How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
Tag: K12
-

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback. -

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
-

New research highlights the importance and challenges of K-12 student engagement
This press release originally appeared online.
Key points:
While there is wide agreement that student engagement plays a vital role in learning, educators continue to face uncertainty about what engagement looks like, how best to measure it, and how to sustain it, according to a new study from Discovery Education.
Education Insights 2025–2026: Fueling Learning Through Engagement captures prevailing attitudes and beliefs on the topic of engagement from 1,398 superintendents, teachers, parents, and students from across the United States. Survey data was collected in May 2025 by Hanover Research on behalf of Discovery Education.
“Discovery Education conducted the Education Insights report to gain a deeper understanding of how engagement is defined, observed, and nurtured in K-12 classrooms nationwide, and we are thankful to the participants who shared their perspectives and insights with us,” said Brian Shaw, Discovery Education’s Chief Executive Officer. “One of the most important findings of this report is that engagement is seen as essential to learning, but is inconsistently defined, observed, and supported in K-12 classrooms. I believe this highlights the need for a more standardized approach to measuring student engagement and connecting it to academic achievement. Discovery Education has embarked on an effort to address those challenges, and we look forward to sharing more as our work progresses.”
Key findings of the Education Insights 2025–2026: Fueling Learning Through Engagement report include:
Engagement is broadly recognized as a key driver of learning and success. Ninety-three percent of educators surveyed agreed that student engagement is a critical metric for understanding overall achievement, and 99 percent of superintendents polled believe student engagement is one of the top predictors of success at school. Finally, 92 percent of students said that engaging lessons make school more enjoyable.
But educators disagree on the top indicators of engagement. Seventy-two percent of teachers rated asking thoughtful questions as the strongest indicator of student engagement. However, 54 percent of superintendents identified performing well on assessments as a top engagement indicator. This is nearly twice as high as teachers, who rank assessments among the lowest indicators of engagement.
School leaders and teachers disagree on if their schools have systems for measuring engagement. While 99 percent of superintendents and 88 percent of principals said their district has an intentional approach for measuring engagement, only 60 percent of teachers agreed. Further, nearly one-third of teachers said that a lack of clear, shared definitions of student engagement is a top challenge to measuring engagement effectively.
Educators and students differ on their perceptions of engagement levels. While 63 percent of students agreed with the statement “Students are highly engaged in school,” only 45 percent of teachers and 51 percent of principals surveyed agreed with the same statement.
Students rate their own engagement much higher than their peers. Seventy percent of elementary students perceived themselves as engaged, but only 42 percent perceived their peers as engaged. Fifty-nine percent of middle school students perceived themselves engaged in learning, but only 36 percent perceived their peers as engaged. Finally, 61 percent of high school students perceived themselves as engaged, but only 39 percent described their peers as engaged.
Proximity to learning changes impressions of AI. Two-thirds of students believe AI could help them learn faster, yet fewer than half of teachers report using AI themselves to complete tasks. Only 57 percent of teachers agreed with the statement “I frequently learn about positive ways students are using AI,” while 87 percent of principals and 98 percent of superintendents agree. Likewise, only 53 percent of teachers agreed with the statement “I am excited about the potential for AI to support teaching and learning,” while 83 percent of principals and 94 percent of superintendents agreed.
Latest posts by eSchool Media Contributors (see all) -

