How well did you keep up with this week’s developments in K-12 education? To find out, take our five-question quiz below. Then, share your score by tagging us on social media with #K12DivePopQuiz.
Tag: News
-

Test yourself on the past week’s K-12 news
This audio is auto-generated. Please let us know if you have feedback. -

Facilitating Deliberative Dialogue in College Classrooms
Academic inquiry and exploring new opinions are cornerstones of higher education, but some students say they’re not encouraged to engage in new ideas on campus. According to 2025 data from Inside Higher Ed and Generation Lab, approximately one in eight Student Voice respondents (13 percent) said they felt “not very” or “not at all” supported in their efforts to explore different perspectives at their college; 7 percent said they were unsure.
More colleges and universities are seeking to establish ways to advance civil discourse and allow students to disagree respectfully, but creating productive classroom dialogue remains a challenge for many professors.
A November webinar hosted by the Association of College and University Educators (ACUE) offered practical insights for instructors looking to build a supportive and thoughtful environment for exchanging ideas.
What’s the need: Constructive dialogue activities help students thrive in and outside the classroom.
“We need to have our students, whether they’re 40 and going back to school or just starting out in higher ed, we need to have adults in this world who are able to have meaningful conversations with others, to solve problems and to understand the viewpoints of others,” said Laurie Pendleton, executive director of faculty success at ACUE, during the webinar.
Such skills can also help students in their careers. “There are critiques of Gen Z [that] they don’t know how to work with each other in the workspace,” Zack Ritter, associate director of strategic initiatives at UCLA’s Center for Community Engagement, said during the webinar. “We’re providing a skill of, how do you listen to someone deeply at the workplace? How do you collaborate and find consensus among a bunch of different people?”
Defining terms: Deliberative dialogue, also called civil discourse or constructive conversation, is distinct from a casual discussion or engaging in debate, Pendleton said.
“When we think about debate, we’re really thinking more about winners and losers,” Pendleton said. “I’m stating my opinion or my facts. You’re stating your opinions and your facts, and we’re looking at who has the stronger case.”
Deliberative dialogue, however, is comparing different views, looking for mutual appreciation and potentially leading to collective action, Pendleton said.
“We’re looking for more shared understanding, things like, ‘I didn’t think about it from that perspective,’ or, ‘That’s interesting evidence; where did it come from?’” she explained.
Setting the stage: One of the common missteps faculty can make when establishing deliberative dialogue is neglecting to lay the groundwork, Ritter said. “You can’t just jump into the hot topic, because people are going to come with different baggage, different hates, different misunderstandings,” he said.
Instead, faculty should facilitate activities that allow students to share more about themselves and their cultures and to learn about their peers. Even better is when the class can build trust by doing some type of action project to solidify their connections, Ritter said, such as volunteering in the community.
Creating a classroom space that is responsive to discussion can also be key, said Adam A. Smith, founder and senior consultant at Smith Education Associates. Smith arranges his classroom to have “pods” of students grouped at desks or tables to allow them to connect in a more intimate way.
Navigating tensions: The goal of a deliberate discussion is not to make everyone comfortable, said Rosina Bolen, director of solidarity, engagement and success initiatives at Mount Saint Mary’s University.
“If everyone’s comfortable, you’re probably not having the kind of conversation that stretches people’s comfort zones,” Bolen said.
Faculty members should be prepared to make mistakes and for students possibly to get offended, and be equipped to handle “hot” or “cold” moments.
A hot moment is when tensions are high and conflict may erupt in the classroom. A cold moment, on the other hand, is when students don’t feel comfortable speaking out and a silent chill descends on the room.
Establishing community guidelines, ground rules or space agreements can be one way to mitigate or navigate uncomfortable situations by providing a working framework of what is or is not appropriate in the dialogue, Bolen said. Instructors should not assume students know the rules of engagement; it is their responsibility to outline the norms of the setting, Smith said.
It can be helpful to name what is happening in the outside world, including any prominent political or social tensions, and how they might inform individuals’ contributions to the conversation, Ritter said. “Naming the inequalities in society that are cutting across a bunch of different identities is also a way to build solidarity in the classroom.”
Professors should also conduct a self-evaluation of what may trigger their own emotional responses and prepare for how they will navigate such feelings so as to not disrupt the larger classroom goal. Similarly, faculty can give students an opportunity to share any of their own behaviors that might lead to misinterpretation.
