This story was produced in partnership with Work Shift and reprinted with permission.
MOBILE, Ala. — Three or four times a week, LaTyra Malone starts her day at Mobile Infirmary hospital at 6:30 a.m. For the next 12 hours, she makes her rounds and visits with patients — asking if they’re in pain, checking vitals, administering fluids. To an outside observer, she appears to be a nurse.
But Malone, 37, is a registered nurse apprentice. Everything she has learned how to do in her nursing classes at Coastal Alabama Community College, she can do at the hospital under the supervision of registered nurse Ondrea Berry, her journeyworker — a term typically used in the skilled trades. Unlike most nursing students who complete their required clinical hours in groups for no pay, Malone gets paid as an employee with benefits. She also gets much more personalized, hands-on learning time.
“It’s like having a little kid attached to your leg all day,” Berry joked.
For Malone, the partnership is invaluable.
“I learn so much more one-on-one,” Malone said. “I might know the basics of disease processes or why we’re giving a certain medicine, but hearing her break it down to me helps a lot.”
The pair work largely as a team, alternating duties to allow Malone a chance to observe and practice. By now, Malone knows the ropes pretty well: In addition to her apprenticeship training and classes, she has 16 years of experience as a certified nursing assistant and a medical assistant. And Berry, who is 25, says she benefits from the working relationship too. “There are teaching moments for both of us,” she said.
Degreed nursing apprenticeships, like the one in Alabama, have emerged nationally as a potential solution to a thorny problem. The national nursing shortage is creeping toward crisis levels, with the demand for RNs like Berry and licensed practical nurses, or LPNs, projected to outstrip the supply for at least the next decade. At the same time, tens of thousands of people like Malone are already working in patient care in hospitals. Many aspire to be nurses — in fact, many certified nursing assistant programs sell the idea that you can start there, quickly land a job and then continue on to become a nurse.
But in reality, that’s a huge leap that requires an entirely different admissions process and English, math and science prerequisites that many nursing assistants don’t have. It also assumes that someone working an eight- or 12-hour shift for $18 an hour can find the time and the money for more education.
“The sort of ‘we are excellent’ ethos in nursing might be self-defeating in that it is weeding out a lot of people who would be amazing nurses,” said Iris Palmer, director for community colleges with the education policy program at New America.
Related: Interested in more news about colleges and universities? Subscribe to our free biweekly higher education newsletter.
Several states, including Texas, North Carolina and Wisconsin, have begun growing registered apprenticeships in nursing — which have approval from the U.S. Department of Labor — to help address this problem. But no state has done quite as much as Alabama in scaling the model.
In 2021, the Alabama Board of Nursing worked with the state legislature to create a nursing apprenticeship license. Normally, nursing students are not licensed until after they graduate and pass a national licensure exam, and therefore they can’t be paid for their supervised clinical hours. The new apprenticeship license allows them to earn while they learn, making nursing school much more accessible for students like Malone and helping to fill critical staffing needs in hospitals.
Since the law passed, 80 employers and 28 colleges and universities in Alabama have jointly created LPN and RN apprenticeship programs for those who are still working toward a degree. Nearly 450 apprentices — the great majority RNs — have completed the program and passed their exam, with more than 500 currently apprenticing. It’s too soon to say whether apprenticeships will solve the nursing shortage in the state, but early data shows benefits for employers and aspiring nurses alike.
Mobile Infirmary has had over 90 nursing apprentices since the hospital’s program began in 2022, first with the LPN apprenticeship and soon after with the RN one. Graduates are required to stay at the hospital for one year after the apprenticeship ends, but most are staying beyond that. Only five have left so far, according to Stefanie Willis-Turner, the director of nursing school partnership and programs at Mobile Infirmary.
The hospital, like many others, already offered tuition reimbursement for employees who wanted to go back to college and move into nursing or another higher-level position. But such programs have notoriously low uptake, in part because most low-income employees can’t front the cost of tuition and also because many don’t know what steps to take.