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
-

New Research Highlights Both the Importance and Challenges of Student Engagement in K-12 Education
A new study reveals that while there is wide agreement that student engagement plays a vital role in learning, educators continue to face uncertainty about what engagement looks like, how best to measure it, and how to sustain it. Education Insights 2025–2026: Fueling Learning Through Engagementcaptures prevailing attitudes and beliefs on the topic of engagement from 1,398 superintendents, teachers, parents, and students from across the United States. Survey data was collected in May 2025 by Hanover Research on behalf of Discovery Education, the creators of essential PreK-12 learning solutions used in classrooms around the world.
“Discovery Education conducted the Education Insights report to gain a deeper understanding of how engagement is defined, observed, and nurtured in K-12 classrooms nationwide, and we are thankful to the participants who shared their perspectives and insights with us,” said Brian Shaw, Discovery Education’s Chief Executive Officer. “One of the most important findings of this report is that engagement is seen as essential to learning, but is inconsistently defined, observed, and supported in K-12 classrooms. I believe this highlights the need for a more standardized approach to measuring student engagement and connecting it to academic achievement. Discovery Education has embarked on an effort to address those challenges, and we look forward to sharing more as our work progresses.”
Key findings of the Education Insights 2025–2026: Fueling Learning Through Engagement report include:
- Engagement is broadly recognized as a key driver of learning and success. 93% of educators surveyed agreed that student engagement is a critical metric for understanding overall achievement, and 99% of superintendents polled believe student engagement is one of the top predictors of success at school. Finally, 92% of students said that engaging lessons make school more enjoyable.
- But educators disagree on the top indicators of engagement. 72% of teachers rated asking thoughtful questions as the strongest indicator of student engagement. However, 54% of superintendents identified performing well on assessments as a top engagement indicator. This is nearly twice as high as teachers, who rank assessments among the lowest indicators of engagement.
- School leaders and teachers disagree on if their schools have systems for measuring engagement. While 99% of superintendents and 88% of principals said their district has an intentional approach for measuring engagement, only 60% of teachers agreed. Further, nearly 1/3 of teachers said that a lack of clear, shared definitions of student engagement is a top challenge to measuring engagement effectively.
- Educators and students differ on their perceptions of engagement levels. While 63% of students agreed with the statement “Students are highly engaged in school,” only 45% of teachers and 51% of principals surveyed agreed with the same statement.
- Students rate their own engagement much higher than their peers. 70% of elementary students perceived themselves as engaged, but only 42% perceived their peers as engaged. 59% of middle school students perceived themselves engaged in learning, but only 36% perceived their peers as engaged. Finally, 61% of high school students perceived themselves as engaged, but only 39% described their peers as engaged.
- Proximity to learning changes impressions of AI. Two-thirds of students believe AI could help them learn faster, yet fewer than half of teachers report using AI themselves to complete tasks. Only 57% of teachers agreed with the statement “I frequently learn about positive ways students are using AI,” while 87% of principals and 98% of superintendents agree. Likewise, only 53% of teachers agreed with the statement “I am excited about the potential for AI to support teaching and learning,” while 83% of principals and 94% of superintendents agreed.
A complete copy of Education Insights 2025–2026: Fueling Learning Through Engagementcan be downloaded here.
On Wednesday, October 8 at 2:00 PM ET, Discovery Education is hosting a special, town hall-style webinar during which education leaders from across the nation will share their thoughts and insights on this report and its findings. Find more details and register for this event here.
For more information about Discovery Education’s award-winning digital resources and professional learning solutions, visit www.discoveryeducation.com, and stay connected with Discovery Education on social media through LinkedIn, Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook.
About Discovery Education
Discovery Education is the worldwide edtech leader whose state-of-the-art, PreK-12, digital solutions help educators engage all students and support higher academic achievement. Through award-winning multimedia content, instructional supports, and innovative classroom tools that are effective, engaging, and easy to use, Discovery Education helps educators deliver powerful learning experiences. Discovery Education serves approximately 4.5 million educators and 45 million students worldwide, and its resources are accessed in over 100 countries and territories. Through partnerships with districts, states, and trusted organizations, Discovery Education empowers teachers with essential edtech solutions that inspire curiosity, build confidence, and accelerate learning. Learn more at www.discoveryeducation.com.Latest posts by eSchool News Contributor (see all) -

