This post is one of many, related to my participation in Harold Jarche’s Personal Knowledge Mastery workshop.
The topic of how expertise is no longer valued today is often discussed. I realize that I am walking through well-trodden pathways, as I bring it up in these reflections on experts today. In The Death of Expertise: The Campaign Against Established Knowledge and Why it Matters, Tom Nichols writes:
These are dangerous times. Never have so many people had access to so much knowledge, and yet been so resistant to learning anything.
In today’s post, I want to think less about the societal and educational concerns I have about the death of expertise and more about how I might continue to attempt to inculcate habits that can keep me from dying that same death, myself. Part of that practice involves finding and curating many experts to help shape my thinking, over time.
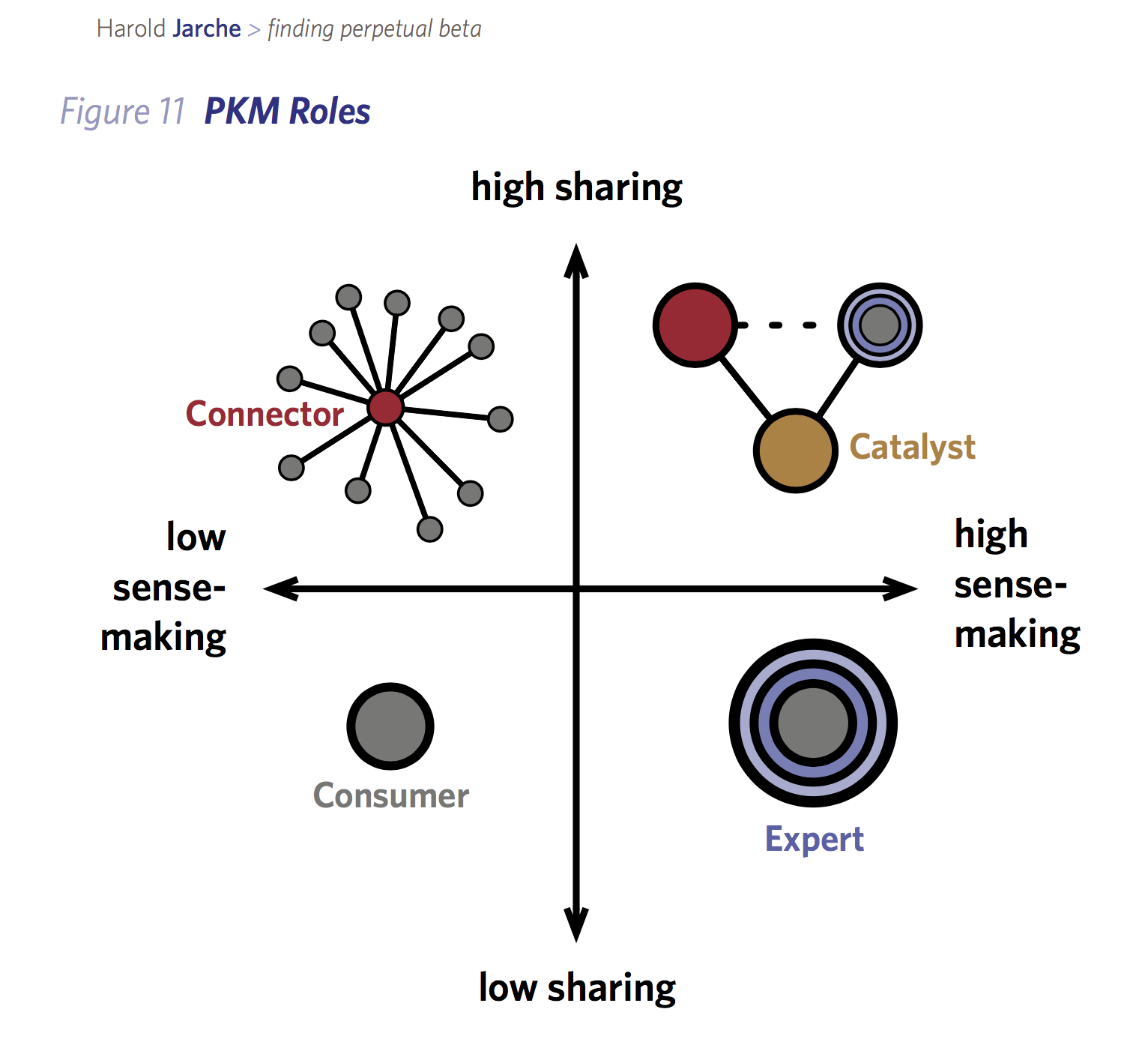
PKM Roles from Harold Jarche
For this topic, Jarche invites us to use a map of personal knowledge mastery (PKM) roles to determine where we currently reside and where we would like to go, in terms of our PKM practice. He offers this graphic as part of his Finding Perpetual Beta book:
On the Y axis, we can sort ourselves into doing high or low amounts of sharing. As I wrote previously, my likelihood of sharing is in direct relation to the topic I’m exploring. However, as Jarche recommended social bookmarking as one way of sharing, perhaps I was selling myself short when I categorized myself as not likely to share anything overly controversial. I have over 35 thousand digital bookmarks on Raindrop.io and add around 10-20 daily. However, I’m more likely to be categorized as highly visible sharing in terms of the Teaching in Higher Ed podcast and the topics I write about on the Teaching in Higher Ed blog.