“I’ve found it successful where students front-load some of their mannerisms and they say, ‘Hey everybody, sometimes I talk really loud, and it doesn’t mean that I’m mad at you, it’s just when I get excited about something, I just talk really loud and I use my hands,’” Ritter explained. “Having folks be vulnerable about their little mannerisms might result in a lot of pain reduction in the future.”
Continuing the conversation: After the formal discussion, faculty should create an opportunity for the class to reflect, Bolen said. How did the conversation go? How did people react? What did students learn?
“That debrief can go a long way towards ameliorating any negative impact on the rest of the course,” Bolen said. “And if something comes up that impacts individual students, it’s a great idea to go and check in with them afterwards and see how they’re doing.”
Deliberative dialogues should not be one-off events that occur in a vacuum, Pendleton said, but can be woven into the curriculum and connected to disciplinary content.
-

More Colleges Celebrate Gifts From Philanthropist MacKenzie Scott
Philanthropist MacKenzie Scott continued her latest giving spree this week, showering millions of dollars on another slew of higher ed institutions.
Scott gave $50 million each to California State University, East Bay, the largest single donation in the university’s history, and to Lehman College, part of the City University of New York system, according to announcements from the institutions on Thursday. (Scott also gifted Lehman College $20 million in 2020 and has given a total of $125 million to campuses across the CUNY system in the last five years.)
Texas A&M University–Kingsville and Seminole State College in Oklahoma also reported Scott gave them their largest gifts ever this week, $38 million and $17 million, respectively.
Scott recently made several new contributions to tribal colleges, as well, including $9 million to Bay Mills Community College in Michigan, $8 million to Blackfeet Community College in Montana and $10 million to College of the Menominee Nation in Wisconsin.
-

No, It’s Not (Mostly) About Tuition
As a kid, I remember science often being taught through myth busting. It was an engaging way to learn to ask questions, even if some examples worked better than others. (When someone responded to “people thought the earth is flat because it looks flat” with “what would it look like if it were round?” it broke my pre-adolescent brain.) The lesson behind the lesson was that science is a good way to fact-check, even if the facts in question seem obvious.
In that spirit, I loved Joshua Goodman and Joseph Wilkelmann’s new NBER paper about community college enrollments. It takes on several widely held myths, subjects them to empirical scrutiny and shows that they’re mostly false. It should be required reading for anyone discussing higher education policy.
The whole thing is worth reading, but I’ll give a few highlights.
- Most of the college enrollment drop over the last 15 years has occurred at community colleges, which typically have the lowest tuition of any sector. If the “high prices are scaring students away” story were true, the opposite would have happened. In fact, the most expensive four-year schools continue to turn people away. Enrollment decline is not primarily about tuition.
- About 30 percent of the reported drop in community college enrollment is a result of two-year colleges starting to offer four-year degrees. When their enrollments move from one category to the other, it causes a drop in one and an increase in the other. It’s actually closer to a measurement error.
- About 60 percent of the enrollment drop comes from students who were on the cusp of either enrolling or going to work; when the low-end job market picked up, those students either left college or skipped it.
- The “flight to quality” story doesn’t work, either. Community colleges didn’t lose many students to four-year schools; they lost them to paid employment.
- Surprisingly, at least to me, the surge in community college enrollments in 2009–10 didn’t lead to a surge in community college graduates. See the point above. When the low-end job market climbed out of the recession, many students decamped. As overall enrollments have dropped, retention and graduation rates have increased.
Taken together, these points refute several popular narratives. First, the most famous universities are not remotely representative of higher education as a sector. Second, the major driver of decline has been the availability of entry-level jobs, not six-figure tuition. Third, there simply has not been a “flight to quality” as the term is often used. The most compelling argument for free community college isn’t that it would somehow stick it to Harvard; it’s that it would enable more students to complete programs by reducing the need to work for pay while going to school. The primary competition for community college students is low-end employment.
Those narratives need to be discredited because they aren’t just wrong; they’re damaging. They put the blame for macroeconomic conditions on institutions that don’t control them, and they divert discussion from measures that would help to measures that are irrelevant at best and actively harmful at worst.
The story that strikes me as much closer to the truth goes like this: Higher education exists in a larger political economy. The increasingly bifurcated economy we have now—growth on the high end and the low end, with a hollowing-out of the middle—creates a sort of gravitational pull on institutions. Elite institutions are thriving, since they draw on the (anxious) upper classes. Low-end employers are thriving. Institutions built to help create a middle class are struggling. If you have a billion-dollar endowment and the stock market is offering double-digit returns, you’re doing great. If you’re a community or state college with flat or declining public funding, you’re struggling.