5 Trends Reshaping K-12 Education Across the U.S. – The 74
Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
Since 2020, interest in homeschooling, microschooling, and other alternatives to conventional education has soared. Entrepreneurial parents and teachers have been building creative schooling options across the U.S. Kerry McDonald, a senior fellow at the Foundation for Economic Education and contributor to The 74, was so inspired by these everyday entrepreneurs that she wrote a book about them: Joyful Learning: How to Find Freedom, Happiness, and Success Beyond Conventional Schooling.The following is an adapted excerpt from McDonald’s book. It is reprinted here with permission from the publisher.
In 2019, I gave a keynote presentation at the Alternative Education Resource Organization’s (AERO) annual conference in Portland, Oregon. Founded in 1989 by Jerry Mintz, AERO has long supported entrepreneurial educators in launching new schools and spaces, with a particular focus on learner‑centered educational models. It was about a month after my previous book Unschooled was published, and I was talking about the gathering interest in unconventional education. Homeschooling numbers were gradually rising, and more microschools and microschooling networks were surfacing. I predicted that these trends would continue, but I said they would remain largely on the edge— as alternative education had for decades. They would offer more choices to some families who were willing to try new things, similar to those of us who eagerly embraced Netflix’s mailed DVDs when they first appeared. But I didn’t think these unconventional models would upend the entire education sector the way Netflix ultimately did with entertainment. I thought they would remain small and niche. I was wrong.
The COVID crisis catapulted peripheral educational trends into the mainstream, not only creating the opportunity for new schools and spaces to emerge but, more importantly, permanently altering the way parents, teachers, and kids think about schooling and learning. The pre‑pandemic tilt toward homeschooling and microschooling has converged with five post‑pandemic trends that are profoundly reshaping American education for families and founders. Together, these trends are shifting the K–12 education sector from being an innovation laggard to an innovation leader.
Trend #1: The growth of homeschooling and microschooling
The nearby microschool for homeschoolers that my children attended before COVID was one of only a sprinkling of schooling alternatives in our area. Now, it’s part of a wide, fast‑growing ecosystem of creative schooling options— both locally and nationally— representing an array of different educational philosophies and approaches. Families today are better able to find an education option that aligns with their preferences. From Maine to Miami to Missouri to Montana, the majority of the innovative schools and spaces I’ve visited have emerged since 2020, and many already have lengthy waitlists, inspiring more would‑be founders. The demand for these options will grow and accelerate over the next ten years, as will the number of homeschooling families, many of whom will be attracted to homeschooling as a direct result of these microschools and related learning models. Indeed, data from the Johns Hopkins University Homeschool Hub reveal that homeschooling numbers continued to grow during the 2023/2024 academic year compared to the prior year in 90 percent of the states that reported homeschooling data, shattering assumptions that homeschooling’s pandemic‑era rise was just a blip. Parents that otherwise wouldn’t have considered a homeschooling option will do so because homeschooling enables them to enroll at their preferred microschool or learning center.
One particularly striking and consistent theme revealed in my conversations with founders as I’ve crisscrossed the country is that their kindergarten classes are filling with students whose parents chose an unconventional education option from the start. These parents aren’t removing their child from a traditional school because of an unpleasant experience or a failure of a school to meet a child’s particular needs. They are opting out of conventional schooling from the get‑go, gravitating toward homeschooling and microschooling before their child even reaches school age. This trend is also likely to accelerate, as younger parents become even more receptive to educational innovation and change.
Trend #2: The adoption of flexible work arrangements
Today’s generation of new parents grew up with a gleeful acceptance of digital technologies and the breakthroughs they have facilitated in everything from healthcare to home entertainment. These parents see the ways in which technology and innovation enable greater personalization and efficiency, and expect these qualities in all their consumer choices. It’s no wonder, then, that parents of young children today are generally more curious about homeschooling and other schooling alternatives. They are often perplexed that traditional education seems so sluggish.
The response to COVID gave these parents license to consider other options for their children’s education. The school closures and extended remote learning during the pandemic empowered parents to take a more active role in their children’s education. That trend persists, as does the remaking of Americans’ work habits. The number of employees working remotely from home rather than at their workplace has more than tripled since 2019.
As more parents enjoy more flexibility in their work schedules, they will seek similar flexibility in their children’s learning schedules. While remote and hybrid work generally remain privileges of the so‑called “laptop class” of higher‑income employees, the growing adoption of flexible work and school arrangements is driving demand for more of these alternative learning models, including many of the ones featured in Joyful Learning that offer full‑time, affordable programming options for parents who don’t have job flexibility. Remote and hybrid work patterns are here to stay, and so is the trend toward more nimble educational models for all.
Trend #3: The expansion of school choice policies
The burst of creative schooling options since 2020 is now occurring all across the United States, in small towns and big cities, in both politically progressive and conservative areas, and in states with and without school choice policies that enable education funding to follow students.
