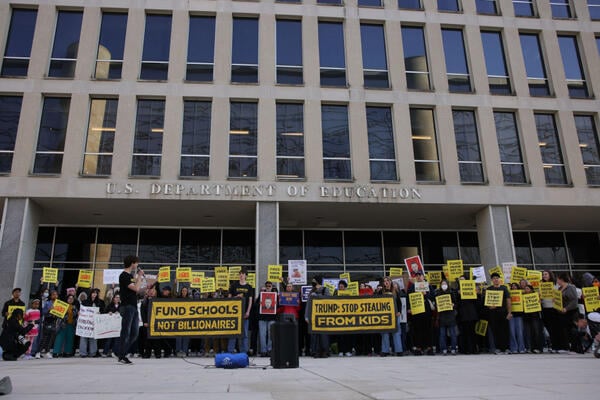
In the face of the Gaza protests, presidents at the nation’s most prestigious campuses were caught between a rock and a hard place—and somehow managed to trip over both.
Pressured on one side by students and faculty demanding moral clarity and action and on the other by donors, trustees and politicians insisting on firm leadership and institutional neutrality, they found themselves in a no-win situation.
In attempting to balance these competing forces, they pleased no one, offering statements too vague to satisfy activists yet too equivocal to reassure their critics.
Instead of navigating the crisis with principled leadership, many stumbled into a public relations disaster, alienating both their campus communities and external stakeholders.
What should have been a moment for measured, thoughtful leadership instead became a showcase of hesitation, miscalculation and rhetorical gymnastics that satisfied neither moral conviction nor strategic pragmatism.
Could Presidents Have Done Better?
Yes, the leading university presidents could have handled the Gaza protests more effectively, but doing so would have required a combination of patience, strategic engagement and deft leadership—qualities that many struggled to summon under intense pressure.
In his forthcoming memoir, former Harvard president Neil Rudenstine argues that navigating the crisis required time, strong relationships with key stakeholders, active faculty involvement and innovative problem-solving—qualities that were largely absent in the response.
- Patience: A Scarce Commodity in a Crisis
Rudenstine’s call for patience underscores a fundamental challenge: Neither protesters nor institutional critics were willing to wait for careful deliberation. Protesters demanded immediate moral clarity and action, while external stakeholders—donors, trustees, politicians—expected firm and unequivocal leadership.
University presidents, caught between these forces, often reacted hastily, issuing statements that satisfied neither side. A more patient approach would have required resisting the impulse to make rapid, reactive pronouncements and instead creating structured, ongoing dialogue with campus constituencies. It would have meant acknowledging the urgency of the moment while also emphasizing the need for thoughtful decision-making.
- Rapport With Stakeholders: The Perils of New Leadership
Building trust with students, faculty, alumni, trustees and external critics is difficult in the best of times, and it is even harder for new university presidents who have not yet cemented their authority or personal relationships within their institutions. Many of the university leaders embroiled in the controversy were relatively new to their positions, inheriting polarized political environments without deep reservoirs of goodwill to draw from.
In moments of crisis, long-standing relationships and credibility matter. Presidents who had not yet established rapport with key stakeholders found themselves viewed with suspicion from all sides, making it difficult to act decisively or persuasively. This underscores the importance of proactive engagement: University leaders must invest in relationship-building early, so that when crises inevitably arise, they have a foundation of trust to rely upon.
- Faculty Engagement: An Untapped Resource
University faculty represent a deep well of institutional knowledge and intellectual expertise, yet in many cases, faculty were sidelined as presidents struggled to navigate the crisis.
A more effective response would have involved drawing on faculty members—especially those with expertise in history, diplomacy, political science and conflict resolution—to help craft statements, advise on messaging and offer guidance on institutional policy.
Faculty could have also served as intermediaries between student activists and administrators, helping to create structured conversations rather than performative clashes. By failing to engage faculty early, many presidents lost an opportunity to ground their responses in scholarly insight and institutional legitimacy.
- Creative Responses: Beyond the Standard Playbook
The default approach to campus protests—issue a statement, enforce campus policies and hope the storm passes—was woefully inadequate in this case. Rudenstine’s emphasis on creativity suggests that university leaders needed to think beyond standard crisis-management tactics. Instead of simply trying to placate or rebuff different constituencies, presidents could have:
- Convened structured debates or forums featuring scholars and public intellectuals with diverse perspectives, transforming conflict into an opportunity for rigorous academic engagement.
- Established faculty-led committees to develop thoughtful, universitywide policies on how the institution engages with global conflicts, providing a long-term framework for future crises.
- Created dedicated spaces for dialogue, ensuring that protesters had a platform for their voices to be heard while also setting clear boundaries on disruptions to academic life.
