On Oct. 24, 1995, Duke University Press published my first book, The Myth of Political Correctness: The Conservative Attack on Higher Education. Looking back 30 years at my book, it can be dispiriting to see how everything today seems the same, only worse. “Political correctness” has been replaced by “woke” as the smear of the moment, but otherwise almost every word of my book could be republished today, with a thousand new examples to buttress every point.
Sometimes the title of the book confused people who mix up a “myth” with a “lie.” As I noted 10 years ago, “When I called political correctness a ‘myth,’ I was never denying the fact that some leftists are intolerant jerks, and sometimes their appalling calls for censorship are successful. My point was that even though political correctness exists, the ‘myth’ about it was the story that leftists controlled college campuses, imposing their evil whims like a ‘new McCarthyism’ or ‘China during the Cultural Revolution.’ In reality, then and now, the far greater threat to freedom on campus came from those on the right seeking to suppress opposing views.”
I had been inspired to write the book by Dinesh D’Souza; I reviewed his best-selling 1991 book, Illiberal Education, for my column in the Daily Illini at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. If D’Souza, a recent college graduate, could publish such a terrible book full of misinformation, then surely I could write a better book. So I did.
But the publishing market was much more interested in the endless parade of conservatives bemoaning the “PC police” and “tenured radicals” than a refutation of these flawed arguments. My book, which I started to write as a graduate student in the Committee on Social Thought at the University of Chicago (home to Saul Bellow, Allan Bloom and Edward Shils), was rejected by more than 50 publishers before I was able to persuade Stanley Fish (whom I had encountered as the editor of Democratic Culture, the newsletter of Gerald Graff and Gregory Jay’s Teachers for a Democratic Culture) to publish it at Duke. My editor (and now also an Inside Higher Ed columnist) was Rachel Toor, who helped to make some sense of my ideas.
In the end, my book failed to shift the debate about academic freedom—not because it was wrong or the facts were refuted, but because it was ignored. From my perspective, I was correct about everything and nobody learned anything from me. And I’ve been writing essentially the same thesis, over and over again, in a second book and essays and hundreds of blog posts.
Looking back at my first book, I think its claims have been proven largely correct over the past three decades (but I might be biased). At the core of the book were the chapters on the “Myth of PC” (examining how many of the leading anecdotes about repression often weren’t accurate) and “Conservative Correctness” (showing the many examples of repression from the right that were ignored by the media and campus critics of PC).
The remaining chapters also still seem on target: “The Cult of Western Culture” (why multiculturalism isn’t taking over colleges and silencing traditional works, and Shakespeare isn’t being banned); “The Myth of Speech Codes” (colleges have always had speech codes, often worse ones using the arbitrary authority of a dean, and what we need are codes that protect free speech); “The Myth of Sexual Correctness” (sexual assault is a serious problem, and feminists often face suppression); and “The Myth of Reverse Discrimination” (white men are not the victims of campus oppression and the “fairy tale of equal opportunity” is false)
Michael Hobbes did an excellent episode of You’re Wrong About in 2021 on political correctness that featured some of the ideas from my book. My position, then and now, is more nuanced than Hobbes’s view of PC as a pure right-wing moral panic. The panic was there, but so were real cases of repression—on both the left and the right.
The cartoonish right-wing belief that colleges had become Maoist institutions of oppression against conservatives prompted too many on the left (and the center) to counter that everything was fine on campus. In truth, free expression has been in serious danger, both against conservatives who were sometimes censored and against leftists who also faced repression. As bad as things seemed in 1995, the repression is far worse today and clearly aimed at the left—and yet the delusions about the PC police on campus are more widespread than ever.
Even in the face of the worst campus repression in American history, many conservatives continue to recite the old, tired myth of political correctness and leftist control of higher education—a myth repeated so often for so long has become a truth in the minds of many.
The worst strategic mistake progressives made in the past three decades was to abandon the cause of free speech. Too many leftists believed in the myth of political correctness; they heard the complaints about free speech and accepted the right-wing argument that only conservatives were being silenced and concluded that free speech was a right-wing plot. They imagined that tenured radicals controlled colleges because everybody said so, and so they clung to the delusion that they could support censorship and it wouldn’t be used against them.