“It amazed me the number of people that wanted to go back to school but didn’t really know where to get started,” Willis-Turner said. “Having a person to help guide them has really been our trigger, and that’s how we run this program.”
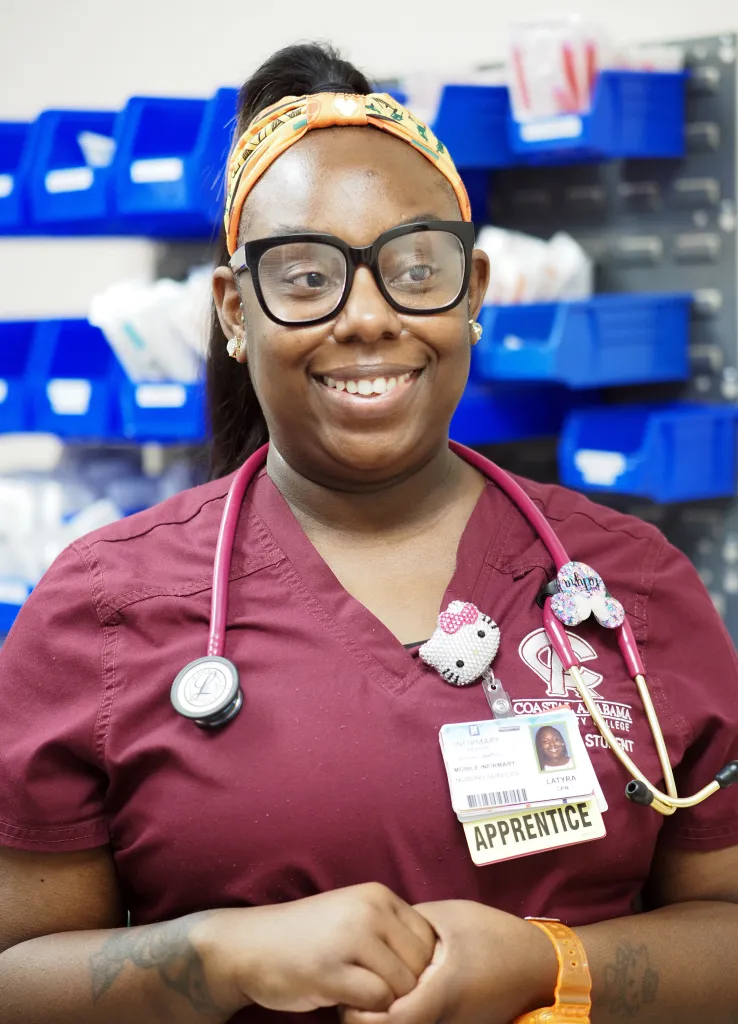

Willis-Turner played a crucial role in recruiting Malone for the apprenticeship. Malone has wanted to be a nurse since she was a teenager when she was president of her high school’s chapter of HOSA-Future Health Professionals, a global student-led organization that promotes careers in health care. But her plans to become a registered nurse were delayed when she became a mother. The financial burden plus the rigid schedules of nursing school made it difficult to make room for parenting, working and studying.
With the apprenticeship, Malone doesn’t have to worry about paying for college, and she can provide for her family while improving her nursing skills. Her path stands in stark contrast to that of Berry, who worked at Dairy Queen throughout nursing school to pay for tuition and health insurance. Berry didn’t have kids to take care of, but she also didn’t have financial support from anyone else in her family. Her only on-the-job training in nursing school was the clinical hours, where she joined a group of students who took turns practicing new skills with just one nurse. Berry says she only attempted two IVs in that time. Malone has done so many she can’t count.
About 75 percent of the apprentices at Mobile Infirmary over the last three years were already working at the hospital. The rest came from surrounding medical facilities. Some even quit their jobs to transfer to Mobile Infirmary for a better chance at getting into the apprenticeship program. In addition to paying students for their work, Mobile Infirmary pays for any tuition that isn’t covered by scholarships or grants. The hospital also provides two uniforms free of charge. And students know they have a guaranteed job after they graduate and pass the nursing exam.
