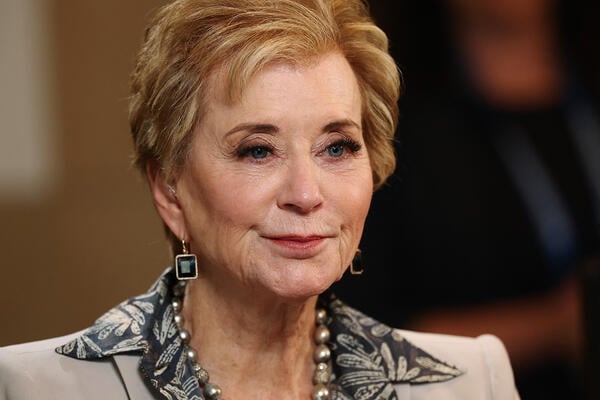
During a hearing Wednesday, U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon defended the Trump administration’s proposal to heavily cut funding for the U.S. Department of Education during the 2026 fiscal year, arguing the reductions were a key step toward winding down the agency.
“We seek to shrink federal bureaucracy, save taxpayer money and empower states who best know their local needs to manage education in this country,” McMahon said before lawmakers on the House Committee on Appropriations’s education subcommittee.
President Donald Trump’s budget request, released at the beginning of the month, would slash funding to the Education Department by 15.3%, or about $12 billion.
The plan calls for eliminating two federal programs aimed at improving college access for disadvantaged and low-income students — TRIO and Gear Up — as well as shifting the responsibility of the Federal Work-Study program to the states. And it would eliminate funding for Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grants, which provide need-based aid to undergraduate students.
It also would reduce funding for the already-diminished Office for Civil Rights, which investigates harassment and discrimination on college campuses and in K-12 schools, by about $49 million, a 35% cut from the previous year.
Republicans on the panel largely lauded the proposal, with many praising the Trump administration’s support for charter schools, which would receive a $60 million funding bump in the budget.
Democrats, however, slammed the budget, arguing the cuts would undermine student success and restrict pathways to higher education.
“Your visions for students aspiring to access and pay for college is particularly grim,” Rep. Rosa DeLauro, the top Democrat on the appropriations committee, said during the hearing. “Some families do not need financial assistance to go to college, but that’s not true for the rest.”
‘You will not have the partnership of Congress’
Trump signed an executive order in March directing McMahon to “take all necessary steps to facilitate the closure of the Department of Education.”
His administration has shared plans to move its key functions to other agencies. In one instance, Trump suggested that operating the student loan portfolio should be the responsibility of the newly-downsized Small Business Administration.
Some Republicans on the panel voiced support for this plan Wednesday. Rep. Jake Ellzey, from Texas, suggested the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services could take over mental health support provided by the Education Department. He also proposed that the U.S. Department of Justice could oversee civil rights matters — an option McMahon floated during her confirmation hearing in February.
On Wednesday, McMahon described the Education Department as a federal funding “pass-through mechanism” and said other agencies could take over the job of distributing allocations from Congress.
“Whether the channels of that funding are through HHS, or whether they’re funneled through the DOJ, or whether they’re funneled through the Treasury or SBA or other departments, the work is going to continue to get done,” McMahon said.
However, Democrats indicated they would not support those efforts.
“You will not have the partnership of Congress in your efforts to destroy the Department of Education,” DeLauro said. “Not on our watch.”
DeLauro also slammed McMahon over recent cuts to the Education Department, which has eliminated about half of its staff and canceled hundreds of millions of dollars worth of grants.
“By recklessly incapacitating the department you lead, you are usurping Congress’ authority and infringing on Congress’ power of the purse,” she said.
Democrats also took issue with the budget’s proposal to shift the responsibility of funding programs to states.
Along with Federal Work-Study, the 2026 proposal would cut funding for other higher education programs, including the Strengthening Institutions Program, which provides grants to help colleges become more financially stable, improve their academic quality and ability to serve low-income students.
On the K-12 side, the budget proposal maintains funding for two major programs intended to support low-income students and those with disabilities. It also proposes combining 18 undisclosed grant programs into a single $2 billion block grant to states. However, the change comes with a $4.5 billion cut to those unnamed programs — an amount DeLauro said states couldn’t cover.
Rep. Madeleine Dean, a Democrat from Pennsylvania, echoed those comments, arguing that her home state couldn’t pick up the tab on programs the Education Department would no longer support.
“That’s called shift and shaft,” Dean said.
Support for TRIO and Gear Up
During the hearing, DeLauro took issue with the Trump administration’s rationale for cutting $1.6 billion allocated to the TRIO and Gear Up programs — the full amount they were allocated in fiscal 2024. In the budget proposal, the administration wrote that “access to college is not the obstacle it was for students of limited means” and said higher education institutions should use their own funding to recruit students.
Yet children of well-off families are much more likely to attend college. Among children of the highest-income families, 92% attended college, compared with 49% of children from the lowest-income families, according to a 2020 Brookings Institution report.
DeLauro asked McMahon what evidence the administration had to back its claim in the budget request.
“Simply because we have more programs reaching into the communities,” McMahon replied, adding that schools are picking up their recruiting efforts, though she did not list examples. “And if they’re not, they should be. Because it is, I believe, up to schools also to be reaching into their communities.”
At least one Republican, Idaho Rep. Mike Simpson, also took issue with proposed cuts to TRIO and Gear Up, noting that the Trump administration’s budget request described them “a relic of the past when financial incentives were needed to motivate” colleges to reach out and increase access to low-income students.
In contrast, Simpson argued the programs are highly effective at supporting low-income and minority communities, and he asked McMahon how the Education Department arrived at eliminating their funding.
“The need for TRIO I don’t think is nearly as strong because there are outreaches from colleges now into local communities, and there should be more of the universities and secondary education levels reaching into those communities,” McMahon replied. “They should be talking to them about college.”