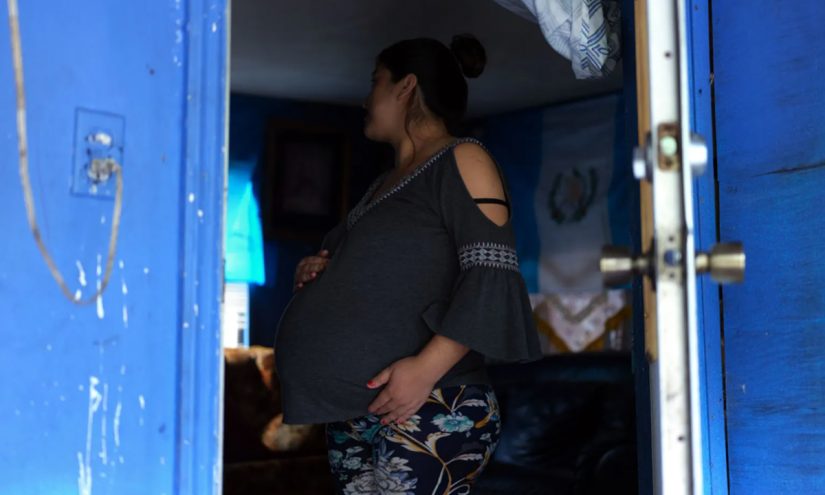
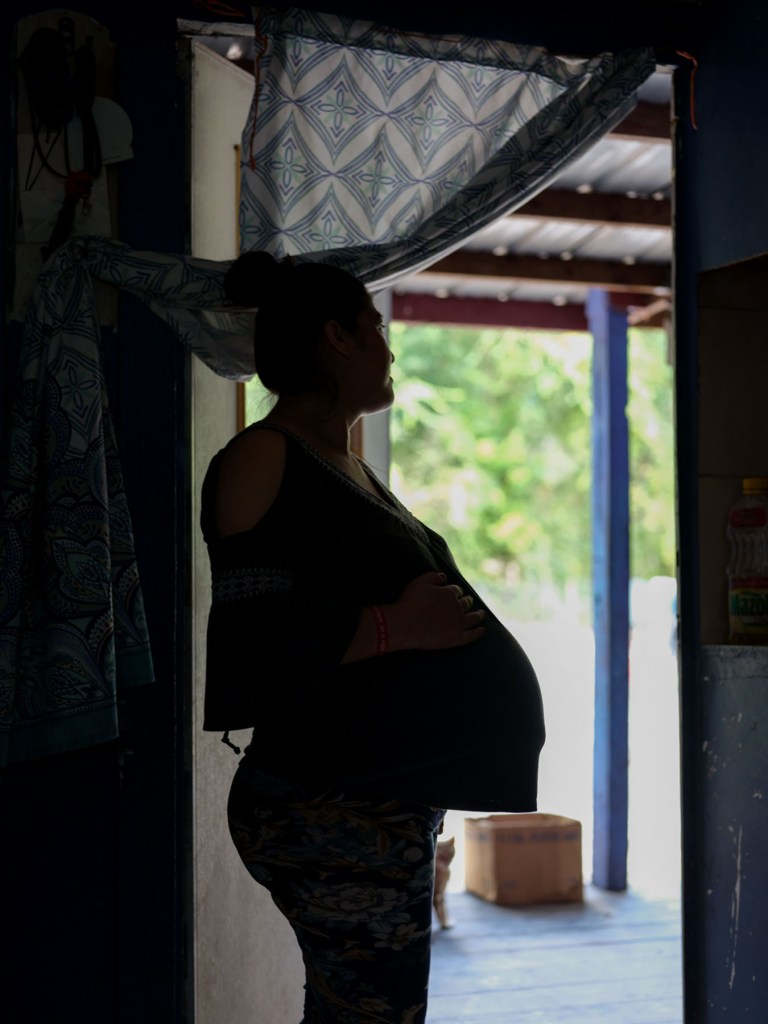
In the lead up to her son’s birth, Jacqueline made plans to call 911 for an ambulance to pick her up from her North Florida home and transport her to a hospital about an hour away.
