President Trump issued two directives targeting international students just hours apart on Wednesday night. One is a ban on entering the U.S. for citizens from 12 countries and heightened visa restrictions for those from another seven. The other bans all international students, researchers and other “exchange visitors” from Harvard University.
The orders represent another escalation of the Trump administration’s simultaneous, and sometimes overlapping, campaigns to both punish Harvard and curtail the number of foreign students studying in the U.S.
Chris Glass, a professor of higher education at Boston College and a member of the college’s Center for International Education, said the combination of the travel ban and the Harvard order are part of the administration’s “flood the zone” strategy for its higher education agenda. He added that the timing of the dual orders, following on the heels of a “seemingly indefinite” pause on student visa interviews and a promise to “aggressively revoke” Chinese students’ visas, seems intended to cause the most chaos possible.
“The timing couldn’t be worse … this is when 70 percent of international students are getting or renewing their visas,” he said. “It injects catastrophic uncertainty, and the uncertainty is the strategy from my perspective.”
On Thursday evening, Harvard filed a legal challenge to the proclamation targeting the university and asked a judge to issue a temporary restraining order against the administration. Judge Allison Burroughs from the District of Massachusetts quickly granted that request and extended the current restraining order issued last month. She set a hearing for June 16.
2017 Again
The last time Trump instituted a travel ban, in his first term, it threw colleges into chaos and left students and researchers stranded for months in the middle of winter break, sending colleges scrambling to find ways to bring them back. Higher ed has been bracing for a repeat of that travel ban since Trump was elected in November; many institutions told their international students to return to campus before the inauguration to avoid the same fate.
The new ban is not as drastic as many predicted; when the White House initially proposed another travel ban in March, officials rolled out a list of 43 potential target countries. But it is more expansive than the 2017 ban—it affects 19 countries instead of eight—and, combined with the administration’s barrage of attacks on international students over the past three months, could be even more damaging to international enrollment.
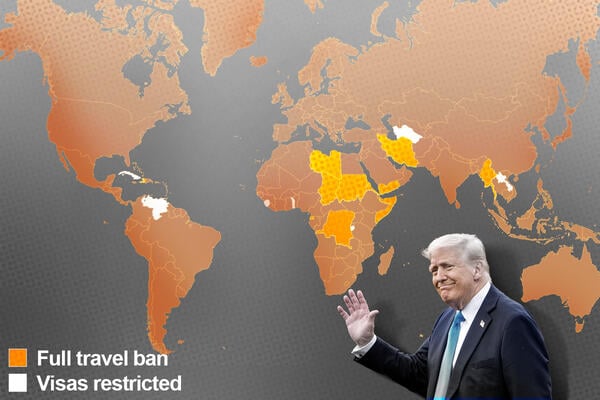
The full ban applies to Afghanistan, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Eritrea, Equatorial Guinea, Haiti, Iran, Libya, Myanmar, Somalia, Sudan and Yemen—largely Middle Eastern and African countries with substantial Muslim populations. Trump also restricted visas from Burundi, Cuba, Laos, Sierra Leone, Togo, Turkmenistan and Venezuela.
The travel ban doesn’t immediately affect students currently in the U.S. or who have already been approved for visas. But with many admitted international students still languishing in a visa process that the State Department halted two weeks ago, it will likely prevent thousands of students from attending in the fall and upend institutions’ projected enrollments.
The countries on the list send a relatively small number of students to U.S. colleges. Of the affected countries, Iran has by far the most students studying in the U.S. It is the 15th most common origin country for international students, with 12,430 studying at American colleges and universities as of fall 2024, according to the latest report from the Institute for International Education.
Still, the order is likely to compound the uncertainty and fear that has grown among international student populations, leading to signs of a large decline in student visa applications. Glass’s research, along with more recent reports, shows a double-digit decline in student visas from March 2024 to this March alone; the latest moves could double that, he said.
“[The] COVID [pandemic] was a disruption of 15 percent,” he said. “This looks like it could be more significant than COVID, if the pause is extended and the uncertainty continues.”
