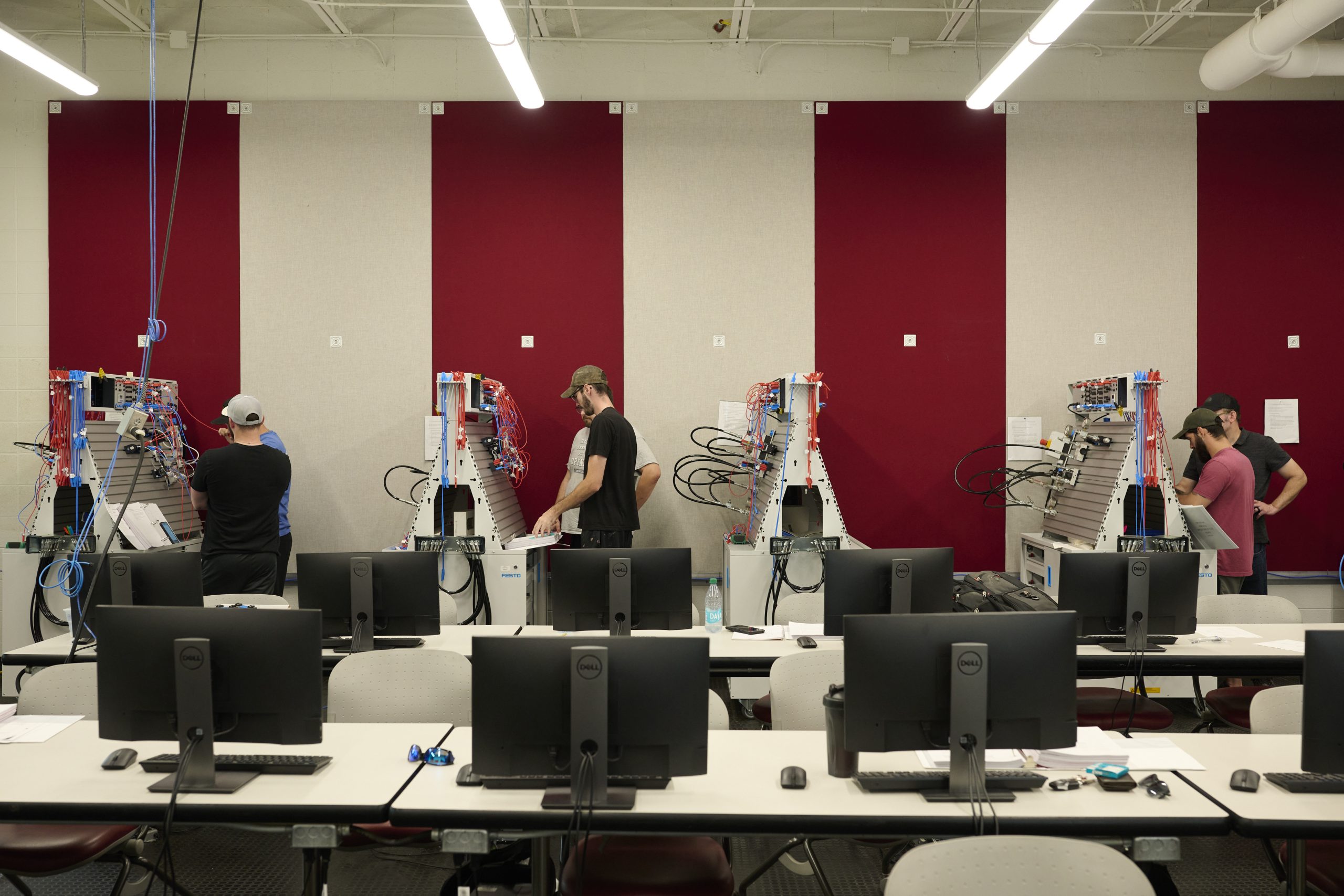
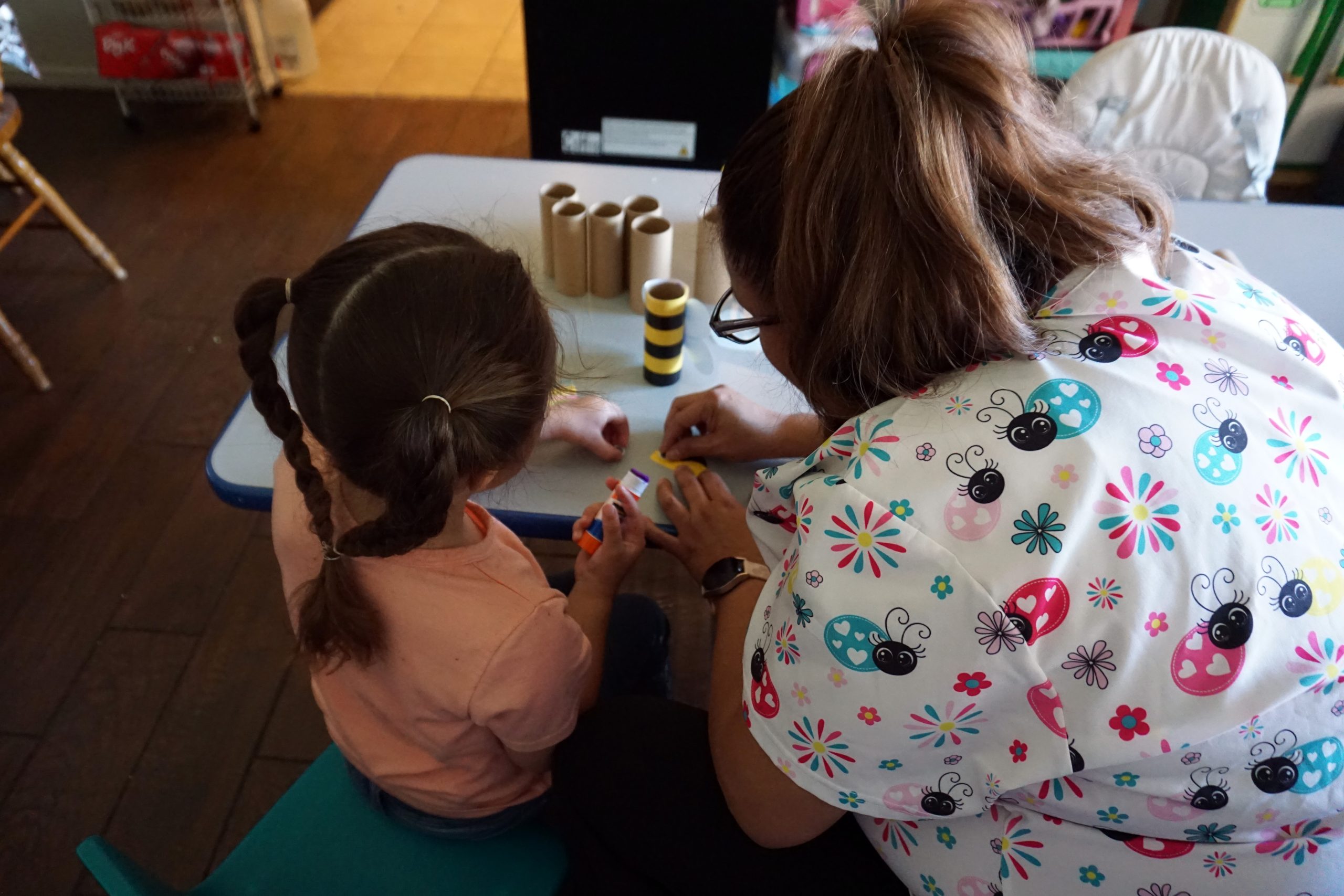
ELYRIA, Ohio — Nolan Norman had no idea what microelectronic manufacturing entailed when his adviser at Midview High suggested he take the school’s new class on it last year.
