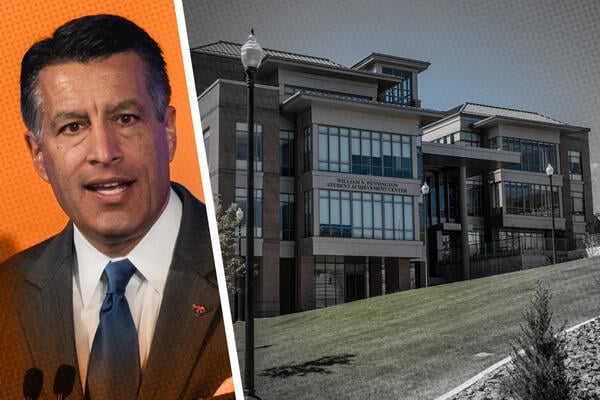
Brian Sandoval, former Republican governor and president of University of Nevada at Reno, is standing up for the university’s undocumented student support program, despite threats of an investigation from the federal government.
Photo illustration by Justin Morrison/Inside Higher Ed | Cheriss May/NurPhoto/Getty Images | Brycia James/iStock/Getty Images
Centers and programs for undocumented students are caught in a politically precarious moment after the Department of Justice called for an investigation of the University of Nevada at Reno’s undocumented student services. Immigrant students’ advocates say the move marks an escalation in the Trump administration’s ongoing crackdown on higher ed benefits for these students. And they worry campus programs supporting undocumented students might pre-emptively scale back or close altogether.
In a letter late last month, DOJ officials directed Education Secretary Linda McMahon to investigate the Nevada university over UndocuPack, its support program for undocumented students.
According to the letter, the DOJ had received reports of the university’s “efforts to assist illegal immigrants” by providing referrals to on- and off-campus resources, student aid, and academic and career support, including helping students find “career opportunities that do not require applicants to provide a Social Security Number.”
“We are referring this matter to the Department of Education to investigate whether UNR is using taxpayer funds [to] subsidize or promote illegal immigration,” the letter read.
The U.S. Department of Education did not respond to a request for comment; Inside Higher Ed received an automatic out-of-office message citing the government shutdown.
But UNR is pushing back. Brian Sandoval, a former Republican governor of Nevada and the university’s first Hispanic president, responded with a forceful defense of the program.
He stressed to students and staff that the UndocuPack program offers supports to all students, regardless of citizenship status, and uses no federal funds. He also emphasized that several state-funded scholarships don’t take immigration or residency status into account; the university doesn’t dole out state or federal aid to anyone ineligible.
“The University has remained in compliance with federal and state law, as well as the Nevada and United States Constitutions regarding adherence to federal and state eligibility requirements for undocumented students for federal aid and scholarships,” Sandoval wrote. “In addition, we have made good, and will continue to make good on our commitment in ensuring a respectful, supportive, and welcoming environment on our campus where all our students have access to the tools they need for success.”
He said the university plans to respond to the proposed investigation “through the appropriate legal channels.”
A ‘Test Case’
The threat to UNR brings fresh worries for undocumented students’ advocates, who say it’s the latest in a string of federal efforts to curb public higher ed benefits for such students.
The Justice Department has already sued five states over policies allowing undocumented students to pay in-state tuition, successfully quashing state laws in Texas and Oklahoma after their attorneys general swiftly sided with the federal government. Over the summer, the Education Department announced it would investigate five universities for offering scholarships intended for undocumented students, claiming such programs violated civil rights law. The department also ended Clinton-era guidance that allowed undocumented students to participate in adult and career and technical education programs in response to Trump’s February executive order demanding that “no taxpayer-funded benefits go to unqualified aliens.”
Diego Sánchez, director of policy and strategy at the Presidents’ Alliance on Higher Education and Immigration, said going after UNR’s UndocuPack program is “part of a broader effort by the administration to intimidate colleges and universities that seek to serve undocumented students.” But it also takes the campaign a step further, “targeting any form of campus support for undocumented students,” including academic and career services. “It’s definitely a pattern of escalating attacks via different avenues of law.”
The DOJ’s letter cites the Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act of 1996, which bars undocumented immigrants from many public benefits, but Sánchez maintains that “no court has ever interpreted PRWORA to bar universities from offering support offices, mentoring resource centers for undocumented students.”
Those kinds of supports for undocumented students exist at colleges and universities across the country. A 2020 study found at least 59 undocumented student resource centers on campuses nationwide, mostly in California but also in other states including Arizona, Colorado, Florida, New Jersey, Oregon, Texas, Utah and Washington.
Sánchez worries that colleges and universities could modify or scrap perfectly lawful programs out of fear after seeing the DOJ chide UNR for such common supports. He also expects the Trump administration to target more programs like UndocuPack.
UNR feels like “a test case,” he said.
Gaby Pacheco, president and CEO of TheDream.US, a scholarship provider for undocumented students, said other colleges and universities with undocumented student supports are already weighing what to do in response to the developments in Nevada.
“Do we duck and hide and lay low so that we don’t get picked on, or do we stand together with others and potentially become a target of this? It’s a question that a lot of people and institutions … are asking themselves,” Pacheco said.
She worries canceling or minimizing undocumented student support programs will send those students a message—“that they don’t belong.” And she doesn’t believe trying to lie low or scale back programs will deflect federal attention.
“This is just month nine into this administration. We still have a full three more years to go,” she said. And the administration seems like it plans to “continue full force until, in essence, there are no policies left where undocumented students have access to higher education.”