Related: Nurses are in high demand. Why can’t nursing schools keep up?
This kind of targeted support is what makes the best apprenticeships successful in boosting individual economic mobility, its advocates say. Another key factor is the type of job an apprenticeship prepares people for. Most health care apprenticeships are for entry-level roles like CNAs, patient care technicians and medical assistants — jobs that, on average, pay $18-$20 an hour.
About half of states offer apprenticeships for LPNs, who make about 50 percent more than that, and half do so for RNs, whose median salaries are close to six figures, according to data from the U.S. Department of Labor. But far fewer apprentices are in those LPN and RN programs — and the majority of RN apprenticeships are for nurses who already have degrees, not for those who are still learning. That means aspiring nurses must still get all the way through the financial and logistical obstacles of nursing school before they can start to work.
Josh Laney helped set up the different model in Alabama when he was director of the state’s Office of Apprenticeship. For a long time, he said, he bought into the “urban legend” that training more people to be certified nursing assistants, especially when they’re young, would get people onto the path to becoming nurses.
“The pitch was, ‘We get you the certificate and then you’re going to work at a hospital because it’s a very high-demand occupation. From there you can go on and move into nursing or whatever else you want to do,’” Laney said. “But there was no specified plan for how to do that — just a low-wage, very stressful and strenuous job.”
The data backs that up. A 2018 study of federal Health Profession Opportunity Grants for CNA training showed that only 3 percent of those who completed the training went on to pursue further education to become an LPN or RN. Only 1 percent obtained an associate degree or above. A study in California showed slightly better odds: 22 percent of people who completed certificate programs at community colleges to become CNAs went on to get a higher-level credential in health care, but only 13 percent became registered nurses within six years.
Because of these outcomes, Laney refused to pursue apprenticeships for CNAs in Alabama. One reason apprenticeships for CNAs and medical assistants are common, however, is that they are jobs that don’t require degrees and have fewer regulations when it comes to training. Setting up a registered apprenticeship for nurses who don’t already have a bachelor’s degree is complex and requires the work of many entities — the nursing board, colleges and employers.
When he went to the state board of nursing to propose LPN and RN apprenticeships, Laney was initially shut down.
“To their credit, they said, ‘Go away, bureaucrat! You’re not industry, you’re not the employer. You don’t really have anything to do with this,’” he recalled. “What I learned there, and what I’ve recommended to every other state who’s tried this, is let the employers carry your water. If they want it, they’ll get it done.”
Related: How one college is tackling the rural nursing shortage
Laney then talked to the Alabama Hospital Association and Alabama Nursing Home Association, to reach employers. Given the shortages they had been experiencing, they bought into the idea and approached the nursing board themselves. Next, Laney’s team got community colleges on board, then universities. With the assurance that apprenticeships wouldn’t cut down on any of the required classes and clinical hours, the nursing board agreed to create the new license, following legislative approval.
Other states embarking on nursing apprenticeships have faced similar challenges.
Apprenticeships aren’t a panacea. They hold promise for creating upward mobility, diversifying the profession and improving the odds a student makes it through to graduation, but they can’t solve all the knotty challenges of the nursing shortage. A lack of instructors in nursing schools — and therefore a lack of available seats for qualified students — is still one of the biggest factors. And in the apprenticeship model, every student needs one-on-one mentorship, meaning hospitals must have enough staff available and willing to work in a mentoring role for up to a year.
Jay Prosser, executive director of the Massachusetts Nursing Council on Workforce Sustainability, knows all that. But he thinks apprenticeships will bring in more “practice-ready” nurses who are more likely to stay in the field long-term, especially those who were already working in patient care in the United States or other countries. Massachusetts is on the cusp of starting a licensed practical nurse apprenticeship with one employer and one academic partner, after working with the state nursing board and colleges for the past year. Unlike in Alabama, the nursing board didn’t need to create a new license, but rather the board judges whether educational programs meet regulations or not.