Education entrepreneurs aren’t waiting around for politicians or public policy to green‑light their ventures or provide greater financial access. They are building their schools and spaces today to meet the mounting needs of families in their communities.
That said, there is little doubt that expansive school choice policies in many states are accelerating entrepreneurial trends. Founders I talk to who are developing national networks of creative schooling options, are intentional about locating in states with generous school choice policies that enable more parents to choose these new learning models. Other entrepreneurs are moving to these states specifically so that they can open their schools in places that enable greater financial accessibility and encourage choice and variety. Jack Johnson Pannell is one example. The founder of a public charter school for boys in Baltimore, Maryland, that primarily serves low‑income students of color, Jack grew discouraged that the experimentation that defined the early charter school movement in the 1990s steadily disappeared, replaced by an emphasis on standardization and testing that can make many—but certainly not all—of today’s charter schools indistinguishable from traditional public schools. He saw in the choice‑enabled microschooling movement the opportunity for ingenuity and accessibility that was a hallmark of the charter sector’s infancy. In 2023, Jack moved to Phoenix, Arizona, to launch Trinity Arch Preparatory School for Boys, a middle school microschool that families are able to access through Arizona’s universal school choice policies.
Trend #4: The advent of new technologies and AI
New technologies are also accelerating the rise of innovative educational models, while making it harder to ignore the inadequacies of one‑size‑fits‑all schooling. The ability to differentiate learning, personalizing it to each student’s present competency level and preferred learning style, has never been easier or more straightforward. It no longer makes sense to say that all second graders or all seventh graders should be doing the same thing, at the same time, in the same way—and failing them if they don’t measure up.
Emerging and maturing technologies help prioritize students over schools and systems, but the widespread introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) tools, and bots like ChatGPT, will hasten this repositioning. New AI bots can act as personal tutors for students, helping them navigate through their set curriculum. The real promise, according to founders focused more on agency‑ based or learner‑directed education, is for AI tools to work for the students themselves, helping them to control their own curriculum.
“We don’t have a set pathway for our learners. It’s personalized,” said Tobin Slaven, cofounder of Acton Academy Fort Lauderdale, which he launched with his wife Martina in 2021. Part of the global Acton Academy microschool network, Tobin’s school prioritizes student‑driven education in which young people set and achieve individual goals in both academic and nonacademic areas, participate in frequent Socratic group discussions, engage in collaborative problem‑solving and shared decision‑making, and embark on their own “hero’s journey” of personal discovery and achievement.
When we spoke in 2024, Tobin had recently founded an educational technology startup building AI companion tools that act as a personal tutor, life coach, and mentor all in one. He sees AI tools like his as being instrumental in helping learners have more independence and autonomy over their learning. Rather than AI bots guiding a student through a pre‑established curriculum, Tobin thinks the truly transformative potential of AI lies in tools that help students lead their own learning—answering their own questions and pursuing their own academic and nonacademic goals.
“When I hear the visions of some other folks in the education space, their visions are very different from mine,” Tobin said, referring to many of today’s emerging AI‑enabled educational technologies. He offered the example of a device known as a jig, used often in carpentry, to further illustrate his point. “The jig tells you exactly where the curves should be, where the cut should be. It’s like a template. The template that most of the AI folks are using is traditional education. It was broken from the start. It’s a bad jig,” Tobin said.
Instead, he sees the potential of AI to help reimagine education rather than reinforce a top‑down, traditional model. He is helping to create a new and better educational jig.
Trend # 5: Openness to new institutions
The final trend that is merging with the others to transform American education is the shift away from established institutions toward newer, more decentralized ones. Some of this is undoubtedly due to emerging technologies that can disrupt entrenched power structures and lead to greater awareness of, and openness to, new ideas, but the trend goes beyond technology. Annual polling by Gallup reveals that Americans’ confidence in a variety of institutions has fallen, with their confidence in public schools at a historic low. Only 26 percent of survey respondents in 2023 indicated that they had a “Great deal/Quite a lot” of confidence in that institution. The good news is that confidence in small business remains high, topping Gallup’s list with 65 percent of Americans expressing a “Great deal/Quite a lot” of confidence in that institution in 2023. The falling favor of public schools occurring at the same time that small businesses continue to be well‑liked creates ideal conditions for today’s education entrepreneurs. Families who are dissatisfied with public schooling may be much more interested in a small school or space operating or opening within their community.
For another signal of the shift away from older, more centralized institutions toward newer, more customized options, look at what the Wall Street Journal calls the “power shift underway in the entertainment industry,” as YouTube increasingly draws viewers away from traditional television networks. Individual YouTube content creators, such as the world’s top YouTuber, MrBeast, who has some 300 million subscribers, appeal to more viewers than the legacy media networks with their more curated content. New content creators are particularly attractive to younger generational cohorts like Gen Z, who prefer decentralized, user‑generated content over traditional, top‑ down media models. Consumers today are looking for more modern, responsive, personalized products and services, especially those being developed by individual entrepreneurs who bear little resemblance to legacy institutions. This is as true in education as it is in entertainment and will be an ongoing, indefinite, and transformational trend in both sectors.
