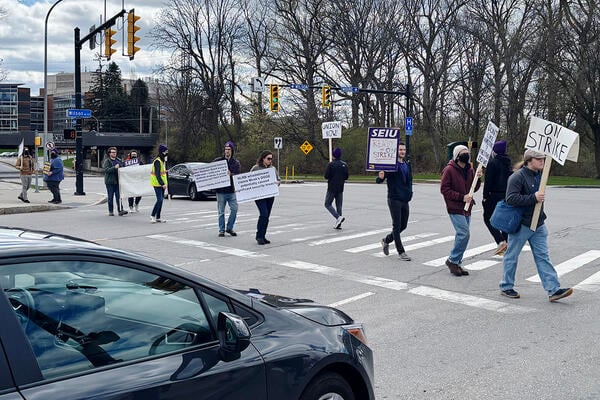
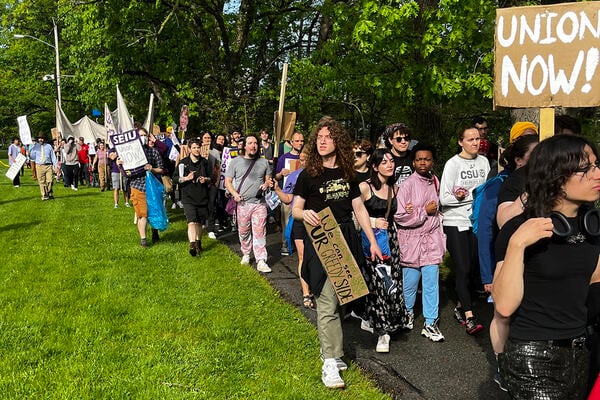For a month this spring, the University of Rochester Graduate Labor Union, a group of Ph.D. student workers, staged a strike. Workers walked off the job, demanding that the university host a private unionization election so they could vote and win recognition of the union—all without having to go through the Trump-era National Labor Relations Board.
But after workers protested during the May 16 commencement ceremony, GLU representatives told them that organizing committee members had voted unanimously to “pause” the strike. And, with fall semester classes starting Monday, the organizers say they have no plans to rekindle it.
“We didn’t achieve what we wanted, which was them giving us a fair process for an election,” said Katie Gregory, a seventh-year environmental sciences Ph.D. worker. But, she said, “none of us consider the fight here to be over in terms of support for a union.”
George Elkind, a fourth-year visual and cultural studies Ph.D. worker, said, “We intend to continue fighting for a fair election process.”
The strike was both a carryover from an intense period of grad student union activity during the Biden administration—roughly 38 percent of grad student workers are unionized, according to a report from last August—and an indication of how President Trump’s return to the White House has raised concerns that the NLRB has become less favorable to unions.
Last year, during Biden’s presidency, University of Rochester officials and GLU organizers discussed plans for a private election, which both parties were amenable to. If they had reached an agreement, the NLRB—which usually handles unionization votes at private nonprofit institutions such as Rochester—wouldn’t have been involved.
But after Trump retook the White House in January—and fired a Democratic NLRB member and the agency’s general counsel—the university changed its tune. In February, a university lawyer told student organizers the institution no longer wanted a private election, citing multiple reasons, according to a document that Ph.D. student workers provided to Inside Higher Ed. Instead, the lawyer wrote, they could pursue an election with the Trump-era NLRB.
Taking that route would be risky—not just for their own prospective union’s chances of winning recognition, but also for the continued rights of grad workers across the country to unionize. Some union supporters worry an NLRB dominated by Trump appointees might use a grad student unionization case such as Rochester’s to overturn the 2016 Columbia University precedent establishing that private nonprofit university grad workers can unionize through the NLRB.
If that precedent were overturned, student workers could continue to unionize at public universities in the states that allow such action, but those at private institutions would have no other path than to seek voluntary recognition from their universities.
So far, GLU hasn’t succeeded in pressuring the University of Rochester once again to back a private union vote that would circumvent the NLRB. Gregory and Elkind both said the outcome of the strike might have been different if more Ph.D. workers had withheld their labor.
The union would have represented more than 1,400 students, Elkind said. About 300 withheld at least a day of work, Gregory said, but having 1,000 strike on day one would’ve sent a very different message.
Elkind said a “more sweeping strike with bigger numbers … would have had [university leaders] at the table within days.”
Both said the Trump administration’s attempts to remove international students from the U.S. had a “chilling effect” on strike participation. Elkind, who said about half of grad students at the university are international, called it “a horror show of a national environment.”
They also pointed to the university’s announcement of “attestation” forms that asked workers to indicate how much they were working—allowing the university to cut off pay for strikers if it wished.
“Clearly, a tactic to impact the strike participation,” Gregory said. The university didn’t move forward with requiring the forms; in an email, Sara Miller, a university spokesperson, said it “never implemented an attestation form and denies any allegation of ‘scare tactics.’”
University representatives also “refused to acknowledge the union as an entity,” Gregory said. For instance, they responded to organizing committee members’ communications as if they were merely students, offering them help with issues such as registration.
“It was a real slap in the face,” she said.
In their May 18 email calling off the strike, GLU members noted the semester was ending, writing that “many grads only have 9-month stipends and do not have labor to withhold during the summer.”
But Elkind and Gregory both said organizing is continuing. And the provost, in a Friday memo, announced new, universitywide minimum stipends for “full-time, full tuition remission PhD students”: $25,000 for nine-month stipends and $34,000 for yearlong stipends.
“I think they’re trying to curb labor organizing and unrest,” Elkind said.
Miller, the university spokesperson, wrote in an email that “the recent stipend update marks another step in implementing the University’s long-standing plans to enhance our graduate programs and was not related, in any way, to students’ prior organizing and/or protest activity.”
In recent years, Miller said, Rochester has expanded support for full-time Ph.D. students to include “subsidized health, dental and vision insurance; childcare benefits; raising stipends, and enhanced access to mental wellbeing and counseling services.”
And again, she said, “the students continue to have and have always had access to the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB).”