When conservatives demanded free speech on campus, the left should have vigorously agreed and established strong protections for free expression on campus. Instead, they let the right win a propaganda war by pretending to be battling for free speech against the social justice warriors. And they lost the opportunity to make free speech a core principle established in higher education.
The war on political correctness succeeded because the enemies it targeted were weak, disorganized leftists who were not, in fact, plotting to destroy conservatives. By contrast, today the right wants to demolish higher education like it’s the East Wing of the White House, and it is willing to use its vast power to do that.
As bad as the skepticism on the left about free speech was, the right’s abandonment of free speech is much worse, both in the degree of rejection and in the impact it has on campuses. It didn’t matter if a leftist argued against free speech because they had essentially no power, on campus or off, to impose their ideas. They had no legislators joining their demands and no donors threatening to turn off the campus money spigot.
Critics of PC had many advantages on their side: Enormous money poured into building organizations and ideas that built the myth of PC, funding groups like the Federalist Society and the National Association of Scholars, and paying individual authors such as Bloom and D’Souza to write and publicize their books. A new media ecosystem of talk radio and the internet spread the myth of PC. And the war on PC recruited principled liberals and even progressives who objected to the excesses of the left.
It will be difficult for progressives to build anything similar. Wealthy donors tend to fund conservative groups, or prefer to put their names on fancy campus buildings. Universities are anxious to create free speech centers, but usually only the kind that conservatives support.
Few conservatives are willing to speak out against the Trump regime. And many centrists and liberals who have spent a generation obsessing about the PC police find it difficult to suddenly turn around and recognize the repression from the right that they’ve been ignoring for decades. A letter condemning the Trump administration’s compact signed by principled conservatives such as Robert George and Keith Whittington is a good start toward building an ideological coalition against right-wing censorship that matches what the right did against the “PC police.”
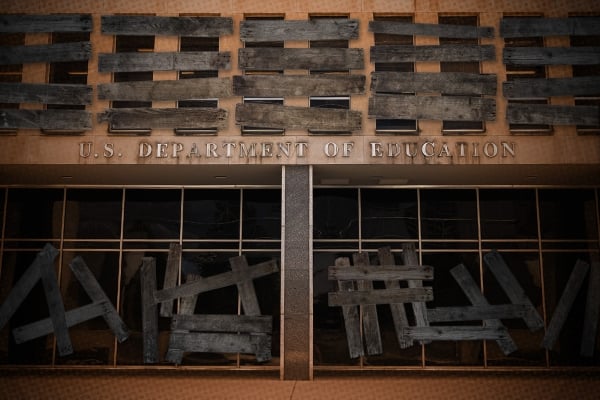
Today, we face the worst attack on academic freedom in American history, one that combines the overwhelming external power of state and federal governments, used for the first time to target free speech, and the internal power of a campus bureaucracy devoted to suppressing controversy.
Unlike political correctness—which often relied upon exaggerated accounts of dubious examples with marginal injustices—there are so many clear-cut cases of terrible repression and extreme violations of due process and academic freedom that it’s difficult for anyone to keep track of them all. The litigation strategy developed by the right of suing every censor is an important step. Telling and retelling the stories of campus censorship today is critical. So is organizing events, on and off campus, about the repression happening today, and challenging those on the right who defend their side’s censorship.
It’s not easy to find solutions when faced with this extraordinary censorship, with unprecedented dismissals and restrictions on speech. But the right-wing attack on political correctness, now over three decades old, offers liberals and progressives a guidebook for how to do it. Quote their words. Demand their reforms. Agree with them and confront their hypocrisy when they reject every free speech policy they’ve been demanding for the past three decades.
The myth of political correctness is still alive 30 years later, invoked to deny and justify the repression from the right. Understanding how the culture wars brought us to this point of authoritarianism is essential to leading us toward the goals of academic freedom and free expression on campus.