Yet once he started fusing metal to circuit boards, he says he was hooked. “When I was little, I thought that wizards made these things,” the 18-year-old joked of the electronics he’s now able to assemble. Despite long “hating” the idea of college, he was motivated to enroll in the microelectronic manufacturing bachelor’s degree program at nearby Lorain County Community College this fall. He’s spent the summer working in a job in the field that gives him both college credit and pays $18 an hour. Said Norman: “Now I’m seeing the path to get to be one of these wizards.”
Norman’s path wasn’t accidental: Two years ago, Lorain County Community College partnered with Midview High to create the course, one of several ways the college is trying to recruit and train more young people for jobs in manufacturing.
Nationally, more than 400,000 manufacturing jobs are going unfilled, many of them in advanced manufacturing, which requires the sort of high-tech skills and postsecondary credentials that Norman is working toward. President Donald Trump is leveraging tariffs in part, he has said, to grow manufacturing jobs in the United States, including those that involve machinery or robotics and training after high school.
Yet as it is, colleges have struggled to add and revise their training based on employer input and prepare students for tomorrow’s jobs, not just today’s. In the area surrounding Lorain County Community College, officials estimate that they’d have to teach four times the number of students to meet today’s unfilled manufacturing jobs.
Gogebic Community College, in rural Michigan, suspended its 22-year-old manufacturing technology program this spring because of low enrollment. “We could not get people into it,” registrar Karen Ball said, speaking in her personal capacity and not on behalf of the institution. “The needs in manufacturing are evolving so quickly, that to stay on top of it is too difficult.”
And then there is the history of manufacturing in communities like Norman’s, where so many factories moved to other countries in recent decades. The manufacturing workforce in the Great Lakes region shrunk by 35 percent between 2000 and 2010, a loss of 1.6 million jobs. But nationwide manufacturing has seen some recovery since then, rising from 11.5 million manufacturing jobs in 2010 to 12.9 million today, according to an analysis by the Economic Innovation Group.
“If your family experienced tumultuous layoffs in steel or automotives, they may see manufacturing as a risky pathway rather than a solid pathway,” said Marisa White, vice president for enrollment management and student services at Lorain County Community College. “Individuals are like, ‘I don’t want my kids to go into something like that.’”
Related: Interested in more news about colleges and universities? Subscribe to our free biweekly higher education newsletter.
White and other Lorain officials, though, have been slowly making strides in adding more students in recent years — and in trying to keep up with the needs of companies.
In addition to partnering with Midview High, staff from the college set up tables at food banks and Boys and Girls Clubs where they answer questions about its manufacturing degree and certificate programs, and even partner with a nearby manufacturing nonprofit that uses holograms and a robot dog to get the attention of high school students. That is paying off, officials say. The college now produces 120 graduates each year in advanced manufacturing — a category that includes industrial engineering tech, mechanical engineering tech, welding, automation and microelectronics — compared to 43, a decade ago.
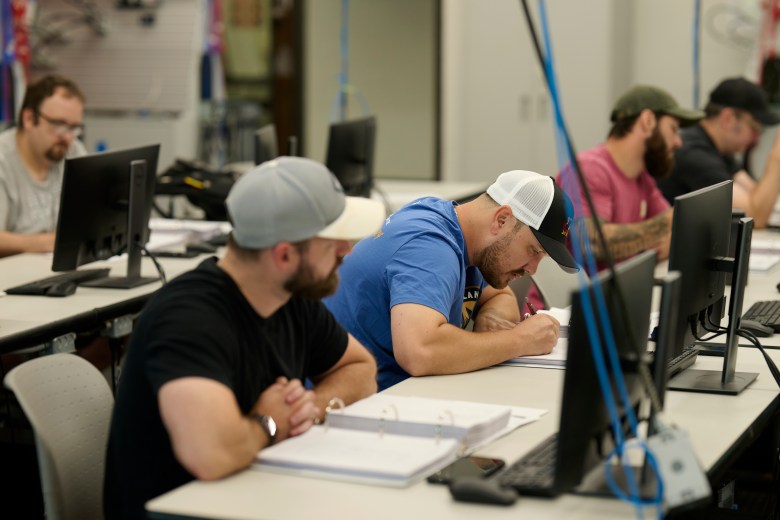
It has also cultivated a large network of local employers and a system to do market research before launching certificate programs. In some cases, it partners with companies that pay for employees to get training at Lorain college. In a classroom on a recent Wednesday, one of those electrician apprentices, Tyler Tector, 25, had rigged a series of plastic tubes to a small air pump. He hoped it would generate enough suction to keep its grip on his lab partner’s smartphone, which dangled precariously in the air (and already had a cracked screen from some previous misadventure).
