How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
Tag: K12
-

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback. -

Trump 2.0: A sea change for K-12
To say the first year of the second Trump administration brought a sea change for federal education policy would be an understatement. From efforts to shutter the U.S. Department of Education to legal battles on issues including staffing cuts, immigration enforcement, and transgender students’ athletic participation, few areas of the K-12 sector have been untouched.
To take a look back at key K-12 developments of President Donald Trump’s first year back in the White House, follow along with us below.
U.S. President-elect Donald Trump takes the oath of office from Chief Justice John Roberts as Trump’s family members look on during inauguration ceremonies at the U.S. Capitol on Jan. 20, 2025, in Washington, D.C.
Chip Somodevilla via Getty Images
January
- On the first day of Trump’s second term in office — Jan. 20, 2025 — his administration rescinded Biden-era guidance discouraging immigration enforcement near schools and other “sensitive areas” like hospitals and churches. The move sparked fear among school communities that enforcement activities would happen on their campuses. That led to districts and community partners informing immigrant families of their constitutional rights and issuing guidance to school staff about protocols to take during any such enforcement actions.
- On Jan. 23, Trump’s U.S. Department of Education eliminated diversity, equity and inclusion efforts within the agency. The agency said at the time that it “removed or archived” hundreds of outward-facing documents — including guidance, reports and training materials — that mention DEI. That included links to resources encouraging educators to incorporate DEI in their classrooms.
- Quick to make an imprint on K-12 policy, the Trump administration on Jan. 24 rescinded Biden-era guidance that said implementing book bans could put school districts in violation of civil rights law.
- Trump on Jan. 29 signed an executive order encouraging the expansion of school choice in states. The order directed the department to develop plans for using its discretionary grant programs “to expand education freedom for America’s families and teachers.”
- Another executive order signed the same day prohibited the use of federal funding for “illegal and discriminatory treatment and indoctrination in K-12 schools, including based on gender ideology and discriminatory equity ideology.”

Linda McMahon, President Donald Trump’s nominee to be Secretary of Education, testifies during her Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee confirmation hearing in the Dirksen Senate Office Building on Feb. 13, 2025, in Washington, D.C.
Win McNamee via Getty Images
February
- Trump signed an executive order on Feb. 4 saying the federal government would rescind all funds from educational programs that allowed transgender girls and women to participate on sports teams that align with their gender identity. LGBTQ+ advocates condemned the action as discriminatory.
- The anti-DEI stance led the newly formed Department of Government Efficiency to cancel about $881 million in multiyear research contracts at the Education Department on Feb. 10. This brought concerns from education researchers about future impact, including data that would be missing to measure chronic absenteeism, student achievement, teacher shortages and other metrics.
- Anti-DEI efforts continued as the Education Department on Feb. 27 announced the launch of an “end DEI” portal for people to report “illegal discriminatory practices.” While the website is no longer live, a lawsuit brought by the American Federation of Teachers and other plaintiffs challenged the agency’s prohibition on considering race in education programs. That case is still pending.

A U.S. Department of Education employee leaves the agency’s headquarters with their belongings on March 20, 2025, in Washington, D.C. On March 11, the agency announced a massive reduction-in-force that shrunk the department workforce.
Win McNamee via Getty Images
March
- Linda McMahon, a former administrator of the Small Business Administration and former president and CEO of World Wrestling Entertainment, was confirmed by the Senate in a 51-45 vote along party lines as secretary of the Education Department on March 3.
- One of the biggest developments this month in the Trump administration’s efforts to shrink the federal education footprint came on March 11 with a massive reduction-in-force order at the Education Department The Education Department’s workforce dropped from 4,133 when Trump was inaugurated to around 2,183 due to those layoffs and previously accepted buyouts.
- McMahon and others joined Trump at the White House on March 20 for an executive order signing ceremony, directing McMahon to “take all necessary steps to facilitate the closure of the Department of Education.”

U.S. Attorney General Pamela Bondi announced a civil lawsuit against Maine Department of Education on April 16, 2025, and said that schools that comply with the administration’s civil rights statute interpretations will be spared.
Retrieved from U.S. Department of Justice.April
- The Trump administration on April 4 announced a major change in Title IX enforcement at schools and colleges: It would tap the U.S. Department of Justice for a Title IX Special Investigations Team. The move marked a shift of some education civil rights investigation and enforcement responsibilities to the Justice Department, which would henceforth help investigate policies allowing transgender students to participate on girls’ and women’s athletic teams and to use facilities aligned with their gender identity.
- On April 4, mass layoffs at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services led to the shuttering of five Office of Head Start regional offices in Boston, New York, Chicago, San Francisco and Seattle. The retrenchment raised alarms among early childhood education advocates, who cautioned that the cuts could lead to service delays and weaken the program. Adding to those concerns, Head Start was zeroed out in a leaked draft fiscal 2026 budget plan for HHS.
- Anxieties continued to increase over the administration’s uptick in Immigration and Customs Enforcement activity. Two Los Angeles Unified School District elementary schools reported that federal agents had attempted to gain entry on April 7 by claiming they had families’ permission to speak to students.
- The administration moved to cut off Maine’s federal K-12 funds, backed by a DOJ civil lawsuit announced April 16 over the state’s transgender student athlete policy. The move came amid other changes to how the Education Department conducts Office for Civil Rights investigations, which included rapid and targeted investigations.
- The Education Department on April 30 cancelled $1 billion in grants initially awarded to districts across the U.S. to support student mental health. The funds — which aimed to help bring more mental health professionals into schools — were discontinued due to “conflict” with Trump administration priorities, according to the agency.

U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon speaks during a Cabinet meeting at the White House on April 30, 2025, in Washington, D.C.
Andrew Harnik via Getty Images
May
- The Trump administration kicked off May by unveiling its federal skinny budget proposal for FY 2026 on May 2. Reflecting the administration’s anti-DEI priorities, proposed cuts included all $70 million for Teacher Quality Partnerships grant that were often used for workforce diversity efforts, all $7 million for Equity Assistance Centers that were established as part of desegregation efforts, all $890 million for English Language Acquisition, and a $49 million cut for OCR. Head Start, however, was spared from the chopping block, as was funding for Title I and the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act. The budget plan also included a $60 million increase for charter schools.
- On May 22, U.S. District Judge Myong Joun issued a preliminary injunction in State of New York v. McMahon that ordered the department be “restored to the status quo” prior to the day President Donald Trump retook office. The agency’s actions since its mass layoffs, Joun said, showed no evidence that the workforce reductions had improved efficiency or that the agency was making progress in working with Congress to close the department. “A department without enough employees to perform statutorily mandated functions is not a department at all,” Joun wrote. “This court cannot be asked to cover its eyes while the Department’s employees are continuously fired and units are transferred out until the Department becomes a shell of itself.”
- The administration also faced legal setbacks on various other fronts in May. A court-approved settlement between the U.S. Department of Agriculture and Maine, issued May 2, prohibited the federal government from freezing school meal funds for the state. The funds were frozen in relation to the state’s Title IX dispute with the Trump administration. Judges also ordered the administration to restore temporary extensions of federal COVID-19 emergency funds on May 6 and to temporarily reinstate the Southern Education Foundation’s Equity Assistance Center on May 30.
- On May 30, the Trump administration released further details on its proposed FY 2026 budget for the Education Department. The more comprehensive budget requested $66.7 billion for the agency, amounting to a $12 billion, or 15.3%, cut from FY 2024 funding levels. The administration’s K-12 Simplified Funding Plan called for merging 18 current competitive formula funding grant programs into one $2 billion formula grant program. The administration said the move would lead to innovation and return power to the states.
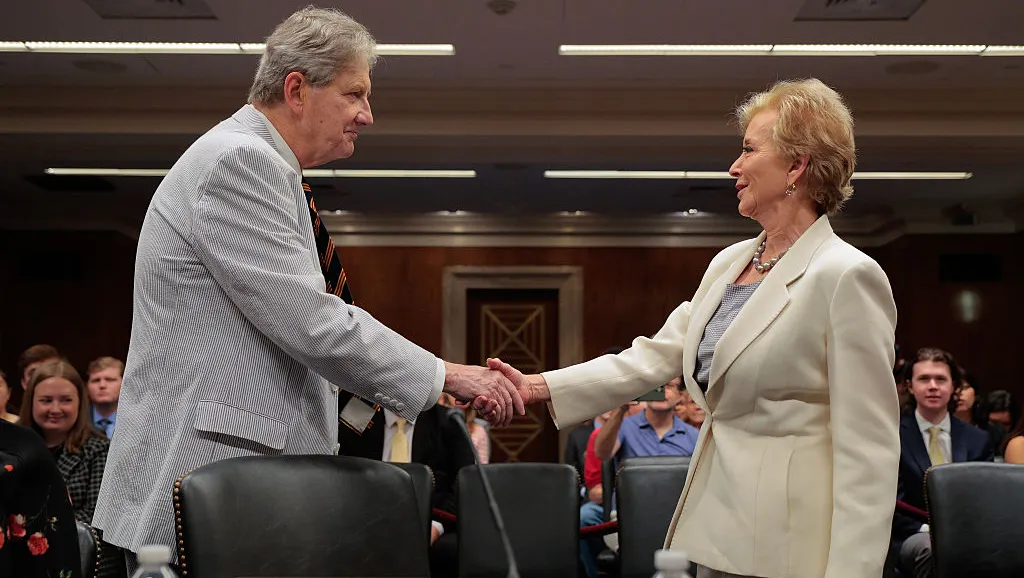

