Senate Republicans are planning to protect the Pell Grant program, keeping the maximum grant award at $7,395 for the coming academic year, despite the Trump administration’s proposal to lower it to $5,710.
The rejection of Pell Grant cuts at a key committee markup Thursday is just the latest rebuke from congressional appropriators as lawmakers in both chambers have appeared wary of President Trump’s plans to shutter offices, gut programs and generally reshape the federal government.
In addition to protecting $22.5 billion for Pell, the GOP also spared TRIO, campus childcare subsidies and numerous other programs that Trump had proposed zeroing out. It also set new staffing standards for the recently gutted Department of Education, increased funding for medical research by $400 million and rejected the National Institutes of Health’s attempt to cap indirect research cost reimbursements at 15 percent. The legislation also restricts other efforts at NIH to change how grants are awarded, though Democrats say “more needs to be done to protect NIH research programs.”
Over all, the Department of Education is going to receive $79 billion and the NIH will get $48.7 billion. In comparison, Trump had requested $66.7 billion for ED and $27.5 billion for NIH.
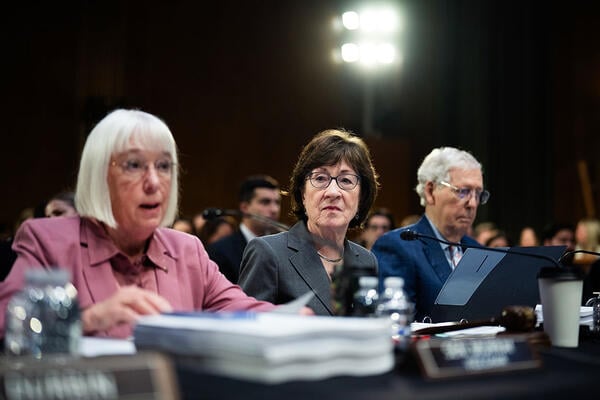
Committee chair Sen. Susan Collins, a Maine Republican, said she was proud of the legislation that advanced Thursday, calling it a bipartisan effort to fund the health and education of American families. She noted that “the appropriations process is the key way that Congress carries out its constitutional responsibility for the power of the purse.”
But Democrats, while overall supportive, noted that they’ve had to make a number of compromises already and warned that Trump could still attempt to make unilateral changes moving forward.
“These are not the bills I would have written on my own, but nonetheless they represent serious bipartisan work to make some truly critical investments in our country and families’ future,” said Sen. Patty Murray, a Washington Democrat and ranking member of the committee. Still, she added, this is only half the battle. “The fact of the matter is we have an administration right now that is intent on ignoring Congress, breaking the law and doing everything it can without transparency to dismantle programs and agencies.”
The Trump administration has repeatedly frozen or cut grant funding, largely declining to spend money that Congress appropriated—moves that Murray and others have decried as illegal. More recently, the administration waited weeks before sending critical funding to states that supports after-school programs, migrant education and adult education. About $7 billion was affected, and colleges had to scramble to find a way to fill the funding gaps before Trump’s Office of Management and Budget finally released the money last week. Meanwhile, colleges are still waiting for the Education Department to open up grant applications for millions in funds.
At NIH, grant cancellations and other changes have slowed the flow of research funding to colleges. Earlier this week the administration briefly paused all new grant awards, infuriating congressional Democrats. Over all, since Trump took office, the biomedical research agency has cut more than 4,000 grants at 600 institutions totaling somewhere between $6.9 billion and $8.2 billion.
Beyond the grant cuts, the Trump administration recently clawed back money that had been allocated to public broadcasting, using a legislative process called rescission. The president is expected to propose a second rescission package in the months to come, this time targeting education dollars. Democrats have warned that using rescissions to change the budget could endanger talks on fiscal year 2026 spending.
So while higher ed lobbyists typically look to the Senate’s spending plan as the framework for what to expect in the final bill, Trump’s willingness to test the limits of executive power complicates the picture.
Still, the Senate’s proposals for the NIH as well as the Education Department, which funds a number of programs at the previous year’s level, is a victory for advocates who spent months warning that Trump’s budget cuts would be devastating for students and research.
“We are not surprised by what we’ve seen. The Senate often works more bipartisanly together, and that was reflected in the markup today,” said Emmanual Guillory, senior director of government relations at the American Council on Education. “In this political environment, flat funding is a win. It’s not ideal, but it is us being mindful of the current realities that we’re in and the financial constraints that we’re in, especially with the upcoming rescissions package that’s supposed to include education.”
That said, Guillory noted that he’s bracing for deeper cuts from the House, which has yet to release its education and health spending proposals.
“I could see the House having a bit more influence [than most years past], as they have had more influence so far this Congress,” he said.
Seeking Guardrails
Democrats did try to amend the bill in order to establish guardrails that would retroactively address Trump’s funding cuts and protect the fiscal year 2026 appropriations from a similar ambush.
Sen. Dick Durbin, an Illinois Democrat, proposed reinstating all college grants frozen or retracted since Jan. 28, with the exception of those pulled due to financial malfeasance. He highlighted how, in Chicago, the cuts have halted infant heart defect research and then ran through a lengthy list of other medical projects affected in other senators’ districts.
“This could happen to any of your states’ research centers. It could hurt any of your families,” he argued.
Later, Sen. Chris Murphy of Connecticut, one of the few Democrats who did not support the bill, sought an inspector general report into whether the Department of Education’s civil rights office is properly following statutes when investigating discrimination complaints and issuing discipline.
The Department of Education’s OCR, along with other agencies, has launched dozens of investigations into alleged civil rights violations at colleges and universities. Those inquiries haven’t followed the required statutory procedures, but colleges have lost funding and faced other consequences.
Murphy proposed withholding OCR funding until the appropriations committee received the IG’s report.
“My worry is simply that the president is going to ignore the will of Congress that is present in this legislation,” he said. “If this does become normalized—if the president of the United States gets to deny funds to universities because they don’t like political viewpoints of the student body or of the faculty—that is a Pandora’s box that is hard to ever again close.”
Sen. Shelley Moore Capito, the West Virginia Republican who leads the education and health subcommittee, shot down both proposals, calling Murphy’s amendment “contrary to the point of the [OCR] office” and Durbin’s “too broad.”
“I think every administration has the prerogative to implement new goals and priorities,” she said.