As the United States moves deeper into the 2020s, the College Meltdown is no longer a speculative concept but a structural reality. The crisis touches nearly every part of the system: enrollment, finances, labor, governance, and the perceived value of a college degree itself. The forces fueling this meltdown are not sudden shocks but accumulated pressures — demographic contraction, policy failures, privatization schemes, student debt burdens, and decades of mission drift — that now converge in 2026 with unprecedented intensity.
The Waning of College Mania
For decades, higher education sold an uncomplicated dream: go to college, get ahead, and move securely into the middle class. This college mania was promoted by policymakers, corporate interests, university marketers, and a compliant media ecosystem. But the spell is breaking. Students at elite universities are skipping classes, disillusioned not only by campus turmoil but by the reality that a degree, even from a prestigious institution, no longer guarantees a stable future. Employers increasingly question the value of credentials that have become inflated, inconsistent, and disconnected from workplace needs.
Yet paradoxically, many jobs still require degrees — not because the work demands them, but because credentialing has become a screening mechanism. The U.S. has built a system in which people must spend tens of thousands of dollars for access to a job that may not even require the knowledge their degree supposedly certifies. This contradiction lies at the heart of the meltdown.
Moody’s Confirms the Meltdown: A Negative Outlook for 2026
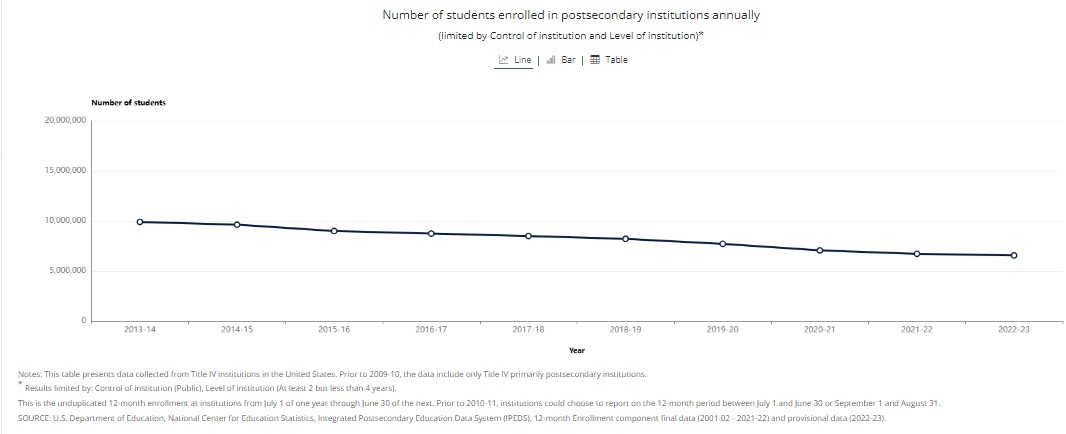
The financial rot is now too deep to ignore. Moody’s Investors Service recently issued a negative outlook for all of U.S. higher education for FY2026, confirming what researchers, debtors, and frontline faculty have been warning for years. Demographic decline continues to shrink the pool of traditional college-age students, leaving hundreds of institutions with no plausible path to enrollment stability.
Moody’s expects expenses to grow 4.4% in 2026, while revenues will grow only 3.5% — and for small tuition-dependent institutions, revenue growth may fall to 2.5–2.7%. In other words, the business model simply no longer works. Institutions are already turning to hiring freezes, early retirements, shared services, layoffs, and mergers. These austerity strategies hit labor and students hardest while preserving administrative bloat at the top, mirroring broader patterns of inequality across the U.S. economy.
Compounding the problem, federal loan reforms — particularly the elimination or capping of Grad PLUS loans — threaten universities that rely on overpriced master’s programs as revenue engines. Many of these programs were built during the boom years as financial lifelines, not academic commitments. The bottom is falling out of that model too.
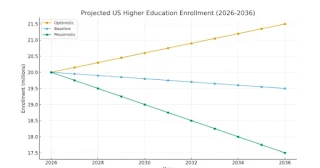
[Image: HEI’s baseline model shows steady losses between 2026 and 2036. And it could get much worse].
White-Collar Unemployment and the Broken Value Proposition
A new generation is confronting economic realities that undermine the old promise of higher education. Recent data show that college graduates now make up roughly 25% of all unemployed Americans, a startling indicator of white-collar contraction. The unemployment rate for bachelor’s degree holders rose to 2.8%, up half a point in a year.
If higher education was once treated as an automatic economic escalator, it is now a much riskier gamble — often with a lifetime of debt attached.
Demographic Collapse and Institutional Failures
The so-called “demographic cliff” is no longer a future event; colleges in the Midwest, Northeast, and South are already competing for shrinking numbers of high-school graduates. Some institutions have resorted to predatory recruitment, deceptive marketing, and desperate discounting — the same tactics that fueled the for-profit college boom and collapse.
Meanwhile, the FAFSA disaster, mismanagement at the Department of Education, and the chaos surrounding federal financial aid verification have caused enrollment delays and intensified uncertainty. Institutions like Phoenix Education Partners (PXED) are already trying to shift blame for their own recruitment failures and history of fraud onto the federal government, signaling a new round of accountability evasion reminiscent of the Corinthian Colleges and ITT Tech eras.
Student Debt, Inequality, and Loss of Legitimacy
Student debt remains above $1.7 trillion, reshaping the life trajectories of millions and reinforcing racial and class disparities. Black borrowers, first-generation students, and low-income communities bear the heaviest burdens. Many institutions — especially elite medical centers and flagship universities — are simultaneously cash-rich and inequality-producing, perpetuating the dual structure of American higher education: privilege for the few, precarity for the many.
Faculty and staff face their own meltdown. Contingent labor now constitutes the majority of the instructional workforce, while administrators grow more numerous and more insulated from accountability. Shared governance is weakened, academic freedom is eroding, and political interference is rising, particularly in states targeting DEI programs, history curricula, and dissent.
The Road Ahead: Contraction, Consolidation, and Possibility
The College Meltdown will continue in 2026. More closures are coming, especially among small private colleges and underfunded regional publics. Mergers will be framed as “strategic realignments,” but for many communities — especially rural and historically marginalized ones — they will represent the loss of an anchor institution.
Yet contraction also opens space for reimagining. The United States could choose to rebuild higher education around equity, public purpose, and social good, rather than market metrics and debt financing. That would require:
-
substantial public reinvestment,
-
free or low-cost pathways for essential programs,
-
accountability for predatory institutions,
-
democratized governance, and
-
a commitment to racial and economic justice.
Whether the nation takes this opportunity remains unclear. What is certain is that the system built on college mania, easy credit, and limitless expansion is collapsing — and Moody’s latest warning simply confirms what students, workers, and communities have felt for years.
The College Meltdown is here. And it’s reshaping the future of higher education in America.