The Leadership Test They Failed
The Gaza protests revealed deep weaknesses in university leadership, exposing the inability of many presidents to navigate the complex intersections of free speech, academic integrity, donor pressure and campus activism. A better response would have required patience, trust-building, faculty engagement and creative problem-solving—qualities that were largely absent in the moment.
The lesson for future leaders is clear: Effective university leadership is not just about managing crises when they arise but about laying the groundwork well in advance, ensuring that when the inevitable storm comes, the institution has the resilience and credibility to weather it.
The High Cost of Leadership: Neil Rudenstine’s Harvard Presidency
In a 2001 Harvard Crimson article entitled “The Final Word on Neil Rudenstine,” Catherine E. Shoichet, now a senior writer for CNN, offers a detailed account of that president’s tenure at Harvard—dissecting both his successes and the significant sacrifices and costs it exacted.
Presidents are chosen to solve particular problems, and Rudenstine was tasked with two major challenges: overseeing Harvard’s first universitywide capital campaign and knitting together a sprawling, fragmented, disjointed institution. As president, he transformed the university’s financial standing—adding billions to its endowment—and initiated wide-ranging administrative reforms, including the re-establishment of the provost position.
His most notable achievement was increasing Harvard’s endowment from roughly $4 billion to $19 billion in just 10 years, laying the financial foundation that sustains the university’s wealth today.
However, the article also stresses the heavy personal toll these challenges took on him—a topic that Rudenstine’s own account surprisingly omits.
Few presidents were better prepared for the job; he had been a respected faculty member, a productive scholar, a well-regarded dean of students, an effective provost and an extraordinarily hard worker. Yet his relentless focus on fundraising and institutional overhaul led to a three-month leave of absence in 1994, fueling rumors of a nervous breakdown. Remarkably, he went on to serve for another seven years after that difficult period.
Shoichet notes that for all his accomplishments, including launching development of a new campus in Allston and revitalizing Harvard’s Afro-American Studies Department and establishing a then-novel interdisciplinary initiative in mind, brain and behavior, his presidency also resulted in a perceived disconnect between the administration and the student body—a criticism that has followed him since his Princeton days.
His reserved public persona, which contrasted with the more overtly engaging styles of his predecessors, led to both admiration for his methodical, inclusive approach and criticism for being too detached from everyday campus life.
The Shoichet article exposes the inherent trade-offs of his approach. Rudenstine’s intensive focus on high-stakes fundraising and administrative restructuring appears to have come at the expense of deeper engagement with the student body. His humility was confused with weakness and a lack of strong convictions. His leave of absence illustrates how the pressures of managing an institution as vast and complex as Harvard can affect even the most capable leaders.
This duality—the balance between transformative success and the personal, institutional costs—forms the crux of Shoichet’s argument.
Her narrative situates Rudenstine within a broader historical context. By comparing his tenure with those of former Harvard presidents such as Nathan M. Pusey and Derek Bok, Shoichet argues convincingly that the challenges Rudenstine faced were unique to a new era of higher education—one marked by rapid expansion, increased institutional complexity and a heightened focus on financial management.
Despite his remarkable achievements, Rudenstine never garnered the same level of acclaim as his illustrious predecessors. In much the same way, many of his successors—including Lawrence Summers, Lawrence Bacow and Claudine Gay—have often been met with ambivalence or even disdain.
The reality is that leading an institution as formidable as Harvard has become nearly impossible. It is no wonder that the average tenure of college presidents nationwide has shrunk from around eight years to just about five—hardly enough time to make a lasting impact.
Rudenstine’s legacy, therefore, is not simply measured by his achievements but by the enduring questions it raises about the nature of leadership in a modern academic institution.
The Daunting Realities of University Leadership: A Seat of Prestige, Not Power
We often imagine university presidents as powerful figures—intellectual stewards shaping the future of higher education. But Rudenstine’s Our Contentious Universities flips this perception on its head. He’s not speaking truth to power; he’s speaking truth about power—revealing that university presidencies are as much about constraint as they are about command.
The title of university president carries an air of authority, but Rudenstine’s message is clear: The power of the office is often more symbolic than substantive. Instead of wielding control, presidents juggle competing interests, manage crises and navigate the impossible demands of faculty, students, donors and politicians. The real truth? The presidency is more burden than throne.
Holding the most prestigious seat in higher education, Rudenstine isn’t telling us how to wield power—he’s telling us how little of it university presidents actually have. His book dismantles the myth of the omnipotent academic leader and replaces it with a far grittier reality: that influence is fragmented, authority is constrained and leadership is often just crisis management in an ivory tower.