It doesn’t have to be this way, of course. The public sector could choose to act as a counterweight, pushing opportunity where we want it to go. That option exists. It has been done before.
But doing that involves first getting the facts right. Kudos to the NBER team for bringing relevant facts to the table. Now we just need to knit them into a compelling narrative.
-
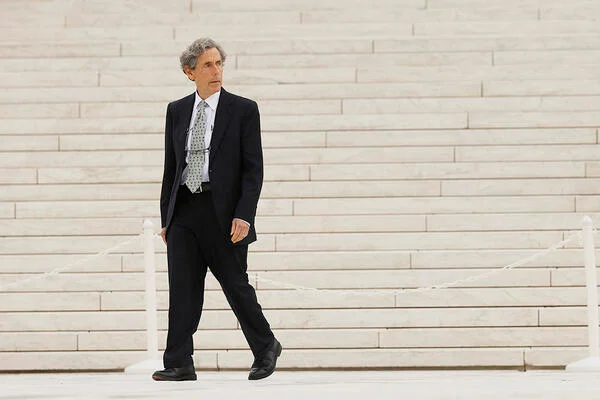

Hispanic Scholarship Fund Illegally Discriminates
Edward Blum founded the American Alliance for Equal Rights and Students for Fair Admissions.
Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images
A new lawsuit argues the Hispanic Scholarship Fund—a nonprofit that says it has provided more than $756 million in scholarships over its 50-year history—is illegally restricting its funding to Hispanics and Latinos. The litigation seeks to bar HSF “from knowing or considering ethnicity in any way” in its Scholars Program.
HSF, which didn’t return requests for comment Thursday, says on its website that it provides $500 to $5,000 scholarships, among other benefits, to 10,000 students annually.
The American Alliance for Equal Rights filed the suit Wednesday against HSF in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia, saying it has non-Hispanic members “who are ready and able to apply for HSF’s program but cannot because of their ethnicity.” Two such unnamed members are Asian American and white, the group said.
“The program bans Blacks, Asians, and Native Americans that aren’t Hispanic,” the American Alliance notes. “But it welcomes whites that are.”
To make its case that the ethnic restriction is illegal, the American Alliance is using a law passed during the Reconstruction era that bans racial discrimination in contracts. And it’s alleging that HSF is entering into contracts with scholarship applicants.
“The HSF Scholars Program is a contract that offers applicants a chance at a lucrative scholarship if they agree to HSF’s terms, assent to its privacy policy, draft several essays, and sign a binding pledge,” the suit says. It goes on to allege that HSF’s terms of use, which applicants must agree to, specifically say, “This is a contract between you and HSF.”
Opening up such “contracts” only to Hispanics and Latinos violates the Civil Rights Act of 1866, which prohibits racial discrimination in contracts, the suit argues.
It’s another example of how the campaign against affirmative action and programs that specifically benefit minorities didn’t end with the 2023 Students for Fair Admissions Supreme Court ruling, which rendered affirmative action in college admissions illegal. The American Alliance was founded by the same man, Edward Blum, who created Students for Fair Admissions, the nonprofit that’s the namesake of the 2023 ruling.
It’s also another example of a suit that uses an Asian plaintiff and a Reconstruction-era law to attempt to open up a minority-specific scholarship to all races and ethnicities. Earlier this year, the Pacific Legal Foundation cited the Ku Klux Klan Act of 1871, which Congress passed to protect African Americans, to attack a financial aid program that helped only Black students at the University of California, San Diego.
That conservative nonprofit law firm sued on behalf of the Californians for Equal Rights Foundation, which said it had multiple “Asian-American high school members who plan to apply to UCSD” and who could’ve been excluded. Before that case reached a hearing, the nonprofit philanthropy that administered the Black Alumni Scholarship Fund announced the fund was being renamed.
Blum told Inside Higher Ed on Thursday that the American Alliance filed its first suit after his other group’s 2023 victory. He estimated it’s filed about 20 more since then.
“There are tens of thousands of students who are affected by race-exclusive scholarship funds, fellowships, internships, things along those lines,” Blum said. “And so it is the mission of the American Alliance for Equal Rights to challenge these racially exclusive programs and policies.”
In the current case, Blum said, “The race exclusivity of this scholarship fund was brought to our attention by a young Asian American student” of “modest financial background.”