On the X axis, our activities are plotted on a continuum more toward high or low sense-making. A prior workshop participant of Jarche’s wrote:
We must make SENSE of everything we find, and that includes prioritising–recognising what is useful now, what will be useful later, and what may not be useful.
Given my propensity for saving gazillions of bookmarks and carefully tagging them for future use, combined with my streak of weekly podcast episodes airing since June of 2014, when it comes to teaching and learning, I’m doing a lot of sense-making on the regular.
These are the (NEW) Experts in My Neighborhood
Taking inspiration from Sesame Street’s People in Your Neighborhood and from Jarche’s activity related to experts, I offer the following notes on experts. When I searched for people within teaching and learning on Mastodon, I found that I was already following a lot of them. I decided to then look at who people I already follow are following:
- Ethan Zuckerman – UMass Amherst, Global Voices, Berkman Klein Center. Formerly MIT Media Lab, Geekcorps, Tripod.com
- Sarah T. Roberts, Ph.D. – Professor, researcher, writer, teacher. I care about content moderation, digital labor, the state of the world. I like animals and synthesizers and games. On the internet since 1993. Mac user since they came out. I like old computers and OSes. I love cooking. Siouxsie is my queen.
- I was intrigued by her having written a content moderation book called Behind the Screen. I know enough about content moderation to know that I know pretty much nothing about content moderation.
- She hasn’t posted in a long while, so I’m not sure how much I’ll regularly have ongoing opportunities to see what she’s currently exploring or otherwise working on
Other Things I Noticed
As I was exploring who people I follow are connected with on Mastodon, I noticed that you can have multiple pinned posts, unlike other social media I’ve used. Many people have an introduction post pinned to the top of their posts, yet also have other things they want to have front and center. One big advantage to Bluesky to me has been the prevalence of starter packs. The main Mastodon account mentioned an upcoming feature involving “packs” around twenty days ago, but said that they’re not sure what they’ll call the feature.
Sometimes, scrolling through social media can be depressing. I decided that the next time I’m getting down on Mastodon, I should just check out what’s happening on the compostodon hashtag. It may be the most hopeful hashtag ever.
The Biggest Delight From the Experience
Another person who was new to me as an expert on Mastodon was JA Westenberg. According to JA Westenberg’s bio, Joan is a tech writer, angel investor, CMO, Founder. A succinct goal is also included on the about page of JoanWestenberg.com:
My goal: to think in public.
As I was winding down my time doing some sensemaking related to experts, I came across a video from Westenberg that was eerily similar to what Jarche has been stressing about us making PKM a practice. I can’t retrace my steps for how I came across Joan’s video on Mastodon, but a video thumbnail quickly caught my eye. Why You Should Write Every Day (Even if You’re Not a Writer) captured my imagination immediately, as I started watching. In addition to the video, there’s a written article of the same title posted, as well.
As I continue to pursue learning through the PKM workshop, I’m blogging more frequently than I may ever have (at least in the last decade for sure). Reading through Joan’s reactions to the excuses we make when we don’t commit to writing resonate hard. We think we don’t have time. How about realizing we’re not writing War and Peace, Joan teases, gently. Too many of us get the stinking thinking that we don’t have anything good to say or that this comes naturally to people who are more talented and articulate than we are. Joan writes:
Writing every day is less about becoming someone who writes, and more about becoming someone who thinks.
Before I conclude this post, I want to be sure to stress the importance I’m gleaning of not thinking of individual experts as the way to practice PKM. Rather, it is through engaging with a community of experts that we will experience the deepest learning. A.J. Jacobs stresses that we should heed his advice:
Thou shalt pay heed to experts (plural) but be skeptical of any one expert (singular)
By cultivating many experts whose potential disagreements may help us cultivate a more nuanced perspective on complex topics. When we seek to learn in the complex domain, the importance of intentionality, intellectual humility, and curiosity becomes even more crucial. Having access to a network of experts helps us navigate complexity more effectively.