The assignment was part of a class in practical applications of fluid power. Tector’s employer, Ford Motor Co., was sending him and a small group of other apprentice electricians to take this class once a week, so they could better work with the growing number of robots at the local engine plant.
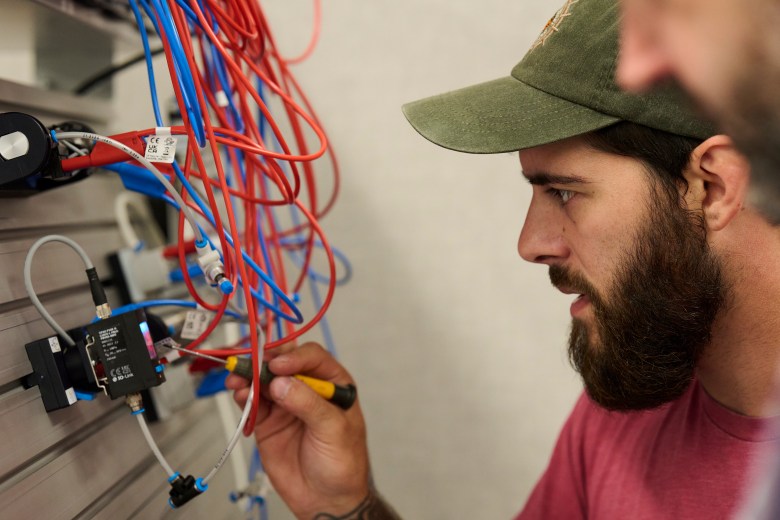

“Robots are the best co-workers,” joked Tector, who added that he’s not worried about bots putting him out of a job because so many humans are needed to fix them. “They do exactly what you tell them to do. They don’t ask questions. They don’t yell and complain.” They are finicky though, he added. If anything in a robot’s area gets bumped out of place even a fraction of an inch, that could throw the machine off and require reprogramming.
So many employers told college officials they need technicians with basic knowledge across a range of trades that the college is starting a new associate degree program in the fall called Multicraft Industrial Maintenance that will include lessons like the one Tector is doing but in a condensed format.
“Because of the high-tech nature of things, employers don’t want students siloed into trades anymore,” said Brian Iselin, an assistant professor in manufacturing who is leading the effort.
Johnny Vanderford, who leads the college’s microelectronic manufacturing degree program, often spends part of his lunch break scouring LinkedIn for the latest job postings by local employers to see what skills they are looking for. His program’s model involves finding every student a paid internship, and students can take classes two days a week or in the evening to have the rest of the time free for paid work in the field.