If “speaking truth to power” is about confronting authority, Our Contentious Universities reveals an unexpected reversal: Often, those in power are the ones struggling to be heard. Rudenstine lays bare the paradox of university leadership—an office that looks commanding from the outside but feels impossibly constrained from within.
The real work of a university president is not about wielding authority but about navigating limits, managing expectations and negotiating between forces that are often beyond their control.
The power we imagine? It’s largely an illusion.
Why University Presidents Have Less Power Than We Think
Through a mix of historical analysis, personal experience and candid reflection, Rudenstine argues that the role of the modern university president is far more constrained than many outsiders assume.
Three overarching arguments structure his book:
- The Paradox of Institutional Wealth and Administrative Complexity
Elite universities have never been wealthier, yet they have become significantly more challenging to manage. The sheer scale and bureaucratic complexity of modern research institutions—coupled with the decentralized governance structures of many elite universities—make it extraordinarily difficult for a president to assert a unifying vision.
Harvard, perhaps the most extreme case, operates under the philosophy of “every tub on its own bottom,” meaning that each of its schools, institutes and centers manages its own budget and academic affairs with substantial autonomy. Its endowment, divided into over 11,000 different funds with various restrictions, further complicates efforts to mobilize financial resources for cross-university initiatives.
But Harvard is not unique in this regard—many elite institutions lack a clear common mission or identity beyond their reputation for excellence. As a result, university presidents often find themselves in the role of coordinators rather than decision-makers, navigating a complex web of faculty interests, donor expectations and institutional traditions.
- Student Protests: A Recurring but Intensifying Challenge
Student activism has long been a defining feature of American higher education, and today’s campus protests are in many ways a continuation of past movements—whether over free speech, civil rights, the Vietnam War, South African apartheid, a living wage and labor rights, or fossil fuel divestment.
Rudenstine reminds readers that campus unrest is not a new phenomenon and, in many cases, past protests were just as contentious as, if not more so than, those of today.
However, he argues that contemporary campus protests present a unique set of challenges that make them especially difficult to resolve.
First, the media and political spotlight on higher education is more intense than ever before, amplifying every controversy into a national debate. Social media accelerates and inflames conflicts, often distorting the reality of what is happening on the ground.
Second, outside political actors—including legislators, donors and advocacy groups—now intervene more aggressively in campus affairs, using protests as flash points in larger ideological battles over academic freedom, free speech and institutional neutrality.
Third, many of today’s most contentious issues—such as foreign conflicts, racial justice and free speech—extend far beyond the authority of any university administration. Unlike past movements that targeted specific institutional policies (e.g., divestment from apartheid South Africa), today’s protests often demand action on global or national issues that university leaders have little power to directly influence.
- The Constraints of the University Presidency
While university presidents are often seen as the face of their institutions, their actual power is far more limited than public perception suggests. Much of their time is spent off campus, engaged in fundraising and alumni relations, rather than in direct governance. This distance often creates a perception—among both students and faculty—that they are out of touch with the daily realities of campus life.
Moreover, while presidents are expected to be moral leaders, crisis managers and public intellectuals, they operate within institutional structures that limit their ability to enact significant change. The vast majority of academic decisions are made at the department and faculty level, not by the president’s office.
Their financial resources, while seemingly vast, are often constrained by donor restrictions and endowment policies. And while they are expected to foster dialogue and intellectual engagement, they must also navigate intense political and ideological pressures that make consensus-building nearly impossible.
The Unwinnable Presidency in a Populist Age of Distrust
Leading an elite university in a populist era of distrust is an unwinnable job. University presidents are expected to be moral leaders, crisis managers and public intellectuals—yet they wield less power than ever before. They must balance the demands of faculty, students, donors, trustees, politicians and the public, all while navigating an institutional landscape that is more fragmented, more scrutinized and more politically charged than at any point in recent history.
Between a rock, a hard place and a social media firestorm, university leaders face an impossible equation. Caught between student activists demanding moral clarity, faculty insisting on academic freedom, donors expecting institutional stability and politicians eager to score ideological points, they must navigate a minefield with no safe path forward.
Every decision, no matter how carefully considered, is met with outrage from one side or another. When every choice is controversial, the safest option is still the wrong one.
Speaking truth to power is one thing—leading an institution when you are the power, yet have none, is another. A university president’s job isn’t to lead; it’s to survive. The modern presidency is less about shaping the intellectual future of a university and more about managing crises, defusing conflicts and enduring public scrutiny.
Part fundraiser, part diplomat, part scapegoat, today’s university leader embodies a paradox: prestigious, powerful and profoundly constrained.
The university presidency is a job where everyone expects everything, but no one is ever satisfied. And yet, the ambitious vie for this job. The challenge for future university leaders is not just to weather the storm but to prove that, even in an era of distrust and division, higher education still has a role to play in the pursuit of truth, knowledge and the public good.