“This nation cannot remedy past discrimination with new discrimination, and I think the vast percentage of Americans agree with that,” Blum said.
-

More Negative Projections for Higher Ed in 2026
Three credit rating agencies have issued unfavorable outlooks for higher education in 2026.
Fitch Ratings issued the latest outlook on Thursday, declaring that it anticipates a “deteriorating credit environment for U.S. Public Finance Higher Education in 2026 relative to 2025.” That outlook is based on various pressures, including concerns about declining enrollment, new limits on federal loan programs and obstacles for international students seeking to study in the U.S.
The organization noted state funding is “vulnerable” due to an “uncertain policy trajectory” that will “generally shift more costs previously borne by the federal government on to the states.”
The rating agency also noted public concerns about “the value proposition of a higher education degree” amid declining job-placement rates and rising concerns about affordability. Fitch anticipates limited revenue growth for colleges as they grapple with those challenges and projected consolidation across the sector, from mergers and closures to restructuring and more.
S&P Global Ratings also issued a negative sector outlook on Tuesday. That analysis cited some of the same concerns raised in the Fitch report. S&P Global warned of “intense competition for students” and rising operating costs for the sector in the year ahead.
“Our sector view is negative, as we expect colleges and universities will struggle to navigate through mounting operating pressures and uncertainty that will require budgetary and programmatic adjustments,” officials at S&P Global Ratings noted on their website.
Moody’s Ratings was the first to issue a sector outlook last month, deeming it negative for many of the same reasons cited by other agencies in their 2026 assessments for higher ed.
-

The NIH Policy Holding Researchers “Hostage”
Rachael Sirianni is one of the thousands of research scientists whose work has been decimated by the Trump administration’s massive cuts to the National Institutes of Health and other federal agencies.
“My lab is crumbling,” said the pediatric brain cancer researcher, who works at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School. “Over the course of the last eight months, I’ve had to shutter more than half of my research program.”
At the same time, she has a backlog of papers she’s still trying to get published in journals that are the best fit for her research and career, including several that charge thousands in fees to make the paper free to access. And if she wants her work to comply with a new NIH policy to expedite public access to federally funded research—part of the agency’s effort to restore trust in science, it says—she may have to start paying even more.
The 2024 Public Access Policy, which took effect July 1, requires federally funded researchers to deposit their accepted peer-reviewed article manuscript into an open-access repository, such as the NIH-managed PubMed Central, immediately after a journal accepts it for publication. But researchers are reporting that some journals, including at least several high-impact titles owned by Elsevier, Wiley and Springer—are charging authors anywhere from $2,000 to more than $10,000 in article processing charges (APCs) to make their work immediately accessible.
While researchers can use their NIH grants to pay for APCs, that’s hard for some to justify in such a precarious funding environment.
“If I had full access to the institutional dollars that normally support my research program, or if I really believed that that grant that scored well is eventually going to get funded, I could risk my research dollars on these open-access fees,” Sirianni said. “But because of the trauma that the Trump administration is imposing on scientists across the country, we are faced with impossible decisions. Do we dedicate our money to the experiments? Do we maintain our research personnel? Do we comply with open-access fees?”
Open-access advocates and experts say that predicament is exposing the limits of the government’s ability to rein in the $19 billion scholarly publishing industry, which is fueled by academic incentive structures that reward researchers for publishing frequently in widely cited, prestigious journals. Meanwhile, the publishing industry—which has long opposed immediate open access in part because it threatens subscription-dependent business models—says the rollout of the policy gives them no choice but to charge APCs.
Zero Embargo
The 2024 policy replaces the 2008 Public Access Policy, which allowed publishers to embargo new peer-reviewed federally funded research articles for 12 months before making them publicly available. That embargo period allowed publishers to turn a profit from selling academic libraries subscriptions to exclusive content; authors who wanted to make their papers publicly accessible before the embargo was lifted typically paid an APC.
The government’s goal in lifting the embargo was to promote “equity and advance the work of restoring the public’s trust in Government science, and to advance American scientific leadership,” Alondra Nelson, the former acting director of the Office of Science and Technology Policy, wrote in a 2022 memo bearing her name. “A federal public access policy consistent with our values of equal opportunity must allow for broad and expeditious sharing of federally funded research—and must allow all Americans to benefit from the returns on our research and development investments without delay.”
Although the Biden administration finalized the policy, the Trump administration is carrying it forward. It was set to take effect across federal agencies on Dec. 31, but NIH director Jay Bhattacharya announced in April that he was implementing it six months ahead of schedule to promote “maximum transparency.”