U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon greets Sen. John Kennedy, R-La., before a hearing of a Senate Appropriations subcommittee about the Education Department’s fiscal year 2026 budget proposal on June 3, 2025, in Washington, D.C.
Chip Somodevilla via Getty Images
June
- The administration’s Title IX crackdown over transgender student athlete policies continued as the Justice Department on June 2 warned California districts of “legal liability” for complying with state policies on the issue. The letter to public school districts in the state came after a transgender athlete won gold in a state high school track and field competition. California responded by suing the Justice Department. The Education Department later announced an OCR investigation had found the state in violation of Title IX and threatened further DOJ action.
- McMahon defended the administration’s education budget proposal at a Senate appropriations subcommittee hearing on June 3, during which she said the administration had set a “responsible” goal for the Education Department’s closure and that improving literacy was her No. 1 priority.
- The Education Department’s court battles over the March reduction-in-force continued as states suing the agency over the layoffs claimed the move had impacted legally required functions such as research and grant distribution. In documents submitted to the U.S. Supreme Court, however, the Education Department said states had “no statutory right to any particular level of government data or guidance.”
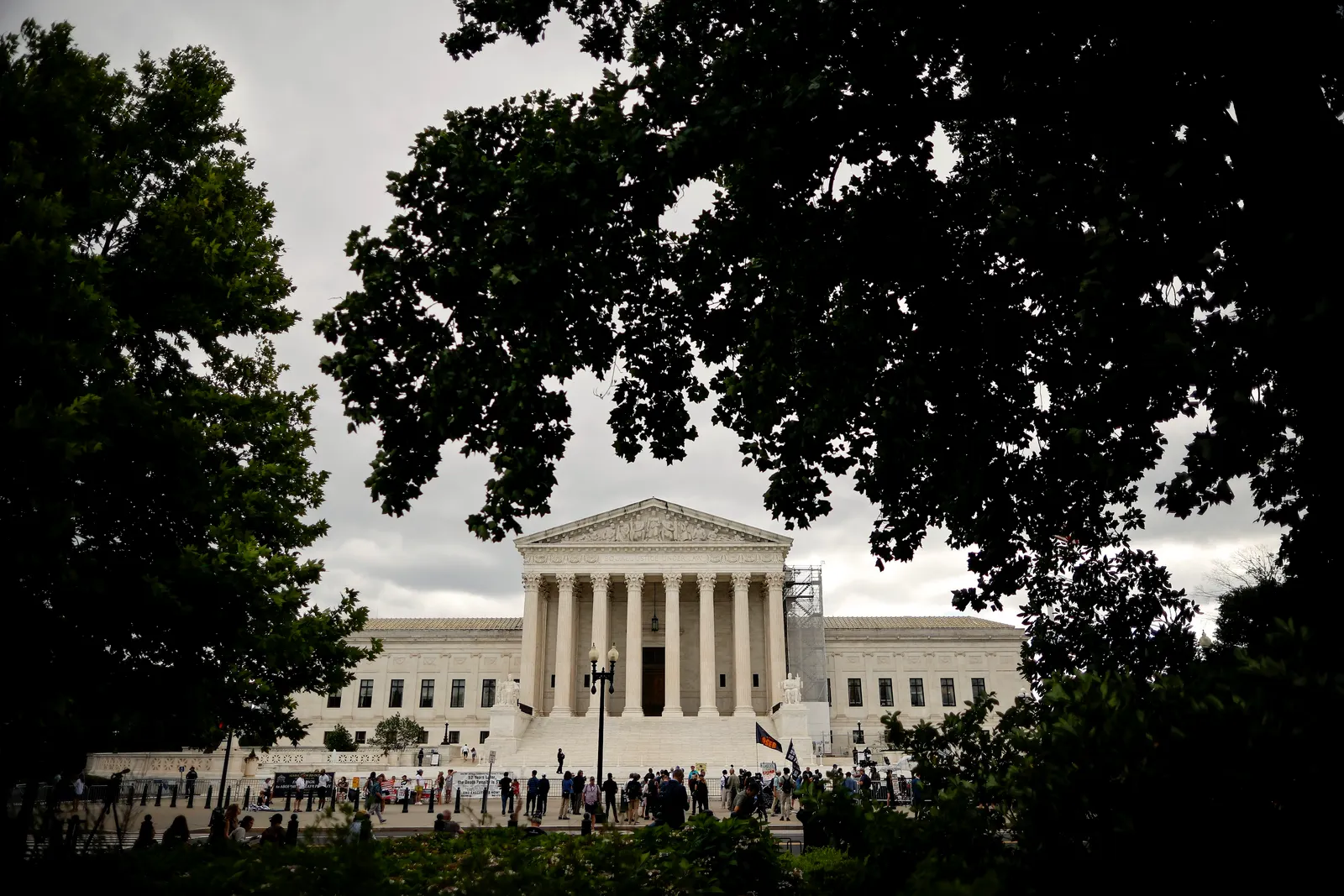