Shortly before completing this manuscript, I spoke again at the annual AERO conference, this time in Minneapolis. Gone was my measured optimism of 2019. In its place was a mountain of evidence showing how popular alternative education models have become since 2020, and how steadily that popularity continues to grow. This isn’t a pandemic- era fad or an educational niche destined for the edges. This is a diverse, decentralized, choice‑filled entrepreneurial movement that is shifting American education from standardization and stagnation toward individualization and innovation.
We are only at the very early stages of a fundamental change in how, where, what, and with whom young people learn. Over the next decade, homeschooling and microschooling numbers will continue to grow, work flexibility will trigger greater demand for schooling flexibility, expanding education choice policies will make creative schooling options more accessible to all, AI and emerging technologies will help create a new “educational jig” fit for the innovation era, and declining confidence in old institutions will enable fresh ones to arise. The future of learning is brighter than ever. Families and founders are finding freedom, happiness, and success beyond conventional schooling, inspiring the growth of today’s joyful learning models and the invention of new ones yet to be imagined.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
-
K-12 Chronic Absenteeism Rates Down From Peak, But Remain Persistently High – The 74
Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
Since hitting a record high in 2022, national chronic absenteeism rates have dropped modestly — by about five percentage points — according to the most recent available data, but still remain persistently higher than pre-pandemic levels.
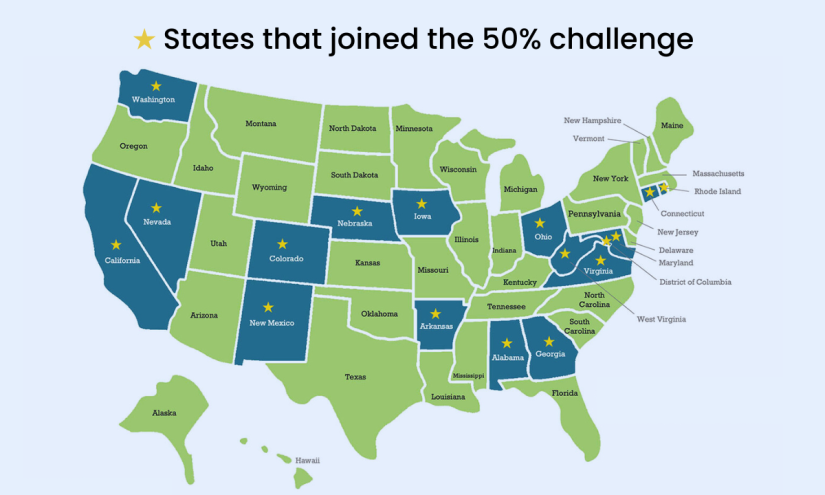
States that joined a national pledge led by three high-profile education advocacy and research groups to cut chronic absenteeism in half over five years fared better. The 16 states and Washington, D.C. posted results “substantially above the average rate” of decline, though exact numbers are not yet available, said Nat Malkus, deputy director of education policy studies at the American Enterprise Institute, one of the trio.
The national chronic absenteeism average dropped from 28.5% in 2022 to 25.4% in 2023, and fell an additional two points to 23.5% in 2024. Virginia, which is among the 16 participating states, cut its chronic absenteeism by 4.4 percentage points, year over year, to 15.7%, as of spring 2024.
Speaking of the states collectively, Malkus told The 74, “That’s good but it’s not as good as we need it to be. I think it points to the need for sustained pressure and a sustained campaign to bring absence rates down and to bring more students back to consistent attendance.”
Last July, AEI and EdTrust, right-and left-leaning think tanks, respectively, and the national nonprofit Attendance Works joined forces to launch The 50% Challenge. This week, the organizations hosted an event in Washington, D.C., to report on their progress, re-up the call to action and hear insights from state, district and community partners on how they are improving student attendance and engagement.
With California and Georgia recently joining, the 16 states and D.C. who signed on to the pledge account for more than a third of all students nationally. While Malkus doesn’t necessarily attribute their better results to the pledge itself, he noted that their participation shows a willingness to commit to the cause and be publicly accountable for their results.
“I will hold their feet to the fire on this goal,” he added during his opening remarks in D.C.
While felt most acutely by students of color and those in poorer districts, the spike in chronic absenteeism — students missing more than 10% of school days a year — cut across districts regardless of size, racial breakdown or income. Chronic absenteeism surged from 13.4% in 2017 to 28.5% in 2022 before beginning to drop in 2023.
Only about one-third of students nationally are in districts that are on pace to cut 2022 absenteeism in half by 2027, according to an AEI report, and rates improved more slowly in 2024 than they did in 2023, “raising the very real possibility that absenteeism rates might never return to pre-pandemic levels.
AEI Research has shown that students with high rates of absenteeism are more likely to fall behind academically and are at a greater risk of dropping out of school. About 8% of all learning loss from the pandemic is attributed just to chronic absenteeism, according to soon-to-be-released AEI research.
The continued disproportionate impacts of chronic absenteeism were confirmed by recent RAND research, which found that in roughly half of urban school districts, more than 30% of students were chronically absent — a far higher share of students than in rural or suburban school districts.
RAND also found that the most commonly reported reason for missing school was sickness and one-quarter of kids did not think that being chronically absent was a problem.
SchoolStatus, a private company that works with districts to reduce chronic absenteeism, also released new numbers this week for some 1.3 million K-12 students across 172 districts in nine states. Districts using proactive interventions, the company reports, drove down chronic absenteeism rates from 21.9% in 2023–24 to 20.9% in 2024–25.
At this week’s event, numerous experts across two panels emphasized the importance of a tiered approach to confronting the issue, which has resisted various remedies. Schools must build enough trust and buy-in with kids and their families that they are willing to share why they are absent in the first place. Once those root causes are identified, it is up to school, district and state leaders to work to remove the barriers.
And while data monitoring must play a significant role, it should be done in a way that is inclusive of families.
“We need to analyze data with families, not at them,” said Augustus Mays, EdTrust’s vice president of partnerships and engagement.