Although Sirianni supports the spirit of NIH’s new open-access policy, she’s worried that high APCs will deter researchers from submitting their work to influential journals that might otherwise be a good fit, to the detriment of the scientific literature.
“There’s absolutely going to be a lot of work that doesn’t get published or gets published in the wrong journal,” Sirianni said. “This policy is harming scientists. Instead of ensuring that research dollars are invested in providing knowledge to the scientific community and to the public, those dollars will be spent on feeding giant publishing corporations more money.”
‘Not Sustainable’?
However, publishers say the NIH’s zero-embargo policy is forcing them to recoup lost subscription revenue through APCs to sustain operational costs, including article selection, curation, peer and editorial review, publication, archiving, and maintenance.
“We are unable to support approaches that aim to make subscription articles immediately and freely available, which are not sustainable in the long term given they undermine the subscription model on which they depend,” an Elsevier spokesperson said in an email to Inside Higher Ed.
“The best method for addressing issues of cost in publication is through a vibrant, competitive, and dynamic publishing marketplace with maximum author choice, including fee-based public access and read-and-publish agreements,” Carl Maxwell, senior vice president of public policy for the Association of American Publishers, who lobbied against the zero-embargo policy, wrote in an email. “We don’t think it’s a good idea to compel researchers to use a one-size-fits-all open access business model that has the potential to require NIH-funded researchers to pay out of pocket to fund the peer review process, in some cases harming their ability to communicate their research results to the scientific community and the general public.”
Caroline Sutton, CEO for the International Association of Scientific, Technical and Medical Publishers, added that researchers’ frustration with the NIH’s new open-access policy “reveals one of the real human impacts of well-intentioned policies that do not fully consider the operational realities of the research ecosystem.”
It also raises long-standing questions about how to sustain that ecosystem.
“Should the responsibility for funding this work lie with the funder? With the research or institutional library? Should publishers not be compensated?” she wrote in an email. “And how can the critical system of checks and balances—which must be resourced—endure if it is not sustainably funded?”
But another sector sustaining the scientific publishing industry is the faculty who produce and peer review research for little to no financial compensation. The most productive are often rewarded instead with tenure, promotion and cachet.
Holding Articles ‘Hostage’
While the NIH policy doesn’t require authors to publish in journals that charge APCs—plenty of reputable, fully open-access journals exist—researchers say where they publish matters to their careers. At most universities, frequently publishing research in prestigious, high-impact journals—including many with hefty APCs—carries more weight with tenure and review committees than publishing in more obscure journals.
But researchers aren’t always clear on a journal’s APC guidelines until they get through the review process and are asked to pay open-access fees to comply with the NIH policy, Rachel Widome, a public health professor at the University of Minnesota, told Inside Higher Ed. She withdrew an article from the Elsevier-owned Sleep Health on how school start times impact adolescents after she realized she’d have to pay a $2,500 fee to upload her accepted manuscript to PubMed Central in compliance with NIH policy.
“When that happens, they’re holding your article hostage,” she said. “Do you start from scratch and submit it to a new journal? It can take six to nine months to go through another review.”
She ended up resubmitting the article to Sleep Health after her NIH grant ended, exempting her from the zero-embargo policy. Although “time has been wasted,” she said the APCs stand to hurt early-career scientists the most. “It’s so critical that they establish a publication record,” Widome said. “If the options of which journals they can submit to are really limited [because of APCs], that hurts their chances of getting her research out and launching her career.”
‘Valuing Prestige’
But those academic incentive structures have also emboldened publishers to levy APCs in response to the NIH’s zero-embargo policy, said Dave Hansen, executive director of the Authors Alliance, a California-based nonprofit that supports authors in disseminating their work.
“So much of the system is wrapped around valuing prestige journals that are published by some of these bigger commercial publishers. That’s really hard for even a big institution like the NIH to nudge researchers away from,” Hansen said, adding that the NIH could de-emphasize prestige factors when evaluating researchers. At the same time, “a lot of publishers recognize that there’s a massive amount of federal funding that they can now demand access to because of this new federal policy.”
The zero-embargo policy isn’t the NIH’s only attempt to regulate the scientific publishing industry. This summer, Bhattacharya proposed capping APCs to weaken the market power of publishers, dilute the scientific elite and “make science accessible not only to the public but also to the broader scientific community, while ending perverse incentives that don’t benefit taxpayers,” he said. But critics say the plan is neither comprehensive enough to dismantle academic incentive structures, nor likely to substantially lower APCs.