The U.S. Supreme Court is pictured on July 1, 2024, in Washington, D.C. On July 14, 2025, the high court allowed the Education Department to temporarily proceed with layoffs that began in March while lower courts determined their legality.
Chip Somodevilla via Getty Images
July
- Nearly half of states sued the Trump administration over $6.2 billion in frozen federal K-12 grant funds in mid-July, which were supposed to be distributed to states and localities by the beginning of the month. Due to the funding freeze, school districts faced “budgetary chaos“ related to after-school programming, services for English learners, and professional development. The frozen funds put education programs at risk, including those related to migrant education, English learner services, professional development, academic enrichment, and before and after-school services. As a result of the states’ lawsuit, the administration began to release the money less than a month after the government’s missed distribution deadline.
- The Trump administration on July 10 restricted education-related programs for some immigrants based on their immigration status, saying “no taxpayer-funded benefits go to unqualified aliens.” The restrictions affected Head Start, tuition for dual enrollment, adult education, and career and technical education training programs. States sued the administration over the restrictions on July 21 and succeeded in winning temporary relief as the administration entered a court agreement four days later to pause them while the lawsuit is pending.
- The Supreme Court on July 14 gave the Education Department the green light to push forward with layoffs that began in March, allowing them temporarily while the question of their legality is argued in the lower courts.
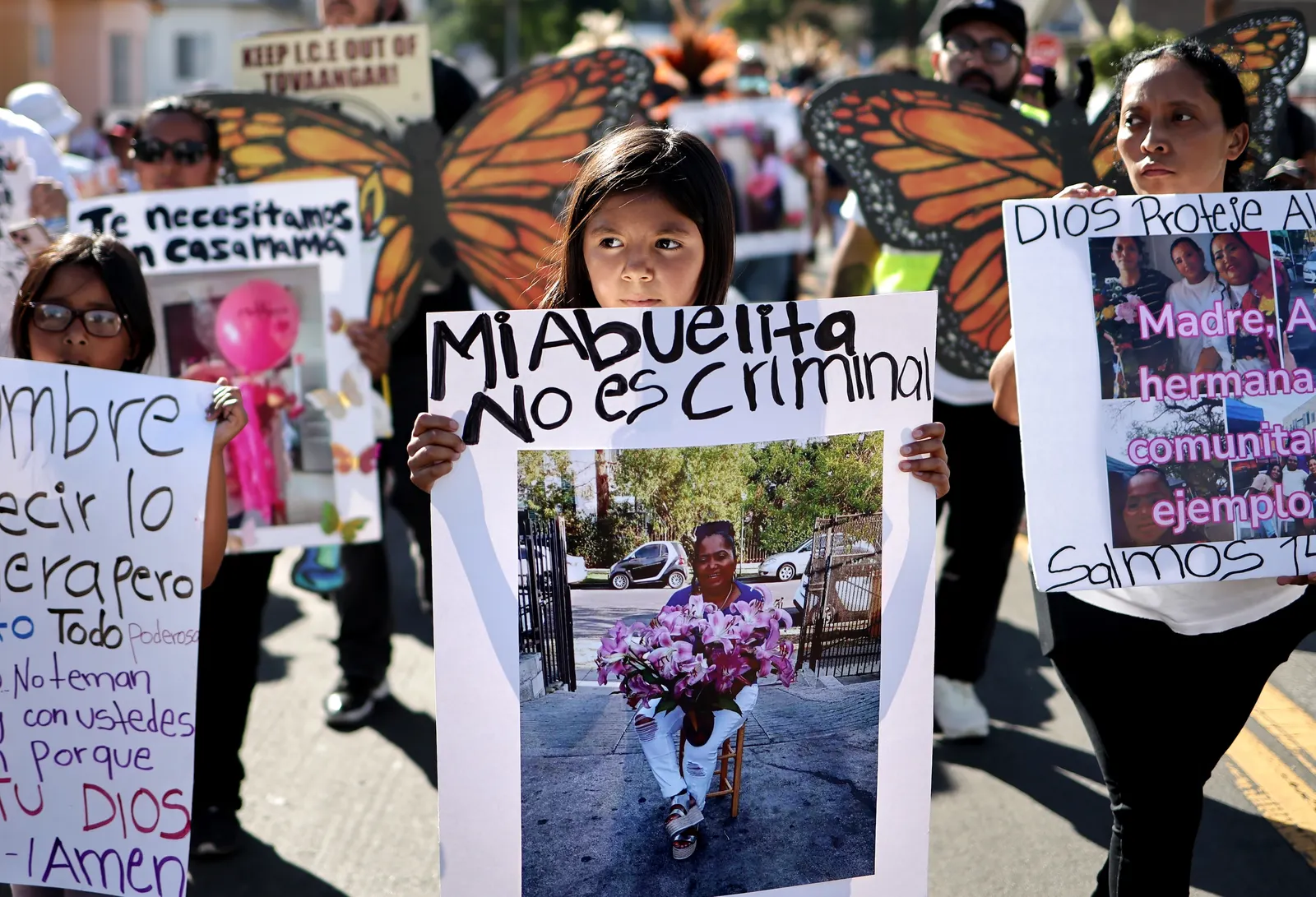
The granddaughter (center) of Emma De Paz, a street vendor detained during ICE activites, carries a sign during a protest on July 1, 2025, in Los Angeles, Calif. Heavy ICE presence in Los Angeles — including on school grounds — sparked outcry over the course of the summer.
Mario Tama via Getty Images
August
- August began with outcry from education policy and legal experts over sweeping anti-DEI guidance released by the Department of Justice on July 30, which affected school district hiring and training practices, as well as programming available to students. Under the guidance, districts could be exposed to legal liability by asking job applicants how their “cultural background informs their teaching,” using recruitment strategies targeting candidates from specific geographic areas or racial backgrounds, training employees on “toxic masculinity,” and asking job candidates to describe how they overcame obstacles — which the department said could amount to “illegal discrimination.”
- As schools open their doors for the 2025-26 school year, reports of ICE enforcement around or on school grounds ramped up, impacting parents during school pickup and drop-offs. Students were also affected by ICE activity, which included a 15-year-old with disabilities being handcuffed as he was registering for classes in Los Angeles.
- The Education Department quietly rescinded Obama-era guidance that called on states and districts to ensure English learners “can participate meaningfully and equally” in school and “have equal access to a high-quality education and the opportunity to achieve their full academic potential.”
- State universal school meal programs faced financial turmoil as President Donald Trump’s “Big, Beautiful Budget” law, which was enacted on July 4, cut Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program and Medicaid — a move that could have severe ripple effects for the same programs.
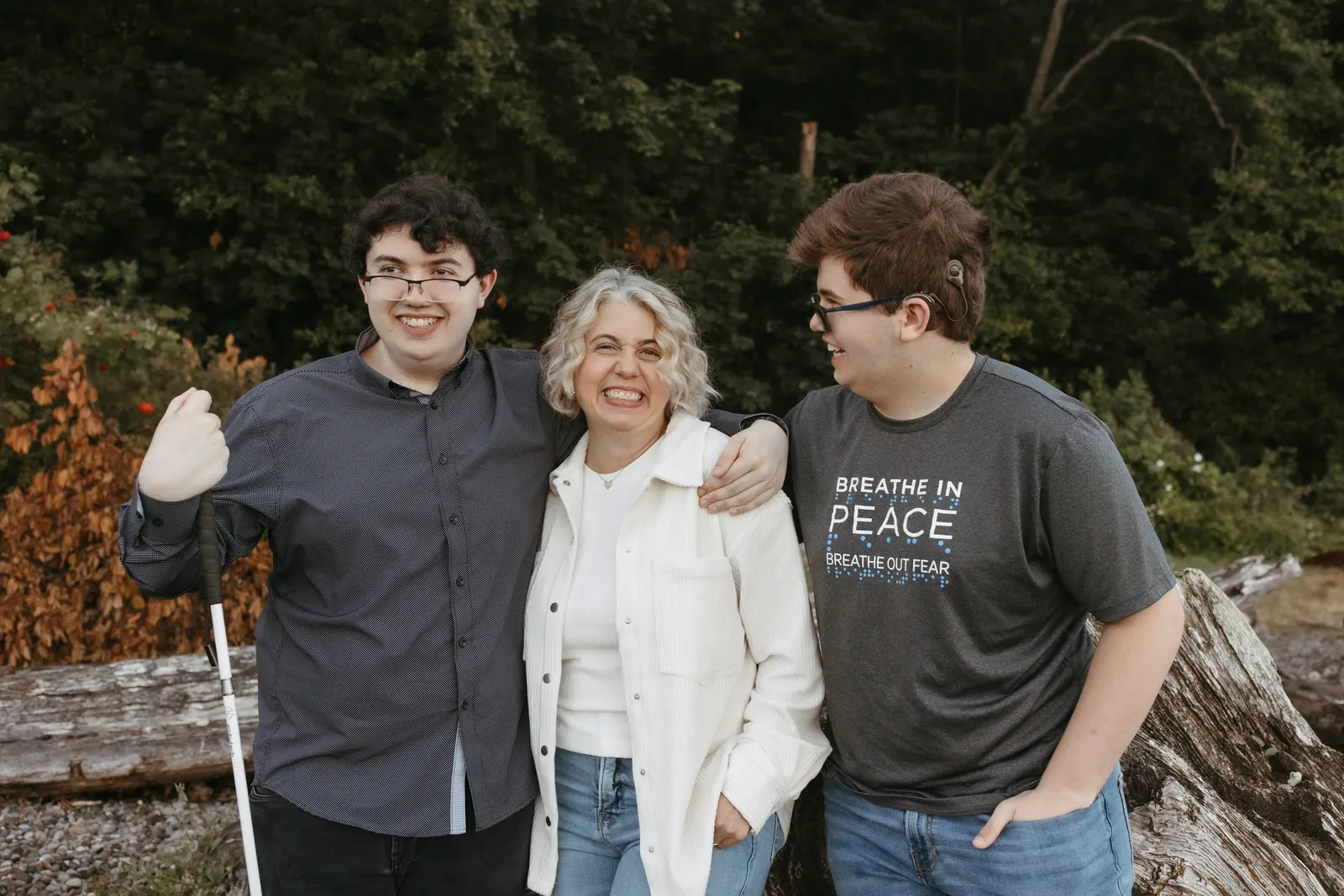

Lanya Elsa (middle) says support through IDEA Part D grants were pivotal for her sons, Conner McKittrick (left) and Dalton McKittrick, who are deafblind. Deafblind programs funded by the grant were left scrambling after abrupt cancellations by the Trump administration which said they were “not in the best interest of the Federal Government.”
Permission granted by Erika Dubois Photography
September
- Families, educators and advocates of children and youth who are both blind and deaf scrambled to reclaim abruptly canceled federal funding after the Education Department sent a notice of noncontinuation for four deafblind projects in Washington, Oregon, Wisconsin and a consortium of New England states. Combined, the four projects’ grants were estimated at $1 million affecting about 1,365 children.
- U.S. Attorney General Pamela Bondi warned in a Sept. 8 memo to the U.S. Department of Justice’s Civil Rights Division that schools must provide parents with the ability to opt their children out of instruction related to gender and sexuality, or risk being targeted by the department. It directed the division to be vigilant of parental rights’ violations at schools and for U.S. district attorneys nationwide to weed out and respond to “credible threats against parents.”
- The Trump administration’s Make America Healthy Again Commission on Sept. 9 released the “Make Our Children Healthy Again” strategy report, which focused partly on school nutrition policies and pointed toward a need to serve healthier meals to schoolchildren. The report called for barring or limiting artificial dyes in food products and improving access to whole, healthy foods in school meals.