The second-time mom and Guatemalan immigrant, who has lived in the country for a decade, would have relied on her husband to drive her to the hospital. But a few months ago he was deported, leaving Jacqueline and her daughter without the family’s primary source of income, transportation and support.
One morning in March, Jacqueline said, her partner was pulled over on his way to work when law enforcement officials discovered he didn’t have a valid driver’s license. Jacqueline’s pregnancy was in its early stages. Her husband fought his case from detention for three months before U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) removed him to Guatemala.
“He was deported and I was left behind, thinking, ‘What am I going to do?’” said Jacqueline, who requested that her last name not be published because she lacks permanent legal status. The couple shares an 8-year-old daughter who was born in, and is a citizen of, the United States.
This summer, as she entered the later stages of this pregnancy amid the Trump administration’s turbocharged immigration enforcement, Jacqueline found herself so fearful of being detained that she avoided leaving her home. Her husband’s car sits in the driveway, but there are no signs of him in the small room Jacqueline shares with her daughter. His belongings — tools, clothes, even personal photos — are with him in Guatemala. The only family pictures Jacqueline has are on her phone.
Her partner was the family’s main provider, rotating between picking strawberries or watermelon and packing pine needles for mulch, depending on the season.
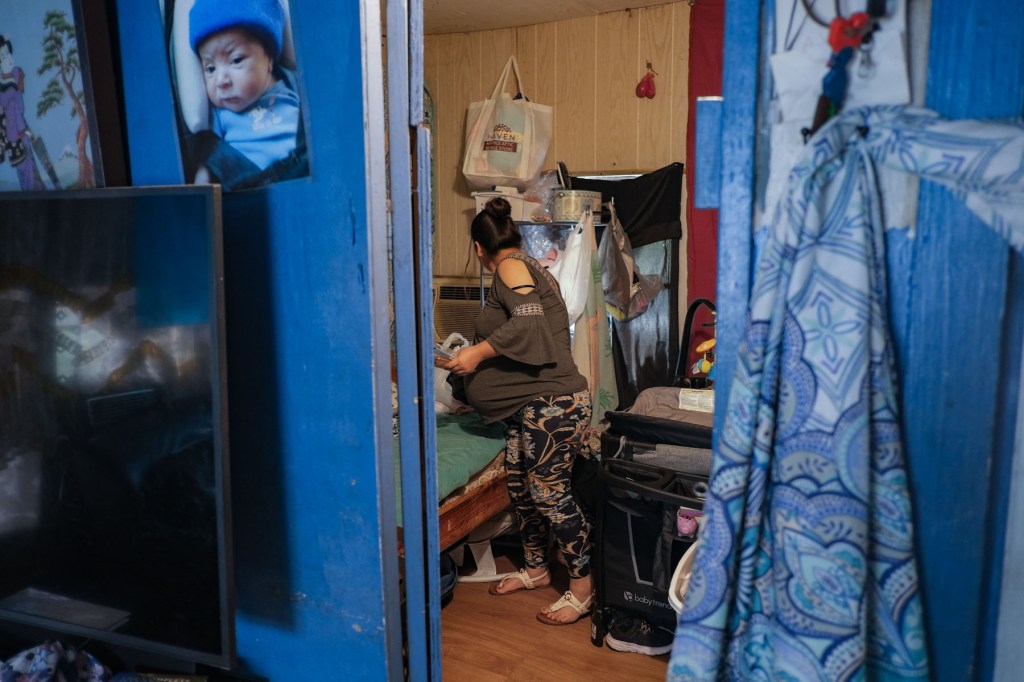
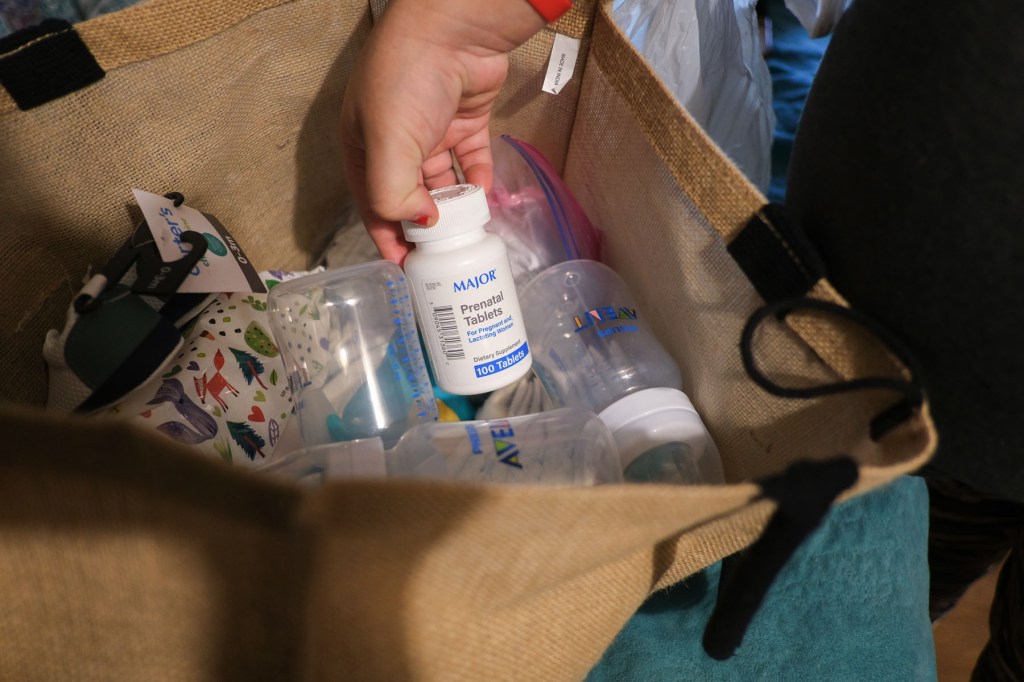
Jacqueline struggled to get the most basic items to welcome a baby: Someone gifted her a used carseat and crib, which sit in the packed room along with onesies and other clothing items she’s collected inside a large plastic bag. She’s hoping that a federal assistance program will cover the cost of formula. A baby tub is still on her list.
Medical care in her rural area has been possible only because a small nonprofit organization nearby that provides prenatal care services offered to pay for Ubers so she could continue regular check-ups. Even if she wasn’t behind the wheel, Jacqueline says that just the act of leaving her home feels risky since her husband’s deportation.