And the frustration researchers are experiencing in the early days of the NIH’s new zero-embargo access policy—which was crafted with some of the same goals as the NIH’s proposed APC caps—is already offering support for those predictions.
“The NIH public-access policy applies to a vast amount of research, but it’s also just a percentage of the overall landscape. There are a number of players here, including the funders, researchers, institutions, publishers and libraries,” said Katie Funk, former program manager for PubMed Central, who helped develop the zero-embargo policy.
“Without addressing the whole system, it just causes confusion,” she added. “Larger conversations need to be had about the costs of publishing. It’s not transparent and it’s pervading the whole system.”
(This article has been updated to correct the name of the UMass medical school.)
-
How Talks Over New Earnings Test Could Ensnare Gainful Employment
Starting next July, colleges and universities’ access to federal student loans will hinge on how much their graduates make after Congress’s new earnings test, known as the Do No Harm standard, takes effect.
This monumental shift in how the federal government holds degree programs accountable is one that’s years in the making. But when Congress passed the law, one key type of degree program was left out—undergraduate certificates.
Lawmakers from both parties have long said holding colleges accountable for cost is critical in order to drive down borrower-default rates and protect students from paying high tuition without a guaranteed return on investment. Yet, the very students and programs Republicans left out of the earnings test are expected to face the worst return on investment, studies show.
Under the so-called Do No Harm test, a program would lose access to federal loans if its average graduate doesn’t earn more than someone with a high school diploma for two out of three consecutive years. And while students enrolled in undergraduate certificate programs only make up about 10 percent of all those receiving federal aid, they account for about half of those who attend programs projected to fail the earnings test, according to research from American University’s Postsecondary Education & Economics Research Center.
For now, a different rule, known as gainful employment, holds certificate programs with a poor return on investment accountable using a similar earnings test and a metric related to a student’s debt. But unlike Do No Harm, the Biden-era gainful-employment rule only applies to certificate programs and for-profit colleges.
According to the Federal Register rule-making notice, the Department of Education and an advisory committee are set to both iron out the details of Do No Harm and rehash the gainful-employment rule during a months-long process known as negotiated rule making. But while the process begins Monday, the initial meeting agenda doesn’t include any discussion about either issue. Instead, the first week of rule making will focus specifically on regulations that expand the Pell Grant to short-term job training programs, and then the committee will break for the holidays.
In the meantime, education experts are left to wonder what the fate of accountability for certificate programs will be—and tensions remain. For-profit institutions remain critical of gainful employment, calling it an uneven playing field. Colleges and universities of all types worry that both metrics are holding them accountable for factors outside of their control. And student and taxpayer advocates stress that it’s important to ensure federal dollars are being put toward programs that pay off.
But when conversations about the accountability measures do kick off, policy experts from all sides agree that the regulations regarding gainful employment, which are not as restricted by the new law, will be the most contentious topic of debate.
“The thing that will take up a lot of oxygen in the room is gainful employment,” said Clare McCann, a former Education Department official who is now the PEER Center’s managing director of policy and operations. “Republicans have come a long way in believing accountability is important. So the desire to settle accountability issues as much as possible, for once and for all, runs pretty deep.”
A Perennial Political Football
Since the Obama administration first established a gainful-employment rule in 2010, Republicans and Democrats have fought over how to hold career education programs accountable.
The first Trump administration made rescinding the Obama-era rule a priority, and then the Biden administration put a stronger iteration in place. This back-and-forth raised speculation that the second Trump administration would once again roll back gainful employment.
However, officials have sent some mixed signals. The administration has pursued deregulation while also opting to defend the Biden rule in court. (A federal judge upheld it earlier this fall.) Further, the Trump administration’s push for greater federal involvement in higher education runs counter to many of its actions in the first term. The Education Department has yet to release its plans for the accountability provisions, fueling uncertainty about the fate of gainful employment.
Key Republican lawmakers, including Sen. Bill Cassidy, chair of the education committee, have said undergraduate certificates were only exempted from the new Do No Harm standard because of the gainful-employment rule. (The senator’s response implies that holding certificates accountable under both standards would be duplicative.)
As it currently stands, gainful employment requires certificate programs at any institution and degree programs at for-profit colleges to pass two tests. The first is similar to the Do No Harm earnings test. The second one, known as the debt-to-earnings ratio, gauges whether the average student earns enough to reasonably pay off their loans. Programs that fail either test are at risk of losing access to all federal student aid, including both loans and the need-based Pell Grant.