Augustus Mays is the vice president of partnerships and engagement at EdTrust. (EdTrust) It’s imperative to understand the individual child beyond the number they represent and to design attendance plans and strategies with families so they feel supported rather than chastised.
“It’s around choosing belonging over punitive punishment,” Mays added.
One major and common mistake schools make is “accountability without relationships,” said Sonja Brookins Santelises, the superintendent of Baltimore City Public Schools.
“You can’t ‘pull people up’ if you don’t have enough knowledge of what they’re really going through,” she said.
Panelists were transparent that all this would require immense funding, staff and community partnerships.
Virginia achieved its noteworthy drop in chronic absenteeism after launching a $418 million education initiative in the fall of 2023, in part after seeing their attendance data sink, with about 1 in 5 students chronically missing school. At least 10% of those funds are earmarked to prioritize attendance solutions in particular, according to panelist Emily Anne Gullickson, the superintendent of public instruction for the Virginia Department of Education.
These strategies are far-reaching, she noted: Because parents had been told throughout the pandemic to keep their kids home at the slightest sign of illness, schools partnered with pediatricians and school nurses to help counter the no-longer-necessary “stay home” narrative.

Hedy Chang is the founder and executive director of Attendance Works. (Attendance Works) Gullickson said she also broke down bureaucratic silos, connecting transportation directors and attendance directors, after realizing the role that transit played in chronic absenteeism. The state now has second chance buses as well as walking and biking “buses,” led by parents or teachers along a fixed route, who pick up students along the way.
And they are “on a mission to move away from seat time and really deliver more flexibility on where, when and how kids are learning,” she said.
“This isn’t one strategy. It’s a set of strategies,” said Attendance Works founder and executive director Hedy Chang, who moderated the panel.
In Connecticut, state leaders have launched the Learning Engagement and Attendance Program, a research-based model that sends trained support staff to families’ homes to build relationships and better understand why their kids are missing school.

Charlene Russell-Tucker is the commissioner of the Connecticut State Department of Education. (Connecticut State Department of Education) A recent study confirmed that six months after the program’s first home visits, attendance rates improved by approximately 10 percentage points for K-8 students, and nearly 16 percentage points for high schoolers, said Charlene Russell-Tucker, the commissioner of the Connecticut State Department of Education.
Schools must also work to motivate kids to want to show up in the first place, panelists said, making it a meaningful place that students believe will support and help them in the long run. The only way to do this is to start with student and family feedback, said Brookins, the Baltimore schools chief.
During the pandemic many parents saw up-close for the first time what their kids’ classrooms and teacher interactions looked like, “and I don’t think a lot of folks liked what they saw for a variety of different reasons,” Brookins said.
“I think it opened up boxes of questions that we — as the education establishment — were unprepared to answer,” she added. But chronic absenteeism cannot be successfully fought without engaging in those uncomfortable conversations.
Disclosure: The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation provides financial support to EdTrust and The 74.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
-

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
-

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
-

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback.How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