“Things got really complicated. He paid our rent — he paid for everything,” she said. “Now, I’m always worried.”
Medical care and support essential to a healthy pregnancy have become harder for people like Jacqueline to obtain following President Donald Trump’s inauguration. Many patients — nervous about encountering immigration officials if they leave their homes, drive on public roads or visit a medical clinic — are skipping virtually all of their pregnancy-related health care. Some are opting to give birth at home with the help of midwives because of the possible presence of ICE at hospitals.
Across the country, medical providers who serve immigrant communities said fewer patients are coming in for prenatal or other pregnancy-related care. As a result, patients are experiencing dangerous complications, advocates and health care providers told The 19th.
“Fear of ICE is pushing my patients and their families away from the very systems meant to protect their health and their pregnancies,” said Dr. Josie Urbina, an OB-GYN in San Francisco.
In January, Trump rescinded a federal policy that protected designated areas including hospitals, health clinics and doctors’ offices from immigration raids. ICE has recently targeted patients in hospital maternity wards and on their way home from prenatal visits.
A majority of Americans believe ICE should not be carrying out immigration enforcement at health centers. A new poll from The 19th and SurveyMonkey conducted in mid-September found that most Americans don’t think ICE should be allowed to detain immigrants at hospitals, their workplace, domestic violence shelters, schools or churches.
Women are more likely to oppose enforcement in these spaces than men. More than two-thirds of women said ICE shouldn’t be allowed to detain immigrants in hospital settings.
Enforcement is only expected to grow as the administration works to meet its ambitious deportation goals. The federal government is pouring more than $170 billion over the next four years into expanding immigration enforcement, the result of Trump’s signature tax-and-spending bill. About $45 billion has been directed to expanding detention facilities; $29.9 billion is to increase ICE activity.