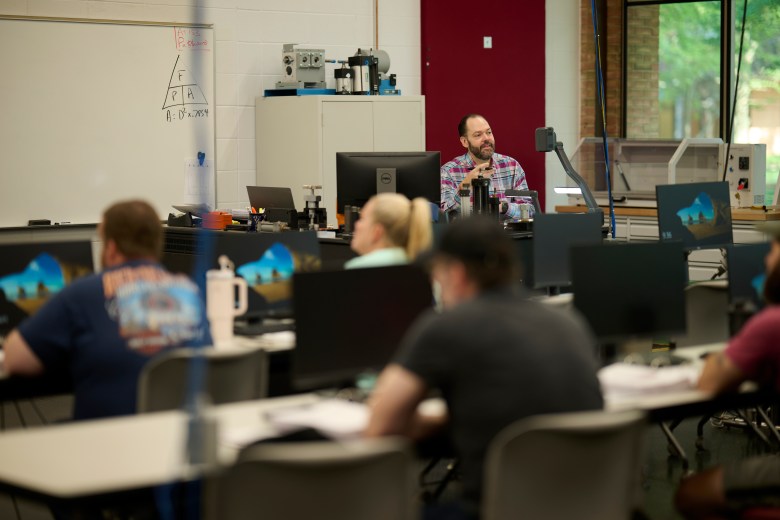

Vanderford pointed to a PowerPoint slide showing more than 90 manufacturing companies in the area he said the college has worked with: “We basically tailor our curriculum to meet their workforce needs.” In some cases that means wedging into a class syllabus training on some specialized machine that might be used at only a handful of employers.
Rather than simply having advisory committees with a few large companies that meet occasionally, today Lorain and many other colleges follow a model that involves frequent discussions with company leaders, instructors directly participating in those meetings and a greater focus on the skills employers need.
“Those relationships take time,” said Shalin Jyotishi, managing director of the Future of Work and Innovation Economy Initiative at the think tank New America. He says that it is hard for other community colleges to replicate best practices from Lorain because they are labor-intensive to enact.
Employers also have a tendency to change their plans. For instance, when Tesla pledged to build an electrical vehicle plant in Flint, Michigan, the local Mott Community College started an EV program, said Jyotishi. But the plant never came. “The college still has a Tesla sign,” he said.
Related: After its college closes, a rural community fights to keep a path to education open
The numbers no longer add up at Gogebic Community College, in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula.
When the college suspended its program in manufacturing technology in May, it had just three students.
As with many programs at the college, a single employee was charged with administering and teaching. Doing all that plus staying on top of nearby companies’ workforce needs was “unsustainable,” said Ball, the registrar.
The few small manufacturers in the area all say they have different needs, rather than one clear set of skills, she said, noting that “you can’t be a generalist in manufacturing.” Even when the college does identify a needed skill to teach, it takes at least six months to a year to get the program approved by college leaders and the accreditor. By then, companies might need something different.
And the pay offered by small manufacturers is often low, despite an expectation of training beyond a high school diploma, said Ball.

Nationwide, automation has reduced the earning power for many manufacturing jobs, said Jyotishi of New America. “For a long time manufacturing was the bedrock of the middle class,” said Jyotishi. “That wage premium for manufacturing has actually gone away.”
And there’s a danger that as colleges aim to please employers, they will create programs that are too narrow, argues Davis Jenkins, senior research scholar at Columbia University’s Community College Research Center. (Editor’s note: The Hechinger Report, which produced this story, is an independent unit of Columbia’s Teachers College.) “You don’t want specific skills training — you don’t want to just train students to work in a fab,” he said, referring to a facility where microchips and other electronics are produced. “Whenever schools buy a lot of specific equipment for training, I worry a lot. What students really need are broader skills.”
Even Lorain doesn’t always find the right fit. During the pandemic, the college started what it calls fast-track programs, which typically run 16 weeks, across a range of professional fields (not just manufacturing). But because of mixed success attracting students, officials recently slimmed the list from 60 to 13, said Tracy Green, vice president of strategic and institutional development at Lorain County Community College. And the college recently started winding down a program in industrial safety because of a lack of student interest, even though there are still a large number of job postings by local companies for jobs with those skills, said Iselin.
