student success? Tell us about it.