That expansion could put even more births at risk. Approximately 250,000 babies are born every year to immigrants without permanent legal status. Already, research has shown these immigrants, who have higher uninsured rates, are less likely to seek prenatal care and are at risk of worse birth outcomes.
Major medical groups, including the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists, World Health Organization and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend regular prenatal and postpartum care as a key tool to combat pregnancy-related death and infant mortality.
According to the federal Office of Women’s Health, infants born to parents who received no prenatal care are three times more likely to have a low birth weight and five times more likely to die than those born to parents who received regular care.
A CDC analysis published last year found infant mortality rates went up the later families began prenatal care: 4.54 deaths per 100,000 live births for families whose prenatal care began in the first trimester, compared with 10.75 in families whose prenatal care began in the third trimester or who did not receive any at all.
“A lot of patients aren’t going to get help,” said Yenny James, the founder and CEO of Paradigm Doulas in the Dallas-Fort Worth metro.

James said she’s seeing an increasing number of emergency cesarean sections because of untreated gestational diabetes, or preeclampsia — a deadly pregnancy complication — that went unnoticed because of lacking prenatal care.
In Denver, OB-GYN Dr. Rebecca Cohen has delivered multiple babies this year for women who have told her that, because they fear endangering themselves or their families, they have received no prenatal care. Several have given birth to babies with fatal fetal anomalies that were never diagnosed because the women did not receive prenatal ultrasounds.
“They were willing to forgo care — their own health care — but to find out that something was devastatingly wrong with their child is when they feel like maybe they should have risked it,” Cohen said. “There’s a sound of a mother’s wail that anybody who has worked labor and delivery has known, and it will haunt you for the rest of your life. To hear that when it could have been prevented, it is just absolutely devastating.”
Early in her pregnancy, Jacqueline received free care at a local clinic. Shortly after her husband’s detention, she called the office to let them know she likely wouldn’t make her next appointment.
“I told them that I probably wouldn’t be able to make my appointments anymore, well, because I’m really afraid given what happened to my husband. And they offered to help,” she said.
Jacqueline and the nonprofit clinic worked out an arrangement: The day of her appointments, someone at the clinic called an Uber to her home, paid for by the clinic, and let her know when it would arrive so she could be ready.
Many people in her small town have come to rely on a single person who does have a valid driver’s license for transportation. That driver recently brought Jacqueline to an appointment with the local office that manages the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children (WIC), which she is relying on for baby formula and food. There were no guarantees that this driver would be available to take her in whenever she goes into labor.
The Biden administration directed ICE not to detain, arrest or take into custody pregnant, postpartum or breastfeeding people simply for breaking immigration laws, except under “exceptional circumstances.” The Trump administration has not formally reversed that policy. But despite the directive, reports from across the country confirm that ICE has detained numerous pregnant immigrants since Trump took office.
James said that until the Biden guidance is formally rescinded, she will continue to encourage pregnant immigrants to print it out and carry it with them.
“I told my doulas — have them print out this ICE directive, have them keep it with them, so that they know and these agents know that we know our rights, our clients know their rights,” James said.

It’s unclear exactly how many pregnant immigrants are being detained by ICE, or have been arrested by the agency. A May report from the office of Democratic Sen. Dick Durbin found 14 pregnant women in a single Louisiana detention facility at the time of staff’s visit.
Another report out of the office of Democratic Sen. Jon Ossoff published in late July found 14 credible reports of mistreatment of pregnant women in immigrant detention. The report cited an anonymous agency official who said they saw pregnant women sleeping on floors in overcrowded intake cells. The partner of a pregnant woman in federal custody said that she bled for days before she was taken to a hospital, where she miscarried alone. A pregnant detainee who spoke to Ossoff’s office said she repeatedly asked for medical attention and was told to “just drink water.” The office received several reports of clients waiting weeks to see a doctor, and that sometimes scheduled appointments were canceled. ICE has disputed the report.
“Pregnant women receive regular prenatal visits, mental health services, nutritional support, and accommodations aligned with community standards of care. Detention of pregnant women is rare and has elevated oversight and review. No pregnant woman has been forced to sleep on the floor,” ICE said in a statement posted on their website.
ICE did not respond to a request for comment.