About 1.4 million students annually use federal aid to attend undergraduate certificate programs, and without gainful employment, advocates worry they are at risk of enrolling in programs that fail to provide a positive return on investment.
New data from the Century Foundation, a left-leaning think tank, showed that while two out of every three programs projected to fail the gainful-employment tests would also fail Do No Harm, about 400 programs could squeeze by, passing the new earnings test while failing the gainful-employment debt-to-earnings ratio. Those programs represent about $528 million in annual Pell Grant disbursements.
“Someone who wanted to take a lot of Pell money by setting up a bad program … could set up a program, which may not require students to take out loans but still is not worth their time or that Pell Grant money,” said Peter Granville, a Century Foundation fellow and author of the report. “That’s a crack which we’re concerned bad actors could go in and use to game the system.”
Advocates like Granville urge the department to not touch gainful employment. Meanwhile, most institutional representatives Inside Higher Ed spoke with said they’d like to see more clarity in the policy proposals about how the Do No Harm test will work and are advocating for at least some changes to make gainful employment more fair. During public comment, the trade association Career Education Colleges and Universities, which represents for-profits, called on ED to “take the opportunity to fully rescind” the gainful-employment rule.
But one institutional representative who will serve as a member of the negotiating committee said that while institutions may want to see changes made to the gainful-employment rule, it seems highly unlikely that it will be fully rescinded the way it was during Trump’s first term.
“Whether it’s the department or negotiators, I think anyone coming in and trying to say, ‘There should just be nothing that applies to nondegree programs,’ seems pretty inconsistent with the language coming out of Congress,” the representative said, speaking on the condition of anonymity to protect his good faith in negotiations. “It also just seems like it would be a really challenging position to defend.”
Some Potential Changes
So if the department doesn’t try to roll gainful employment back entirely, could they change the regulations in other ways? Experts, advocates and institutions have several ideas if they do.
Advocates for for-profit institutions have argued for years that all programs should be subject to the gainful-employment rule. But one policy expert, who asked to speak anonymously since the department has yet to release its proposals, said that stripping gainful employment down to the bare bones to directly mirror the Do No Harm test seems unlikely.
“Congress left out undergraduate certs, and that’s the only fair reading of the law. So … presumably you can’t do the exact same thing as the Do No Harm measure for undergraduate certs,” the source said.
Instead, the expert hopes that the department will do what it can to better level the playing field while maintaining accountability for certificate programs. One way of doing that, the source suggested, is to lower the ages of adults with high school diplomas that are used in comparison and extend the time before earnings are measured.
Currently under gainful employment, the earnings premium test compares the income of certificate and degree holders three years after graduation to adults ages 25 to 34. That means a 21-year-old with a certificate in phlebotomy could be compared to a 34-year-old flight attendant.
The Do No Harm test is expected to use data for the same age group and compare it to students four years after they graduate, but since the gainful-employment rule has other stipulations like the debt-to-earnings ratio and the higher penalty of losing Pell Grants, the expert said they would “like to see a better, more reasonable comparison group.”
Other potential changes on the table could include eliminating the debt-to-earnings test but keeping the Pell-eligibility penalty for both certificate and for-profit programs or opting to maintain gainful employment for certificate programs while for-profit programs would only be subjected to the Do No Harm test. But, for each policy expert that proposed one of these ideas, another suggested that it could lead to legal challenges.
In general, policy experts said, until the issue papers are published, it will be difficult to predict what the Trump administration plans to do.
Preston Cooper, a senior fellow at the American Enterprise Institute, a right-leaning think tank, will be serving on the negotiating committee. He said he understands the argument that it’s not fair to hold for-profit institutions to a higher standard, but he wants to ensure “the strongest accountability that we can possibly get.”
“As the taxpayer representative, I certainly find it compelling … because if we have weaker accountability, then we’re losing more money on Pell Grants and student loans,” he said. “But ultimately, it will come down to what they decide to propose in the issue papers.”
-

An Unjust Suspension in Oklahoma
University of Oklahoma officials suspended graduate teaching assistant Mel Curth from teaching on Sunday after a student, Samantha Fulnecky, complained about getting a failing grade on an assignment. The incident has sparked a lot of debate about whether Fulnecky’s essay, which repeatedly invoked the Bible and denounced transgender people (including, reportedly, her instructor) as “demonic,” deserved a poor grade for its lack of academic rigor or if Fulnecky was unjustly punished for her religiously motivated political opinions.