House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries, D-NY, speaks at a news conference on Oct. 15, 2025, about the federal government shutdown, flanked by members of the House Democratic Caucus, outside the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C.
Alex Wong via Getty Images
October
- Oct. 1 marked the first day of a prolonged federal government shutdown after Congress could not come to agreement on sticking points on the 2026 fiscal year budget. The Office of Management and Budget issued a memo a week before the shutdown threatening mass firings of federal employees should the shutdown come to fruition.
- The 4th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals dealt a blow to Virginia’s Fairfax County Public Schools in its Title IX legal battle with the Trump administration on Oct. 1, when the court denied the district’s request to temporarily block funding restrictions issued by the Education Department. The Trump administration put Fairfax schools’ federal funding on “reimbursement only” status after the agency said the district violated Title IX by allowing transgender students to use bathrooms aligning with their gender identity.
- On Oct. 10, some 466 Education Department employees — including most staff at the Office of Special Education Programs — received RIF notices as part of the wider shutdown-related effort to lay off federal employees. The layoffs particularly caused concern among special education advocates over the potential effects on funding and implementation of programs under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act.
- An Oct. 28 preliminary injunction paused RIF notices issued during the shutdown.
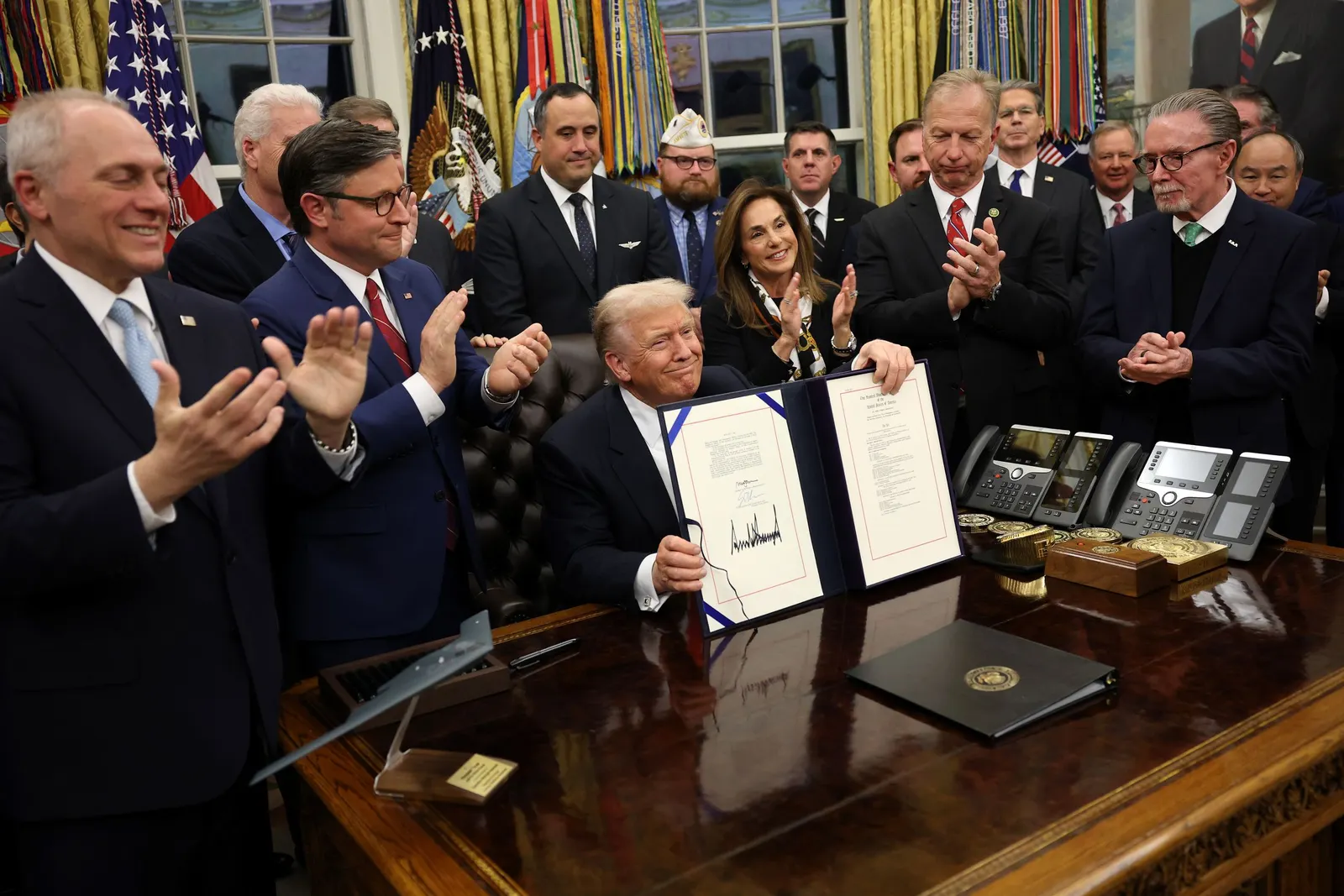

President Donald Trump holds up federal legislation he signed on Nov. 12, 2025, to reopen the federal government during a ceremony with Republican lawmakers and business leaders in the Oval Office in Washington, D.C.
Win McNamee via Getty Images
November
- The federal government shutdown ended on Nov. 12 when Trump signed a continuing resolution to reopen the federal government and fund the Education Department through Jan. 30. The continuing resolution required back pay for employees furloughed during the shutdown and rescission of the RIFs issued on Oct. 10. The agency was also prohibited from issuing further RIFs through Jan. 30.
- Moving one step closer toward dismantling the Education Department, the Trump administration announced on Nov. 18 that it would transfer the agency’s management of six programs to other federal agencies. Special education, civil rights enforcement and financial aid were not impacted by the announcement. Affected programs, however, included the Office of Elementary and Secondary Education, Indian education programs, international education and foreign language studies, and the Office of Postsecondary Education’s institution-based grants.
- A coalition of school districts, employee unions and a disability rights organization amended a lawsuit on Nov. 25 seeking to halt the outsourcing of Education Department programs through the interagency agreements announced on Nov. 18. The lawsuit said that moving the department’s core programming to other agencies is illegal and would be harmful to K-12 and higher education students, families and educators.
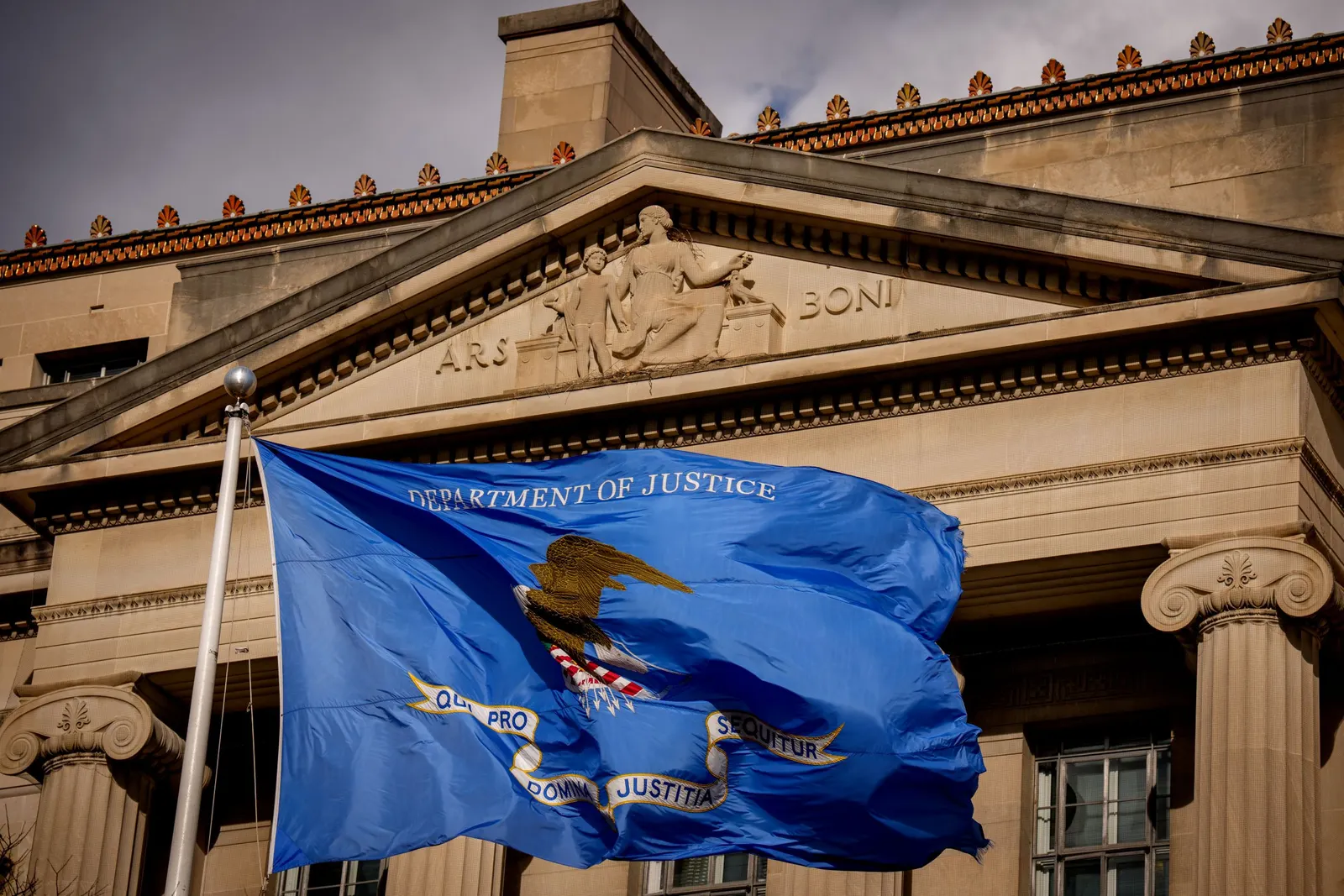