Fear of being detained is a major contributor of stress for pregnant immigrants. Research shows that even when pregnant patients do receive medical care, prenatal stress puts many at greater risk of complicated births and poor outcomes, including premature birth and low infant birth weight. Babies born after an immigration raid are at a 24 percent higher risk of low birth weight, according to one study.
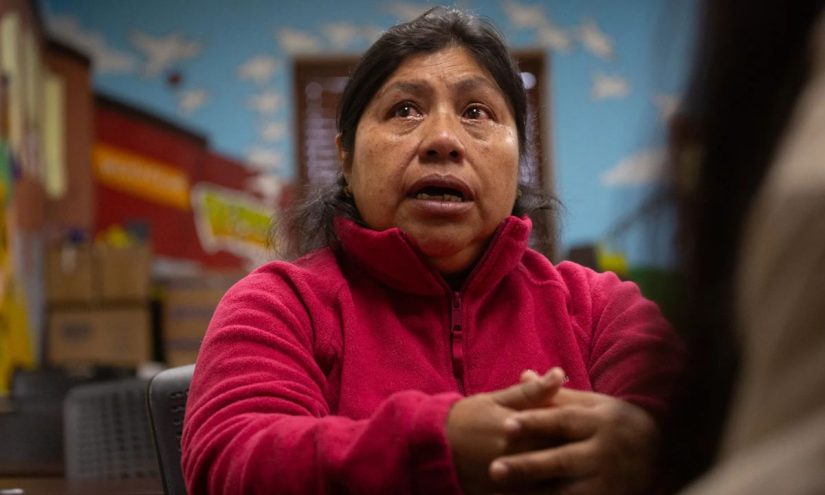
Monica, 38, is expecting her fourth child in November. The Tucson resident, who requested that her last name not be published out of fear of being detained, has lived in the United States for two decades but has no legal immigration status.
This pregnancy has been unlike the others, she said: While Monica has continued with her prenatal care appointments, her anxiety levels about her immigration situation have colored her experience. Her other children, who are in their teens, are U.S. citizens but grappling with the stress of their parents’ situation. Her husband also doesn’t have authorization to live in the country.
“We try to be out and about much less, and to take precautions,” she said. “Whenever we do leave the house, we have it in the back of our minds.”
Monica said she has seen reports of ICE being allowed inside hospitals, and she is worried about facing immigration officers while or following her birth. Her plan is to have her partner and a group of friends at the hospital to make sure she’s never alone.
“My biggest fear is going to the hospital,” she said.
Stress like Monica’s makes pregnancy more dangerous.

“In our hospital, every doctor I’ve talked to — and these are doctors that have been there 20 years — all are saying these past six months they’ve seen worse obstetrics outcomes than ever in their career,” Dr. Parker Duncan Diaz, a family physician in Santa Rosa, California, whose clinic mostly cares for Latinx patients. That’s included more preterm labor and more pregnant patients with severe hypertension.
“I don’t know what’s causing it, but my bias is that it is the impact of this horribly toxic stress environment,” he added, specifically noting the stress caused by the threat of immigration enforcement.
In recent months, Dr. Caitlin Bernard, an Indiana-based OB-GYN, has seen a number of pregnant patients seeking emergency attention who have not received any prenatal health care. One was 31 weeks, approaching the end of her pregnancy. Another was more than 20 weeks pregnant when she came to Bernard’s office, having developed complications from a molar pregnancy — a rare condition that means a healthy birth is impossible and that without early treatment can result in vaginal bleeding, thyroid problems and even cancer.
“Anytime you’re not able to access that early prenatal care, we do see complications with that,” she said. “And many of these things can absolutely be life-threatening for both the moms and the babies.”
Dr. Daisy Leon-Martinez, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist in San Francisco, said she now regularly cares for patients in her labor and delivery ward who have been transferred to her hospital because of newly developed pregnancy complications. These are often their first doctors’ visits since becoming pregnant. Many of those patients have told her that they did not want to seek prenatal care for fear of encountering immigration officials.
During regular visits, she added, she has advised people with pregnancy complications that they would be best served by a hospital stay — only to be told that her patients no longer feel safe going to the hospital.