The Massachusetts Nursing Council on Workforce Sustainability is also creating a nursing apprenticeship network in the state, to make it easier for different institutions and programs to exchange ideas.
Prosser said one of the biggest barriers was making sure that the scope of practice for apprentices was clearly defined. He worked with local colleges to make sure of this. Prosser had previously worked as an assistant chief nursing officer in Birmingham, Alabama, and moved to Massachusetts in 2021 with the idea of apprenticeships already in mind.
Several other states have also created nursing apprenticeships for students who don’t already have a degree, but they’re limited to single institutions. In 2023, Texas began offering nursing apprenticeships for students who hadn’t already earned a degree in a collaboration between South Texas College and the Texas Workforce Commission.
The University of Wisconsin Health system has created a portfolio of nine registered apprenticeship programs, including an RN program launched in 2023 and a handful of other apprenticeship-style programs. Bridgett Willey, director of allied health education and career pathways, said the hospital started with entry-level apprenticeships, like medical assistants, before proposing degreed programs.
“There’s still kind of a myth that the colleges are going to do all this on their own,” Willey said. “Well, that’s not true. Employers have to sponsor, because we’re the ones hiring the apprentices and often supporting tuition costs, as well.”
Related: No college degree, no problem? Not so fast
The outcomes from the entry-level apprentice programs helped convince the health system that it was worth investing more. A three-year study showed that staff retention rates for those who participated in the hospital’s apprenticeships were 22% higher than for those who didn’t. In the two-year-old RN program, attrition is less than 10% so far — significantly lower than the attrition rate the hospital has seen with traditional students who participate in clinicals at the hospital.
UW Health supports efforts to scale their apprenticeship model across the state, but so far they haven’t panned out. Willey said employers are interested, but conversations often stall when questions arise about how to create more clinical capacity and find funding sources to support apprentices.
Even so, Eric Dunker, founding executive director of the National Center for the Apprenticeship Degree, which is affiliated with Reach University, predicts that nursing apprenticeships are about to see major growth, as teaching apprenticeships did five years ago. Earlier this year, Reach University received a $1 million grant to expand apprenticeships in behavioral health, and is planning for nursing ones. The strict licensing regulations for nursing make it more complicated than scaling up teaching apprenticeships, but Dunker sees the possibility of expanding them if nursing boards, colleges and employers all come to the table, as they did in Alabama.
“There’s a lot of entry-level health care apprenticeships,” Dunker said. “But the key is upward mobility, which is nursing and nurse practitioners. There’s typically been a bottleneck in stacking these pathways, but that’s where you’re starting to see more states and systems become a little more creative.”
Tyler Sturdivant, Coastal Alabama Community College’s associate dean of nursing, knows what that looks like. Figuring out the logistics of setting up an apprenticeship program was a challenge, he said, and required hiring an additional staff member to liaise between the college and hospital partners. But three years into the apprenticeship program for LPNs and RNs, the school is seeing higher completion rates than for traditional students.
This means they’re producing more licensed nurses to fill positions and someday mentor, or even teach, other apprentices.
On a typical Friday morning in September at Mobile Infirmary, Malone and Berry visited a 70-year-old man who came in for a urinary tract infection that then weakened him. That day, the apprentice and journeyworker switched out his bed for one lower to the ground to reduce the fall risk, taught him how to raise the bed so he could sit upright, updated him on a plan for physical therapy and adjusted his socks for him.
Malone appeared comfortable and confident, taking the lead in the patient’s care while Berry assisted her. Malone says the many hours of practice she’s had through the apprenticeship has made her feel prepared for the job and ready to continue to follow her dreams. One day, she wants to become a nurse practitioner specializing in mental health.
“I won’t feel complete until I actually become a nurse,” Malone says. “I thought I was going to be one sooner, but bumps in the road happened and I ended up having a child. If it wasn’t for the apprenticeship, I probably wouldn’t be here now.”
Contact editor Lawrie Mifflin at 212-678-4078 or on email at [email protected].
This story was produced in partnership with Work Shift and reprinted with permission.