However, this debate about grading obscures the far more important question at hand about academic freedom: Should instructors be suspended from their classes without due process and proof of misconduct?
The answer is clear, and everyone—liberal or conservative, anti-trans or pro–trans rights—should agree with this basic concept: No instructor should be suspended from teaching without being found guilty of misconduct. This is a fundamental tenet of justice: innocent until proven guilty.
Banning an instructor from the classroom is one of the most serious violations of academic freedom because it so clearly abridges the freedom to teach. It prohibits a teacher entirely from expressing their ideas in the classroom. It deprives students of the opportunity to hear from their teacher. And it sends a chilling message to the entire campus that expressing the wrong ideas can be punished without due process. Instructors should only be removed from classes when they are committing irreparable harm to students—for example, by physically endangering them, or by refusing to teach their classes. But there is no irreparable harm in a grade dispute, because grade appeals allow students to receive a just result. Grading disputes do not justify emergency action.
Let us consider the worst-case scenario here: The instructor gave a lousy grade to a student who called them (and all trans people) “demonic.” It might be deserving of a grade appeal and measures taken to protect the student from unfair grading. However, we have no evidence of any general misconduct or bias in grading. We have one public complaint from a particularly obnoxious student and no other allegations of any wrongdoing.
An instructor who gives a wrong grade on an assignment to one incredibly offensive student may have fallen short of our ideals for a teacher. But even if this allegation was thoroughly investigated and definitely proven, it would not by itself justify removing an instructor from teaching as a punishment. It certainly cannot justify an interim suspension without proof of misconduct.
Imagine if a Christian student with a Jewish instructor had referred to Jews as a “demonic” force. Would we be so quick to denounce the teacher who objected to such vile hatred and regarded it as unworthy of academic work? It’s only the hatred of trans people that sparks a very different reaction today. But even if the instructor’s response was understandable, it still could be wrong. Still, the determination by a body of faculty experts about whether it was wrong has not yet been determined, and until it is, a suspension is unjustified.
Incredibly, this violation of basic rights by the University of Oklahoma was denounced by conservatives as inadequate. State Sen. Shane Jett (R-Shawnee), chair of the Oklahoma Freedom Caucus, declared, “Placing the instructor on leave is not sufficient. It’s another weak and cowardly response.” The Freedom Caucus called for “cuts to state funding for higher education institutions until free speech and religious liberty are verifiably protected so conservatives are no longer targeted.”
The conservatives clamoring for blood in Oklahoma should question whether they really want to endorse the idea of administrators suspending any professor accused of saying or doing something that upsets a student.
As I have long argued, interim suspensions violate academic freedom by suppressing speech without proof of misconduct. It’s time for people on all sides in all cases to condemn interim suspensions on a universal, consistent and principled basis.
If the Oklahoma TA is found to be guilty of violating academic standards after a fair hearing, and if the determination of academic experts is that she made a terrible mistake and is incapable of learning from it, then a suspension from teaching could be justified. But academic freedom requires due process, and we fundamentally betray it when we punish people before finding them guilty of misconduct.
-

Purdue Professor Declines MLA Prize Due to Policies on Gaza
She had been awarded the prize for her book Ghostly Pasts, Capitalist Presence: A Social History of Fear in Colonial Bengal, published in August 2024.
Tithi Bhattacharya, a history professor at Purdue University, formally declined the Modern Language Association’s Aldo and Jeanne Scaglione Prize for South Asian Studies in protest of decisions by the MLA regarding Israel’s attacks on Gaza.
“This decision is not a reflection of the committee’s rigorous work or the value of the prize itself, but a stand taken in light of the institutional silence and policy decisions made by the Modern Language Association regarding the ongoing genocide in Palestine, including the MLA leadership’s appalling suppression of the Delegate Assembly’s right to vote on a proposed resolution to boycott, sanction, and divest from Israel,” Bhattacharya wrote Wednesday in a blog post about her decision.
She had been awarded the 2025 prize for her book Ghostly Pasts, Capitalist Presence: A Social History of Fear in Colonial Bengal, published in August 2024.
“I also hope that by declining, I can contribute to the urgent conversation about the ethical responsibilities of professional academic organizations when facing colonialism, brutal state violence, and genocide,” Bhattacharya wrote. “My book, which my generous colleagues on the committee have recognized, is about how colonial capitalism does not even spare ghosts. Against such power, I still believe our weapon remains solidarity.”