The exterior of the Robert F. Kennedy Department of Justice building on Dec. 19, 2025, in Washington, D.C. The Justice Department continued to take a greater role in Education Department matters in December by, for example, suing Minneapolis Public Schools.
Andrew Harnik via Getty Images
December
- The Department of Justice continued to take a greater role in enforcing the Trump administration’s K-12 priorities as the agency announced on Dec. 8 it would join a lawsuit against Virginia’s Loudoun County School Board involving two Christian high school boys who were suspended after complaining about a transgender student in their locker room.
- That same week, the Justice Department sued Minneapolis Public Schools on Dec. 9 over a teacher union agreement that the agency alleged was racially discriminatory because it included diversity-oriented goals for recruiting and retaining Black men.
- A federal judge on Dec. 19 ordered the Education Department to permanently reinstate cancelled mental health grants in 16 states. The order said the April cancellation of the school-based and professional development funding was unlawful and had caused “significant disruption” to the 16 plaintiff states. Court documents said the canceled grants totaled $1 billion nationwide. The Trump administration had issued $208 million in new mental health grants under revised priorities the week before the Dec. 19 order.
-

Why K-12 educators need data literacy, not just data
Key points:
Walk into any data meeting at a K-12 school today, and you’ll likely see a familiar scene: educators huddled around printed reports, highlighters in hand, trying to make sense of student data spread across multiple dashboards. If you’ve ever left one of these meetings feeling mentally exhausted without clear next steps, you’re not alone. The problem isn’t that we lack data in education, but rather that most dashboards show us the past–not the path ahead. It’s like trying to drive while only looking in the rearview mirror.
The education sector sits on massive amounts of student data, yet most schools lack data maturity. They’ve committed to using data and may even have systems that centralize records. But they haven’t embraced what’s possible when we move from having data to using it well; from describing what happened to predicting what’s likely to happen if nothing changes.
We have dashboards–now what?
Every district has dashboards. We can see attendance rates, assessment scores, and demographic breakdowns. These tools tell us what happened, which is useful–but increasingly insufficient for the challenges facing K-12 schools. By the time we’re reacting to chronic absenteeism or declining grades, we’re already behind. And, when does an educator have time to sit down, pull up multiple dashboards, and interpret what they say about each student?
The power of any data dashboard isn’t in the dashboard itself. It’s in the conversations that happen around it. This is where data literacy becomes essential, and it goes far beyond simply reading a chart or calculating an average.
Data literacy means asking better questions and approaching data with curiosity. It requires recognizing that the answers we get are entirely driven by the questions we ask. A teacher who asks, “Which students failed the last assessment?” will get very different insights than one who asks, “Which students showed growth but still haven’t reached proficiency, and what patterns exist among them?”
We must also acknowledge the emotional dimension of data in schools. Some educators have been burned when data was used punitively instead of for improvement. That resistance is understandable, but not sustainable. The solution isn’t to check professional expertise at the door. It’s to approach data with both curiosity and courage, questioning it in healthy ways while embracing it as a tool for problem-solving.
From descriptive to predictive: What’s possible
Let’s distinguish between types of analytics. Descriptive analytics tell us what happened: Jorge was absent 15 days last semester. Diagnostic analytics tell us why: Jorge lives in a household without reliable transportation, and his absences cluster on Mondays and Fridays.
Now we get to the game-changers: predictive and prescriptive analytics. Predictive analytics use historical patterns to forecast what’s likely to happen: Based on current trends, Jorge is at 80 percent risk of chronic absenteeism by year’s end. Prescriptive analytics go further by helping the educator understand what they should do to intervene. If we connect Jorge’s family with transportation support and assign a mentor for weekly check-ins, we can likely reduce his absence risk by 60 percent.
The technology to do this already exists. Machine learning can identify patterns across thousands of student records that would take humans months to discern. AI can surface early warning signs before problems become crises. These tools amplify teacher judgment, serving up insights and allowing educators to focus their expertise where it matters most.
The cultural shift required
Before any school rushes to adopt the next analytics tool, it’s worth pausing to ask: What actually happens when someone uses data in their daily work?
Data use is deeply human. It’s about noticing patterns, interpreting meaning, and deciding what to do next. That process looks different for every educator, and it’s shaped by the environment in which they work: how much time they have to meet with colleagues, how easily they can access the right data, and whether the culture encourages curiosity or compliance.
Technology can surface patterns, but culture determines whether those patterns lead to action. The same dashboard can spark collaboration in one school and defensiveness in another. That’s why new tools require attention to governance, trust, and professional learning–not just software configuration.
At the end of the day, the goal isn’t simply to use data more often, but to use it more effectively.
Moving toward this future requires a fundamental shift in how we think about data: from a compliance exercise to a strategic asset. The most resilient schools in the coming years will have cultures where data is pervasive, shared transparently, and accessible in near real-time to the people who need it. Think of it as an instructional co-pilot rather than a monkey on the back.
This means moving away from data locked in the central office, requiring a 10-step approval process to access. Instead, imagine a decentralized approach where a fifth-grade team can instantly generate insights about their students’ reading growth, or where a high school counselor can identify seniors at risk of not graduating with enough time to intervene.
This kind of data democratization requires significant change management. It demands training, clear protocols, and trust. But the payoff is educators empowered to make daily decisions grounded in timely, relevant information.
Turning data into wisdom
Data has been part of education from the very beginning. Attendance records, report cards, and gradebooks have always informed teaching. What’s different now is the volume of data available and the sophistication of tools to analyze it. K-12 educators don’t need to become data scientists, but they do need to become data literate: curious, critical consumers of information who can ask powerful questions and interpret results within the rich context of their professional expertise.
The schools that harness their data effectively will be able to identify struggling students earlier, personalize interventions more effectively, and use educator time more strategically. But this future requires us to move beyond the dashboard and invest in the human capacity to transform data into wisdom. That transformation starts with data literacy, and it starts now.
Latest posts by eSchool Media Contributors (see all) -