In his proclamation announcing the travel ban, Trump wrote that the targeted countries had “deficient” vetting and screening processes for visa applicants, or had “taken advantage of the United States in their exploitation of our visa system and their historic failure to accept back their removable nationals.”
Sarah Spreitzer, vice president and chief of staff for government relations at the American Council on Education, said the rationale outlined in the travel ban—that students pose a unique national security threat and have been overstaying their visas—doesn’t align with reality.
“If this is for national security concerns, our students are some of the most vetted visas out there,” she said. “And I don’t know if our students actually overstay their visas very often.”
Fanta Aw, the president of NAFSA, an association of international educators, echoed Spreitzer and said that international students are already “among the most tracked individuals entering the United States.”
“Actions such as halting student visa issuance and implementing nationality-based travel bans do not enhance national security,” she wrote in an email. “Instead, they weaken it—undermining our economy, diminishing our global competitiveness and eroding our country’s ability to effectively engage with the global population.”
The 2017 travel ban was amended twice after being challenged in the courts and eventually exempted nonimmigrant visas, including student and exchange visas. Spreitzer said the administration’s outsize focus on student visa holders over the last few months makes that outcome less likely, but only time—and the courts—will tell.
Havoc at Harvard
The travel ban came on the heels of another White House proclamation Wednesday night, this one banning foreign students and scholars from attending Harvard.
Trump restricted visa applicants from entering the country “solely or principally to participate in a course of study at Harvard University or in an exchange visitor program hosted by Harvard,” claiming that allowing foreign students on campus would be “detrimental to the interests of the United States because, in my judgment, Harvard’s conduct has rendered it an unsuitable destination for foreign students and researchers.”
A Harvard spokesperson wrote that the proclamation is “another illegal retaliatory step taken by the administration in violation of Harvard’s first amendment rights” and that the university “will continue to protect its international students.”
The proclamation is the latest jab in a weeks-long fight over international students on Harvard’s campus. Last month the Trump administration attempted to revoke Harvard’s Student Exchange and Visitor Program certification, which would have banned the university from enrolling international students altogether, affecting not just visa applicants but also foreign students and researchers currently on campus. Harvard challenged the effort in court, and a judge swiftly granted the university an injunction; on Monday, the Trump administration lost its appeal to overturn that decision.
Harvard amended that lawsuit to include a challenge to the newest proclamation, calling it “an unlawful evasion of the Court’s order.”
“When the Court enjoined the Secretary [of State’s] efforts to revoke Harvard’s certifications and force its students to transfer or depart the country, the President sought to achieve the same result by refusing to allow Harvard students to enter in the first place,” the amended suit reads.
Unlike the SEVP decertification attempt, Trump’s executive proclamation doesn’t immediately affect international students currently enrolled at Harvard, only those who have yet to secure visas—though it does instruct the State Department to determine whether current students “should have their visas revoked.”
The proclamation runs through a gamut of justifications for its international student ban. Trump cites data on increasing campus crime rates in the interest of student safety, alleges discrimination in the admissions process that he claims foreign students exacerbate and points to academic partnerships and financial contributions from countries like China that he says endanger U.S. national security interests.
Notably, Trump also says Harvard has failed to cooperate with the administration’s demands for student misconduct records; the university has provided data on “only three students,” which Trump wrote was evidence that “it either is not fully reporting its disciplinary records for foreign students or is not seriously policing its foreign students.”
Glass said the move is almost certainly an attempt to work around the court injunction using executive powers rather than the visa bureaucracy. And making the issue about constitutional authority in the national security realm—rather than whether the proper SEVP decertification process was followed—could change the legal calculus in court.
“That’s what’s going to set a precedent for generations,” Glass said. “Will the precedent of autonomy and academic freedom at Harvard win in the courts? Or will the precedent of national security powers for the government win the day?”
(This story has been updated to correct the list of banned countries to include Republic of the Congo.)