Reclaiming the Visionary College Presidency: The Legacy of the Big Three B’s
At a time when the university presidency has become synonymous with crisis management, political crossfire and institutional paralysis, we would do well to reclaim an older vision of academic leadership—one embodied by the Big Three B’s: Derek Bok, William Bowen and Kingman Brewster.
These men were not just administrators; they were visionaries. They understood that a great university is not simply a collection of departments, endowments and buildings, but a living intellectual community that requires bold leadership, principled decision-making and a deep appreciation for the institution’s unique identity.
Unlike today’s university presidents, who often appear hemmed in by competing pressures, Bok, Bowen and Brewster exuded a sense of command. They were coalition builders who understood how to navigate the tensions of their time—not by appeasement or retreat, but by articulating a clear and compelling vision for their institutions.
They did not shy away from controversy; they faced it head-on, using their moral authority and intellectual gravitas to persuade rather than merely pacify. Their leadership was not about survival—it was about transformation.
The Power of Institutional Identity
One of the defining strengths of these presidents was their deep understanding of what made their universities distinctive. They did not try to turn their institutions into all-purpose, generic centers of higher learning. Instead, they leaned into their unique strengths and traditions, reinforcing the core values that defined them.
- Kingman Brewster at Yale championed the arts and humanities, elevating Yale as a beacon of intellectual and cultural leadership. He understood that Yale’s prestige was not just in its research output, but in its commitment to a broad, humanistic education that shaped future leaders in the arts, government and public service.
- William Bowen at Princeton preserved and reinforced the university’s distinctive commitment to undergraduate education, mentoring and close faculty-student engagement. He saw Princeton as the ideal blend of a research university and a liberal arts college, where students could experience the best of both worlds.
- Derek Bok at Harvard expanded the university’s reach and redefined its role in shaping society. He recognized Harvard’s unique position as an institution that was not just educating students, but cultivating thought leaders in law, government, business and the sciences. Bok’s presidency was marked by efforts to bring in a broader, more diverse array of scholars and students who were shaping the world outside the academy.
These men understood that universities are not interchangeable—they have distinctive missions, histories and cultures that must be nurtured, not diluted. They resisted the impulse to make their institutions all things to all people and instead worked to sharpen and deepen their defining strengths.
Leadership With Gravitas and Moral Authority
What made the Big Three B’s remarkable was not just their institutional savvy, but their personal presence and sense of moral authority. These were men who commanded respect, not because of their titles, but because they embodied the very ideals their universities stood for. They were not timid bureaucrats, nor were they detached figureheads. They were intellectuals, statesmen and educators who carried themselves with the weight of their institutions behind them.
More importantly, they were unafraid to make tough decisions and stand firm in the face of opposition. Brewster took a bold stance in support of civil rights and coeducation and against the Vietnam War, even when it made him a target of political backlash. Bowen helped lead Princeton through transformative changes in financial aid and faculty governance, navigating opposition with both decisiveness and diplomacy. Bok spearheaded Harvard’s expansion into applied learning and professional education, while also defending the university’s core commitment to academic freedom.
Each of these presidents had the ability to thread the needle—to stand up for their principles without alienating key constituencies. They were neither populists nor technocrats; they were strategic leaders who understood how to bring faculty, students, trustees and alumni into alignment around a shared purpose.
Reclaiming a Lost Model of Leadership
The contrast between the Big Three B’s and today’s university presidents is stark. Where they projected confidence and authority, many modern university leaders appear cautious and reactive. It’s quipped that their present-day counterparts can’t go to the bathroom without consulting their general counsel. Where the Big Three articulated grand visions for their institutions, many of today’s presidents are consumed by damage control. Where they commanded the respect of faculty and students, today’s leaders often seem disconnected from both.
Of course, the world of higher education has changed. Universities are larger, more complex and more deeply entangled in political and cultural battles than ever before. But that is precisely why we need a new generation of university presidents who can reclaim the mantle of true leadership.
The university presidency should not be reduced to a balancing act of donor relations, media messaging and political risk management. It must once again become a platform for vision, courage and institution-building.
The lesson of the Big Three B’s is clear: Great universities do not thrive under timid leadership. They flourish when they are guided by bold, intellectually rigorous and morally grounded presidents who understand both the weight of their office and the enduring value of higher education. The future of our great universities depends on whether we can find leaders who, like Bok, Bowen and Brewster, embody the very ideals their institutions were meant to uphold.
Steven Mintz is professor of history at the University of Texas at Austin and recipient of the AAC&U’s 2025 President’s Award for Outstanding Contributions to Liberal Education.