Basing K-12 Funding on California School Enrollment Could Bring Problems – The 74
Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
This story was originally published by CalMatters. Sign up for their newsletters.
For years, California schools have pushed to change the way the state pays for K-12 education: by basing funding on enrollment, instead of attendance. That’s the way 45 other states do it, and it would mean an extra $6 billion annually in school coffers.
But such a move might cause more harm than good in the long run, because linking funding to enrollment means schools have little incentive to lure students to class every day, according to a report released Tuesday by the nonpartisan Legislative Analyst’s Office. Without that incentive, attendance would drop, and students would suffer.
If the Legislature wants to boost school funding, analysts argued, it should use the existing attendance-based model and funnel more money to schools with high numbers of low-income students, students in foster care and English learners.
When it comes to attendance, money talks, the report noted. For more than a century, California has funded schools based on average daily attendance – how many students show up every day. In the 1980s and ’90s, the state started to look at alternatives. A pilot study from that time period showed that attendance at high schools rose 5.4% and attendance at elementary schools rose 3.1% when those schools had a financial incentive to boost attendance.
This is not the time to ease up on attendance matters, the report said. Although attendance has improved somewhat since campuses closed during the pandemic, it remains well below pre-COVID-19 levels. In 2019, nearly 96% of students showed up to school every day. The number dropped to about 90% during COVID-19, when most schools switched to remote learning, but still remains about 2 percentage points below its previous high.
Attendance is tied to a host of student success measurements. Students with strong attendance tend to have higher test scores, higher levels of reading proficiency and higher graduation rates.
“It’s a thoughtful analysis that weighs the pros and cons,” said Hedy Chang, president of the nonprofit research and advocacy organization Attendance Works. “For some districts there might be benefits to a funding switch, but it also helps when districts have a concrete incentive for encouraging kids to show up.”
True cost of educating kids
Schools have long asked the Legislature to change the funding formula, which they say doesn’t cover the actual costs of educating students, especially those with high needs. The issue came up repeatedly at a recent conference of the California School Boards Association, and there’s been at least one recent bill that addressed the issue.
The bill, by former Sen. Anthony Portantino, a Democrat from the La Cañada Flintridge area, initially called for a change to the funding formula, but the final version merely asked the Legislative Analyst’s Office to study the issue. The bill passed in 2024.
A 2022 report by Policy Analysis for California Education also noted the risks of removing schools’ financial incentive to prioritize attendance. But it also said that increasing school funding overall would give districts more stability.
Enrollment is a better funding metric because schools have to plan for the number of students who sign up, not the number who show up, said Troy Flint, spokesman for the California School Boards Association.
He also noted that schools with higher rates of absenteeism also tend to have higher numbers of students who need extra help, such as English learners, migrant students and low-income students. Tying funding to daily attendance — which in some districts is as low as 60% — brings less money to those schools, ultimately hurting the students who need the most assistance, he said.
“It just compounds the problem, creating a vicious cycle,” Flint said.
To really boost attendance, schools need extra funding to serve those students.
Switching to an enrollment-based funding model would increase K-12 funding by more than $6 billion, according to the Legislative Analyst’s Office. Currently, schools receive about $15,000 annually per student through the state’s main funding mechanism, the Local Control Funding Formula, with an additional $7,000 coming from the federal government, block grants, lottery money, special education funds and other sources. Overall, California spent more than $100 billion on schools last year, according to the Legislative Analyst.
Motivated by money?
Flint’s group also questioned whether schools are solely motivated by money to entice students to class.
“Most people in education desperately want kids in class every day,” Flint said. “These are some of the most dedicated, motivated people I’ve met, and they care greatly about students’ welfare.”
Josh Schultz, superintendent of the Napa County Office of Education, agreed. Napa schools that are funded through attendance actually have lower attendance than schools that are considered “basic aid,” and funded through local property taxes. Both types of schools have high numbers of English learners and migrant students.
“I can understand the logic (of the LAO’s assertion) but I don’t know if it bears out in reality, at least here,” Schultz said. “Both kinds of schools see great value in having kids show up to school every day.”
This article was originally published on CalMatters and was republished under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives license.
Did you use this article in your work?
We’d love to hear how The 74’s reporting is helping educators, researchers, and policymakers. Tell us how
-

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
-

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
-

6 trends to watch for K-12 in 2026
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.Declining birthrates and growing competition from school choice threaten public school enrollment counts — and therefore school district budgets. Student data privacy concerns are on the rise and only complicated by the explosive rise in artificial intelligence tools and usage. And administrators are continuing to adjust to new policy priorities for curriculum, staffing and more under the second Trump administration. These are but a few of the challenges facing public schools in 2026.
As we head into a new calendar year — and the second half of the 2025-26 school year — here are six trends for K-12 leaders to watch.
Education funding faces pressure from multiple directions
Education funding will face pressures on several fronts in 2026, including strained state coffers, unpredictability in federal funding and competition for local dollars.
Marguerite Roza, director of Edunomics Lab and a research professor at Georgetown University’s McCourt School of Public Policy, predicts flat but stable federal funding for schools in 2026.
Still, state and local education systems are bracing for more uncertainty when it comes to federal funding cycles, according to education researchers and professionals. Last summer, many states and districts were caught off guard when the Trump administration froze federal funding for multiple programs. Likewise, some states and districts worry about potential federal funding restrictions if their policies don’t align with the Trump administration’s priorities.
Roza said that while federal education funding in 2025 was “very drama-infused,” states were level-funded from the previous year, with allocations for Title I and the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act — the two largest pots of federal K-12 money — distributed to states as usual.
And since Congress did not finalize a fiscal year 2026 budget for the U.S. Education Department in 2025, all eyes will be on actions to be taken before the next appropriations deadline on Jan. 30.
At the state level, a fall 2025 fiscal survey from the National Association of State Budget Officers found that 23 states projected general fund spending to decline or remain flat in FY 2026 budgets compared to FY 2025 levels.
This has school systems jockeying for state dollars against other state-supported programs like healthcare and public safety. “If districts were hoping for some big new investment from the states, I would say, ‘This is not your year,’” Roza said.
At the local level, shifting public school enrollment will influence allocations for per-pupil spending, leading to less funding for districts with declining enrollments. That drop in revenue means school systems will need to make tough decisions on closing or consolidating schools and shrinking their workforce, Roza said.
Closing schools is “hard for communities,” and localities will likely approach this in a variety of ways in 2026, Roza said.
Competition for students heats up
Several factors influencing shifts in public school enrollment will continue into the new year, including a shrinking population of young children and a growth in private school choice programs.
The public school versus private school choice debate will intensify as more states launch voucher programs in the 2026-27 school year that use taxpayer dollars to fund private school tuition — and while a nationwide school choice program prepares for a 2027 launch.