The current enforcement environment is challenging immigrant advocates, who are continuing to encourage immigrants to seek appropriate medical care while acknowledging that doing so is increasingly risky.
Lupe Rodríguez, the executive director of the National Latina Institute for Reproductive Justice, said her organization is urging pregnant immigrants to seek the health care that they need, and to be proactive about making plans for themselves and their families in the event that they are detained.
“We can’t know for certain about any given [health care center] whether or not it’s going to be safe. One of the things that we’ve been seeing is leadership at some of these health centers — big hospitals and clinics — have said that they will provide the kind of protection that folks need, that they don’t want folks to be afraid of care,” Rodriguez said.
While those statements signal the intentions of a hospital’s leadership, Rodriguez said, “we still know that there are individuals within some of those care centers that are part of the reporting mechanism or are intimidating people.”
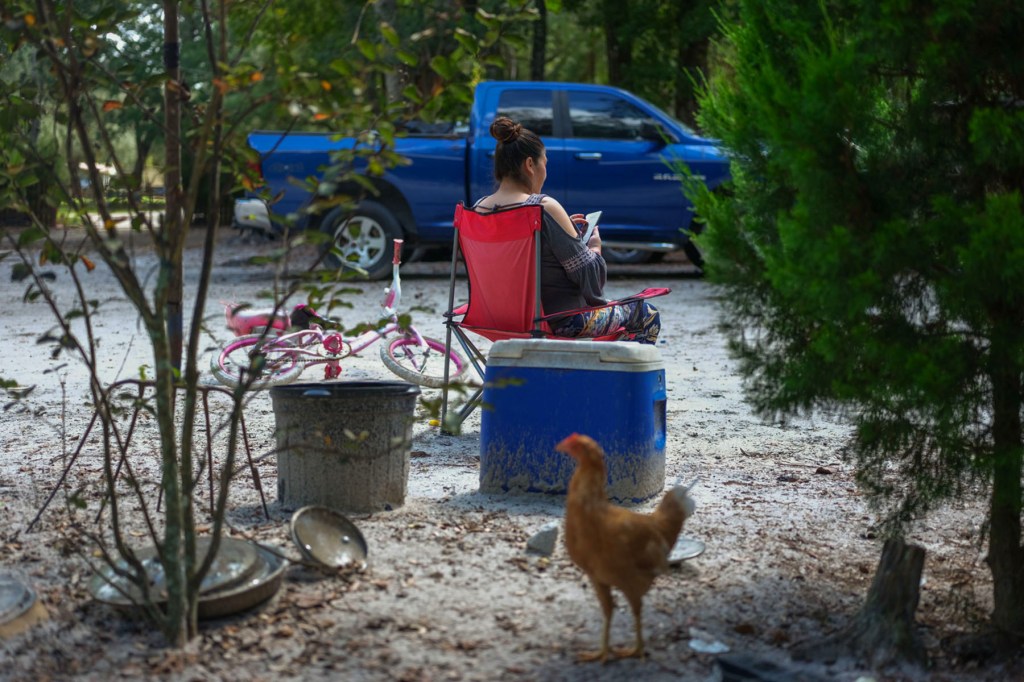

Jacqueline approached the last days of her pregnancy hopeful that the place she had chosen — a large university hospital that workers at her local clinic recommended — would be a safe place for her to give birth.
One night at the end of September, when labor pains grew too intense, she called for an ambulance and made it to the hospital. When she got there, she asked her providers if there were any ICE agents near the building. She had heard of a man at a local hospital being detained after having surgery. They told her there were none they were aware of.
She went on to deliver her baby under general anesthesia after a long, difficult labor. “I didn’t even hear him cry when they pulled him out,” she said. Her only relative left in the area was taking care of her daughter, so she recovered alone at the hospital for five days before heading home in an Uber that a social worker procured for her and her son.
“If my husband was here, he would have been there with me at the hospital,” Jacqueline said while recovering at home. “He would be here taking care of me, of us. I wouldn’t be worried about the things I still want to get for the baby.”
This story was originally reported by Mel Leonor Barclay and Shefali Luthra of The 19th. Meet Mel and Shefali and read more of their reporting on gender, politics and policy.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter