In a move that has sparked legal action from nearly half the country, the Trump administration has frozen more than $6 billion in education funds to 23 states and the District of Columbia. The decision, issued by the U.S. Department of Education in late June 2025, follows a broader pattern of halted federal support for state and local programs, many of which were previously protected by court rulings.
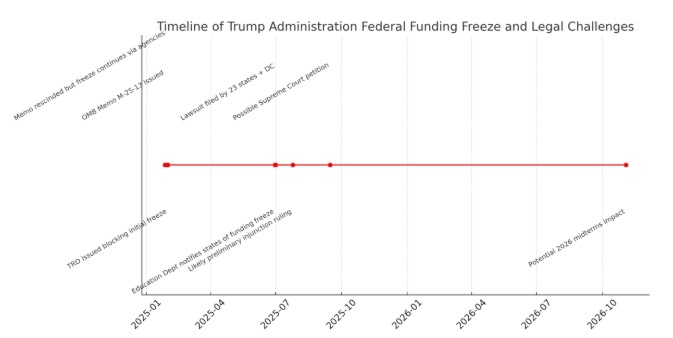
The funding pause is linked to the Trump administration’s January 2025 memorandum from the Office of Management and Budget (OMB Memo M-25-13), which directed federal agencies to withhold disbursements from thousands of grant and aid programs. The stated purpose was to align spending with the administration’s priorities, though the policy has been challenged as lacking legal authority. The memo was later rescinded, but its effects have continued through new administrative directives.
In this latest instance, the Department of Education cited a need to review Title II and Title IV programs under the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA), including programs for teacher development, after-school enrichment, and English language learners.
The decision disproportionately affected Democratic-led states, with California alone facing the loss of $939 million.
States impacted include Arizona, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, Oregon, Rhode Island, Vermont, Washington, Wisconsin, and the District of Columbia.
On June 30, attorneys general from those jurisdictions filed suit in Rhode Island, arguing that the Education Department lacks the authority to unilaterally withhold funds that Congress has already appropriated. They assert that the freeze violates both statutory obligations and constitutional principles, including the separation of powers. The lawsuit follows earlier court rulings from January and February in which judges issued temporary restraining orders and preliminary injunctions to stop the administration from freezing other categories of grants. Those cases were largely brought by Democracy Forward, a legal advocacy organization that has played a leading role in contesting the OMB memo.
Although the administration has defended the funding freeze as a necessary review of federal spending, courts have questioned the legality of such actions. In March, a federal court criticized the lack of statutory basis for the freezes, and Democracy Forward issued a detailed brief outlining the harm to nonprofit programs, environmental projects, and public services. That brief emphasized the breadth of affected programs and the legal overreach involved.
The broader legal battle continues. While some funding has been restored through court action, the Education Department’s freeze represents a new front in ongoing disputes between the Trump administration and state governments. Plaintiffs argue that withholding these funds sets a precedent that undermines established appropriations and legislative intent. More lawsuits are expected.
The Trump administration’s freeze on education funding to 23 states opens several legal and political paths, each with different implications depending on how courts and federal agencies proceed. Below are the most likely possibilities based on current legal precedent, federal authority, and political conditions:
Courts Overturn the Freeze, Funding Restored
The most immediate and probable outcome is that courts will order the Education Department to restore the frozen funds, as they did earlier this year with other parts of the federal grant freeze. Courts have already found that the administration lacked statutory authority to suspend programs that Congress explicitly funded. If this logic holds, the education freeze will likely be ruled unlawful and states will receive the funds—possibly with retroactive reimbursement for missed payments.
Partial Restoration, Continued Legal Conflict
The administration may attempt to restore only some of the funding—especially those programs that have garnered the most public or bipartisan support—while continuing to block others. In this scenario, the courts could issue narrow rulings or temporary injunctions that apply to specific funding streams. This would prolong litigation and administrative uncertainty, potentially pushing the issue into 2026 or the next presidential term.
Supreme Court Intervention
If the lower courts issue conflicting rulings or the Trump administration loses significant cases, the Justice Department may seek Supreme Court review. The Court could use this as an opportunity to clarify executive authority over grant disbursement. Depending on the composition of the Court and its interpretation of separation of powers, this could either curtail future executive control over federal spending—or affirm broader authority to “review” or condition funding.
Legislative Response
Congress, particularly if Democrats control at least one chamber in 2025-2026, could pass legislation to prohibit similar funding freezes in the future or require automatic disbursement of appropriated funds. However, any such legislation would likely face veto threats or require a veto-proof majority, making this a longer-term fix rather than a short-term remedy.
Further Administrative Retaliation or Expansion
If courts delay action or issue narrow rulings, the Trump administration could expand the use of funding freezes to other agencies or sectors, testing the limits of executive control. The precedent set by OMB Memo M-25-13 could be repurposed in other contexts—such as public health, housing, or infrastructure—creating broader instability in federal-state relations.
Political Mobilization and Fallout
States may respond by increasing pressure on Congress and federal courts while using the issue as a rallying point in the 2026 midterm elections. Public schools, educators, and parents may amplify the issue if it leads to job losses, school closures, or reduced services. The freeze could become a political liability for the Trump administration, especially in battleground states that rely heavily on federal education support.
In sum, the most likely near-term result is court-mandated restoration of the withheld funds. But depending on how aggressively the administration continues to test the boundaries of federal authority, the dispute could escalate into a broader constitutional and political conflict over the power to allocate and control federal funds.
Sources
Democracy Forward, “Initial Policy Memo on Federal Grant Freezes,” March 12, 2025.
CBS News, “Democratic states sue Trump administration over halted education funds,” July 1, 2025.
Reuters, “Trump asks US court to end judicial overreach, allow funding freezes,” February 11, 2025.
Wikipedia, “2025 United States federal government grant pause.”
The Daily Beast, “GOP Lawmakers Blast Trump Chief Russell Vought for Freezing Education Money,” July 2025.
The Guardian, “Nothing like this in American history: the crisis of Trump’s assault on the rule of law,” March 9, 2025.