Robert Enlow, president and CEO of EdChoice, a nonprofit research and school choice advocacy organization, predicts more families will choose options that aren’t necessarily their neighborhood public school.
“There’s no doubt that the demand for choice has continued since COVID,” Enlow said.
The number of students participating in state-led universal private school choice programs has grown from about 64,000 in 2022-23 to 1.3 million in 2024-25, according to EdChoice. Still, most students — about 49.6 million — attend public schools, based on fall 2022 numbers, the most recently available federal data.
The large population of public school students is why federal and state investments are needed for public schools, according to private school choice opponents. Vouchers leave public schools with fewer resources to meet the needs of their students, which contributes to equity gaps, they say.
Opponents also say that private school choice programs lack transparency and accountability.
“Voucher students lose most of their legal protections under special education and civil rights laws, and voucher programs use public dollars to fund private schools that can and do discriminate against students and employees in ways that are not lawful in public schools, said a Dec. 18 letter from Public Funds Public Schools, a nonprofit advocating for investments and support for public schools. The letter sent to the Internal Revenue Service was in response to calls for public comments ahead of formal rulemaking for the national private school choice program.
Enlow and others predict that some Democratic-led states will join Republican-led states in opting into the national school choice program, which will fund certain expenses for both public and public schools. Those expenses could include tuition and fees, books and supplies, tutoring, payments for services for students with disabilities, computer equipment and internet, and transportation.
“Any traditional public school that says they can’t afford computers or transportation is not thinking how this program could help them,” Enlow said.
District leaders will navigate more teacher layoffs, retention challenges
As student enrollment in public schools is expected to continue declining, and thereby strain K-12 budgets in 2026, states and districts will have to “reimagine and redesign the teacher workforce” — looking at how to best use new technologies, what roles only teachers can fill, and “how to best attract, support and retain the most effective teacher workforce,” said Heather Peske, president of the National Council on Teacher Quality, in an email to K-12 Dive.
More staff layoffs are likely as dropping enrollment leads to deeper district budget cuts, Peske said. This will force district leaders to reckon with any “reduction in force” policies that ignore teacher performance, she added.
Peske also predicted that shrinking state and local K-12 budgets will create more opportunities for districts to consider differentiated pay models — which compensate certain educators more than others — to attract and retain teachers in high-need schools, subjects and regions.
Some K-12 researchers have said declining enrollment and related budget cuts, alongside mass pandemic-era hiring of teachers supported by federal emergency aid funds, have led to a reversal in widespread teacher shortages.
But Paige Shoemaker DeMio, senior analyst for K-12 education policy at the Center for American Progress, said she expects district budget cuts to strain working conditions for teachers and retention rates to drop. Tighter budgets will mean less funding to support teachers, and more responsibilities will be put on their plate, which in turn will increase teacher burnout and drive educators out of classrooms, she said.
Uncertainty to persist as federal changes continue
Districts in 2025 already felt the pressure to change their diversity, equity, inclusion and LGBTQ+ policies after the Trump administration cracked down on race-based and sex-based initiatives. In many instances, the administration has attempted to strong-arm states and districts into complying with its policies by threatening the loss of federal funding. That tactic, rarely used under other administrations, is likely to continue under this one in 2026, civil rights enforcement experts said.
The departments of Education and Justice, for example, have suggested continued use of stringent compliance methods to enforce Title IX and Title VI, which protect students from discrimination based, respectively, on sex and race.
Federal policies are also impacting immigration enforcement on or around school grounds, pushing districts to consider virtual learning options and to offer know-your-rights training or legal counsel for families. The aggressive enforcement has affected students’ attendance, performance and sense of safety, district leaders have said.
In 2026, the trickle-down from federal policies to districts and students will likely continue to impact school operations, said Sasha Pudelski, director of advocacy for AASA, The School Superintendents Association.
“For traditional federal funding and policy processes, it’s been challenging for superintendents to determine what the ‘new normal’ is, compared to a one-time aberration or one-off,” Pudelski said. That’s making planning and preparation difficult for district leaders, she added.
“School district leaders are facing mounting uncertainty and should brace for more in 2026,” Pudelski added.
States will take reins on achievement and absenteeism
The new year will see schools doubling down on supports to raise achievement and lower chronic absenteeism, according to education researchers, professionals and nonprofit organizations.
The stubbornness of low achievement rates — as indicated by last year’s release of 4th and 8th grade math and reading results from the 2024 National Assessment of Educational Progress — means there will be continued momentum to drive scores up, according to education experts.
States will take the helm on much of this work, said Nakia Towns, president of Accelerate, a nonprofit organization that conducts research and provides grants for learning interventions. Some of those efforts will include ensuring that the use of high-quality curriculum materials is driving desired student outcomes, she said.
To that end, Towns predicts states will take more leadership in guiding districts toward outcomes-based contracting for academic resources like tutoring and professional development. They’ll be looking at “which interventions get you the best bang for your buck,” she said.
To help raise achievement and drive up student engagement, schools and districts will home in on strategies to combat chronic absenteeism by expanding real-world educational experiences and opportunities like career and technical education courses, internships and STEAM offerings, according to education experts.
District and school leaders also will monitor whether 2025’s shift in prohibiting student cell phone use during the school day will move the needle on achievement.
Additionally, education experts are watching out for how federal influence will impact academics under the Trump administration. That includes, for example, how the U.S. Department of Education will react to states’ requests for waivers for accountability measures under the Every Student Succeeds Act, according to education professionals and stakeholders.
During a Sept. 18 panel discussion at the Reagan Institute Summit on Education in Washington, D.C., several education leaders said they were open to state assessment flexibilities from the federal government, but they predicted states will want to retain accountability standards.
“I think for a state, accountability and accountability systems might be the most important lever that we have to drive academic results for kids in systems and schools,” said Cade Brumley, Louisiana’s superintendent of education, during the discussion.
Work remains for AI literacy, guidance and online protections
In 2025, Congress increasingly debated and explored federal policy solutions for protecting children and teens online, especially as newer artificial intelligence tools rapidly became available. Jeremy Roschelle, co-executive director of learning sciences research at Digital Promise, said he expects to see more legislative action on student online privacy and safety, especially at the federal level, in 2026.
“We need it,” Roschelle said. “I think people have lived through social media and the harmful effects there can be for youth, and there’s lots to worry about as we get even more powerful tools.”
Pati Ruiz, director of learning technology research at Digital Promise, said she’s hopeful that in 2026 there will be a greater focus on prioritizing teachers input when implementing AI tools in classrooms. That means more lessons on AI literacy for educators will roll out to help instructors critically and appropriately use AI tools, she said.
With at least 32 states having already released their own AI guidance for schools, Ruiz predicts that even more states will continue to put out K-12 recommendations on these tools. Ruiz added that she expects some states will update and revise their initial AI education guidance to be more comprehensive and useful for districts and schools, especially involving their responsible technology use policies.
-