One provision in Trump’s new “one big, beautiful bill” promises a boost to manufacturing education, however. For the first time, the law will allow low-income students to use federal Pell Grants for short-term certificate programs, in what is known as Workforce Pell. It’s a change many community college leaders have been calling for for years as they have created more short-term programs in response to demand by students and employers who want to quickly gain new skills in fast-changing areas, including manufacturing. But that program won’t be up and running until the 2026-27 academic year.
The promise of a big new employer moving to town can galvanize student interest in manufacturing.
In Ohio, the talk for years has been a $28 billion Intel chip manufacturing plant under construction in Columbus. The facility is expected to bring some 3,000 jobs to the area, and the company has committed $50 million to workforce education in the state, including $2 million to Lorain County Community College, which it used to buy new classroom equipment, support student scholarships, and pay for program development and instructor training.

The top graduates in Lorain County Community College’s microelectronic manufacturing program each year typically get internships at Intel’s closest existing plant, which is in Chandler, Arizona, a suburb of Phoenix. It’s a motivator to work hard in their classes, some students say.
Lia Douglas, a student in the microelectronic manufacturing program at Lorain, scored one of those slots and headed to Arizona last summer. The experience, though, was sobering.
“My plan really was to make a good impression with my internship, get a job maybe in Arizona even if it was for a year or two, and then try to move back to Ohio when they have an Ohio plant,” she said.
But one day last July, all the employees were unexpectedly summoned to an all-hands call where the company announced a wave of layoffs and reductions in some benefits that had interested Douglas, including a sabbatical program. This year, Intel announced that the opening of the Ohio plant has been delayed until 2030.
“I learned I had a little too much faith in a company and the promises of a company,” she said. “And it reminded me that at the end of the day, the company has to make money.”
She’s still glad she chose Lorain’s program, which has landed her several local internships and opened her eyes to the many small and mid-sized manufacturers in the area.
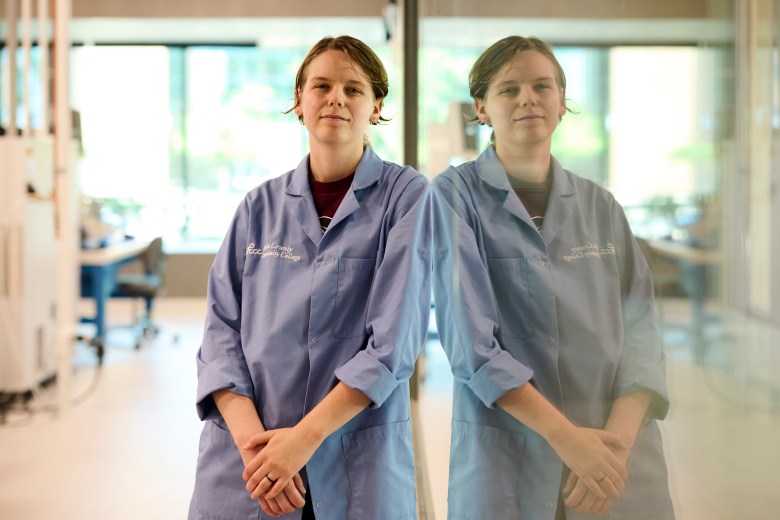

And she has been hooked on a career in making things ever since she was in middle school and a family friend taught her a bit of welding. Her hero was Adam Savage, co-host of the TV show “MythBusters,” who she even got to meet at a comic book convention in Cleveland.
Douglas complains that students are told in high school that they either have to choose a trade for hands-on work or an academic track to prepare for a career behind a desk that might involve design and project management. She says that as manufacturing changes, there’s plenty of room to do both. In fact, she says, when a group of doctoral students from Kent State University recently visited the college’s clean room, she was amused to see them struggle with some of the tools the students routinely use in the microelectronic manufacturing program.
“It takes as much brainpower to figure out what is the right tool for the right process as getting a Ph.D.,” she said.
Contact editor Caroline Preston at 212-870-8965, via Signal at CarolineP.83 or on email at [email protected].
This story about manufacturing jobs was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.