Best Sites & Apps for K-12 Education Games
This article was updated December 2025.
Game-based learning turns potentially tedious study time into an adventurous knowledge quest, complete with catchy soundtracks and digital rewards. It helps keep kids engaged with the subject matter and motivated to pursue greater expertise. Best of all, web- or app-based gameplay integrates easily into both online and in-person classes.
We’ve curated the best K-12 educational game sites and apps, arranged according to cost. Many are free (or offer free basic accounts), while some provide progress tracking and analysis tools for teachers. All are remarkably creative and will help kids enjoy learning.
Best Free K-12 Education Games
LangGuesser
Listen to a brief clip of someone speaking, then click on a country where that language is spoken. It may “sound” easy, but it’s surprising how tricky it is to distinguish unfamiliar spoken languages from one another. No account required, but do create an account in order to track your progress. A great exercise for any language class.Brilliant
Brilliant employs colorful professional graphics and gamified learning to help kids master STEM topics such as algebra and computer science. Exercises start with the basics and gradually build to more complex problems. Each answer, whether correct or incorrect, has an accompanying explanation to aid in understanding the topic. Best of all, Brilliant provides completely free access to its premium account for educators and administrators with school email addresses.GeoGuesser Name The Countries – Geography Quiz Game
There are 195 recognized countries in the world. How many can you identify on an unmarked map, and how fast can you do it? Eight different versions add to the possible challenges. A great way to learn and practice geopolitical knowledge. Free, no account required.Quizzity
A super simple but challenging geography quiz. How close can you place the pin to the city-level location provided? The worldwide map includes nothing but political borders to the province/state level. What I liked about this game is that players earn points for being close, even when incorrect. In this way, users are encouraged to keep trying and learning.Vocab Scrabble
Can you improve your English vocabulary by playing online Scrabble? Yes, according to AE Studio’s Vocab Scrabble, a simple-yet-challenging digital version of the beloved word game. The rules are elementary. Or shall I say basic? Perhaps fundamental? Click “start playing” and the five-minute countdown begins. Like Scrabble, the player receives a selection of letters with which to compose words. Unlike Scrabble, the selection changes after each word created. No account required.New York Times Games Subscription | iOS Android
While not strictly speaking educational games, these standout puzzles from The New York Times clearly require users to exercise language, math, and logic skills. Non-subscribers can play the following inventive games for free: Wordle, Sudoku, Connections, Pips, Strands, and the daily Mini Crossword for free. My favorite is Connections, the devilishly tricky word game that asks users to create four sets of related words. Players must carefully consider all possible meanings of each word before making their choices. And be sure to try creating your own Wordle game, which can be shared with friends, colleagues, and students. Games offer difficulty levels, hints post-game analysis. Available via website or app.Prodigy English
From the makers of the popular Prodigy Math, Prodigy English is a gamified English language learning program that features all the fun bells and whistles of gaming, from creating worlds to boosting energy with correct answers. A suite of teachers’ tools includes assessments and reports. Aligned to Common Core reading and language standards for grades 1 to 6. Best of all, the premium Prodigy English is fully free to educators.Prodigy Math
An award-winning, standards-aligned online math game designed for grades 1-8, Prodigy is modeled on popular fantasy-style multiplayer games. Students select and customize an avatar, and then prepare to battle math problems. Free basic account includes core gameplay and basic pet features. Prodigy Math is fully free to educators.Ducksters
This easy-to-navigate site affords a wide range of educational digital games for students or anyone who enjoys gameplay and learning. Included are math, word, geography, and puzzle games as well as classic games such as chess, checkers, backgammon, mahjong, and more. But it’s not just fun and games at Duckster. An extensive collection of illustrated lessons in history, biography, geography, and science are accompanied by quizzes and links to the relevant games. No account required to play or learn.Khan Academy Kids
An award-winning, free iOs or Android app, Khan Academy Kids offers a comprehensive collection of educational math, literacy, and music games and activities for kids aged 2-8 years. Top-rated by users, this free app includes no ads—and no subscription is needed.Puzzle Playground
From the publisher of Math Playground, Puzzle Playground is a free game-based learning site that uses puzzles of every kind to engage kids’ imaginations. Don’t think “jigsaw” because these amazingly creative puzzles go far beyond shape-fitting. Instead, these varied digital puzzles will keep kids of any age busy challenging their problem-solving, trial-and-error, spatial reasoning, and perseverance skills. Super fun too.Best Free Virtual Escape Rooms for Schools
These top free virtual escape rooms combine the best elements of gameplay — suspense, skill, knowledge, and speed. Arranged according to age suitability.Moose Math – Duck Duck Moose iOs Android
A multi-level math game that allows kids ages 3-7 to earn rewards and decorate cities by solving math problems disguised as adventures. Common Core-aligned for kindergarten and first grade.Wordscapes iOs Android
Wordscape combines the best features of crossword puzzles, word connect, and word anagram games, all accompanied by scenery designed to relax and focus the mind.Mind Games
Don’t worry, this site doesn’t advocate gaslighting or psychological manipulation. Rather it’s a collection of free online number, word and logic games, brain teasers, sudoku, crosswords, and more. Free with (blockable) ads. For a premium ad free gaming, visit adfreegames.com, where users pay only $10 for a full year of access.Solving the Rubik’s Cube!
From educator Ryan Chadwick comes this top-notch digital tutorial for one of the most challenging hands-on puzzles ever. Includes images and advice to boost your speed solving Rubik’s cube. Free, no account required.Annenberg Classroom That’s Your Right
Kids play alone or in multiplayer mode to learn and practice their Bill of Rights expertise. With high-quality graphics and music and three levels of difficulty, this free game is an excellent way to support civics education for middle and high school students. Additional resources include a Constitution guide, review of Supreme Court cases, and lesson plans.Funbrain
Browse K-8 educational games by grade level, popularity, and topics such as math, grammar, and vocabulary. New games include chess, sudoku, and What on Earth?! (geography). Free, no registration required.iCivics Games
A rich resource for social studies education, the nonprofit iCivics was founded by Supreme Court Justice Sandra Day O’Connor in 2009 to educate Americans about our democracy. The site includes an educational portal for learning about civics and standards-based games and curricula.Little Alchemy 2
Air. Earth. Fire. Water. Simply creative. Simply brilliant. iOs and Android too. For makers and imaginers of any age.National Geographic Kids
Free quizzes and games in topics ranging from animals and bugs to solving ciphers.PBS Kids Games
Dozens of free games, from math to social-emotional learning, will delight younger learners. No account required on this user-friendly website. English and Spanish. New games include Nature Sights and Sounds, Puppy Pet Care, Road Repair, and many more.Play4A
A deceptively simple interface allows users to play surprisingly challenging games for free. In addition, teachers create gamified quizzes, then share the code with their students. A jaunty musical soundtrack adds to the enjoyment.RoomRecess
Find 140+ free learning games in a wide variety of subjects, including math, language arts, typing and keyboard skills, digital puzzles, and more. Games are grouped by grades as well as topics. Highly popular with teachers and students alike.Tate Kids
Explore art-based games and quizzes on this super appealing, highly visual site from Great Britain’s Tate Museum. Activities focus on learning and discovery rather than test scores. An exceptional way to get kids thinking about and making art. Free.HoloLAB Champions (Educators Edition)
Players in this remarkable virtual chemistry lab will measure, weigh, pour, and heat in a series of competitive lab skills games. No safety goggles required—but don’t forget your virtual pair! Free for educators. HoloLAB Champions is available in English on Steam for the Oculus Rift and VIVE VR platforms. Free to educators.NASA Space Place
NASA invites users to investigate Earth and outer space via games that ask big questions such as, “How does NASA talk to its faraway spacecraft?” and “How does the sun make energy?” Free and fascinating.
Best Freemium K-12 Education Games
Factile
Clue: The best known and loved quiz game show in American history. Response: What is Jeopardy!? Factile, with its sleek, sophisticated interface, allows users to create and share Jeopardy!-like quiz games, in addition to playing publicly available games. Create games manually or allow AI to populate the game board with clues related to your chosen topics. Free account users can create up to three custom games, share and embed games and play public games. Transparent pricing allows for easy comparison among account options, with Home/School Basic at $48 annually and Home/School Plus under $100 annually.GrooveLit
Groovelit’s COPPA- and FERPA-compliant gamified writing practice helps students in grades 4-10 find their voice. Teachers can create new writing games or make use of ready-made games with adjustable player settings. Customizable to state standards. Groovelit Basic provides unlimited free access to gamified writing practice and unlimited students per game, while Groovelit Go adds individualized feedback/analysis and other premium features.Education.Com Games
With nearly 1,000 high-quality, engaging educational games covering math, science, social studies, and English, Education has something for every preK-8 student. Basic members can access three free downloads per month, while premium members have unlimited access to all Education.com resources. Premium-only features include Guided Lessons, Collections, and more.ABCya Free Games of the Week
More than 300 lively educational games and mobile apps for preK-6 students. Games can be searched by Common Core State Standards, as well as Next Generation Science Standards. Six new free games released every week. Free for desktop use, premium plan for mobile devices.Arcademics
An award-winning, innovative site for K-8 game-based learning in math, language arts, geography, and other subjects, Arcademics includes an educational portal that allows teachers to monitor student progress, generate detailed reports, and assess student learning. Free basic account provides most features and is ad-supported. Free 30-day trial. No credit card required.Oodlu
An online education gaming platform, Oodlu is perfect for learners of any age with some reading ability. Teachers create their own games using the built-in question bank, and analytics provide progress reports for each student. Free standard account.Blooket
A wonderful gamified learning/quiz platform with a user-friendly interface, Blooket offers nine different game modes and runs on student devices as well as desktop computers. Free basic account allows for unlimited sets and edits, unique game modes, and question set search for up to 60 players.Turtle Diary Online Games
An extensive collection of games, videos, quizzes, lesson plans, and other digital tools for preK-5 students, searchable by topic, grade, and Common Core standard. Free and premium accounts.Gimkit
Created by a high school student, Gimkit bills itself as a game show for the classroom. Kids can earn in-game cash with correct answers and invest the money in upgrades and power-ups. Reports for educators are generated after every game played. A second program, Gimkit Ink, allows students to publish and share their schoolwork. $4.99/month, or group pricing for schools. A 30-day free trial of Gimkit Pro can be converted to a free basic account.Kahoot
One of the most popular sites for gamifying the classroom. Teachers create games and quizzes and students answer them on their mobile devices. You’ll find a plan for every budget: free basic, pro, and premium.Knoword
A fine, fast-paced vocabulary game. Educators can create their own word packs and track student progress. Free basic accounts allow play of all public word packs, sharing, and exporting, while the moderately priced Pro and Team accounts allow unlimited word pack creation and assignments.Legends of Learning
A fine collection of standards-aligned science and math games for K-8 students. Free teacher accounts, with premium features for school and district-level accounts. Bonus: Learn about the games before signing up here. Be sure to check out their free upcoming game-based STEM competitions.
Best Premium K12 Education Games
Geoguessr
A unique and visually captivating geography brainteaser that encourages children to decipher locations using hints from Google Street View and Mapillary visuals. Ideal for fostering cognitive abilities and logical reasoning, while providing an entertaining and immersive experience.Math Playground
Explore this extensive selection of math, logic, skills, and word games for kids in grades K-6. Created by educator Coleen King, Math Playground is kidSAFE/COPPA Certified and includes only COPPA-certified children’s ads. Shareable in Google Classroom.Vocabulary Spelling City
Three dozen free games cover topics including vocabulary, spelling, phonics, and language arts. Each game includes several variations, so the total number of games to play exceeds 100. Just start playing- no account needed. Looking for premium content? Head over to the new site for premium games at VocabularyA-Z.comBuzzmath
Buzzmath provides more than 14,000 interactive math questions, as well as manipulable objects, audio text reading, math glossary, brain teasers, badges, and digital rewards. Teachers can personalize learning for each student with this standards-aligned supplementary math resource.Sumdog
Sumdog’s standards-based math and spelling practice platform aims to boost student learning and confidence with adaptive personalized gameplay. A hit with kids and research-validated to boot. Free 30-day trial.MinecraftEdu
A block-based graphics game, designed for education, that allows students to build and explore virtual worlds. Built-in educator controls support a safe and education-directed experience. The abundant classroom resources include lesson plans, training for educators, challenge building, and more.Skoolbo
Skoolbo offers educational games for reading, writing, numeracy, languages, science, art, music, and logic. Digital books and step-by-step animated lessons support young learners as well. Various plans for classes and schools, with the first month free.Enjoy our content? Make sure to add Tech & Learning as a preferred source on Google to keep up with our latest news, how-tos, profiles, events, and more.
-

Final Exam: Test yourself on the past year’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.How well did you keep up with this year’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our 10-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
-

Week In Review: K-12 Dive Awards and AI’s march in curriculum
Industry Dive is an Informa TechTarget business.
This website is owned and operated by Informa TechTarget, part of a global network that informs, influences and connects the world’s technology buyers and sellers. All copyright resides with them. Informa PLC’s registered office is 5 Howick Place, London SW1P 1WG. Registered in England and Wales. TechTarget, Inc.’s registered office is 275 Grove St. Newton, MA 02466.
