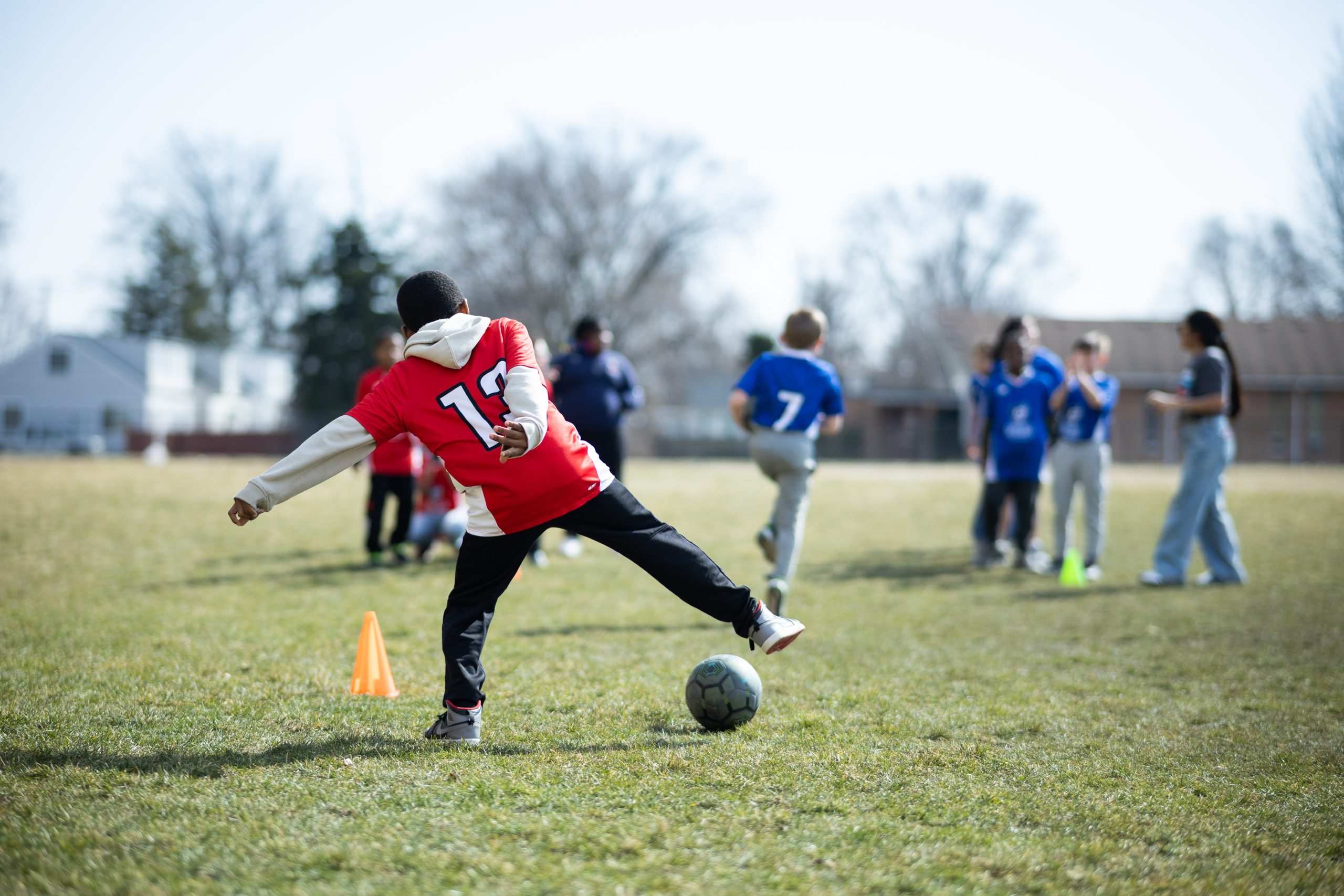
CLEVELAND — In a public school cafeteria here, 6- and 7-year olds were taking turns sketching their ideas for a building made of toothpicks and gummy bears. Their task: to design a structure strong enough to support a single subject notebook.
It was a challenge meant to test their abilities to plan ahead, work as a team and overcome setbacks. But first, they had to resist the urge to eat the building materials.
Zayden Barnes, a first grader at Clara E. Westropp School of the Arts, picked up a blue gummy bear and sniffed it. “That smells good,” he said, licking his lips.
Mia Navarro, another first grader, held a green gummy bear to her nose and inhaled deeply. “I can’t stop smelling them!” she exclaimed. “I just want to eat it, but I can’t!”
The lesson in engineering and self-control was part of an after-school program run by the nonprofit Horizon Education Centers. It’s one of a dwindling number of after-school options in a city with one of the highest child poverty rates of any large urban area in the country.
Last year, Horizon and other nonprofit after-school providers reached more than 7,000 students in Cleveland public schools, buoyed by $17 million in pandemic recovery aid. But when the money ran out at the end of that school year, nonprofits here had to drop sites, shed staff and shrink enrollment. Horizon, which was in five public schools last year, is now in just one.
Similar setbacks can be seen across the country, as after-school programs struggle to replace billions in federal relief money. While a few states are helping to fill the gap, Ohio isn’t among them. And many providers fear more cuts are coming, as the Trump administration continues its campaign to slash government spending and end “equity-related” grants and contracts.
The after-school sector plays a critical role in the nation’s economy, providing close to 8 million students, or nearly 14 percent of all school-aged children, with a safe place to go while their parents work. It offers homework help, enriching activities, healthy snacks and physical exercise — often for a fee, but sometimes for free.
Related: A lot goes on in classrooms from kindergarten to high school. Keep up with our free weekly newsletter on K-12 education.
Done well, after-school programs can strengthen students’ social and emotional skills, increase their engagement with and attendance in school, and reduce their risk of substance abuse or criminal activity. In some cases, they can help improve grades and test scores, too.
Yet the sector, which has existed for more than 100 years, has long been hobbled by inadequate funding, staffing shortages and uneven quality. There are long waitlists for many programs, and low-income families often struggle to find affordable options.
In a recent survey by the nonprofit Afterschool Alliance, more than 80 percent of program leaders said they were concerned about their program’s future, and more than 40 percent said they worried they’d have to close permanently.
“The state of afterschool in America feels very grim,” said Alison Black, executive director of the Cleveland affiliate of America Scores, a nonprofit that teaches soccer and poetry to students in 13 cities across North America.
After-school programs emerged in the second half of the 19th century, in philanthropic settlement houses that provided English courses and health care to the children of immigrants, according to a Rand Corporation report. They multiplied after Congress passed child labor laws in the 1930s, and again during World War II, when women entered the workforce in large numbers.
In those early days, the programs functioned mostly as child care, offering a solution to the problem of the “latchkey kid.” But they began to take on a broader role in the 1960s, when the programs started to be seen as a way to both reduce youth crime and provide kids with positive role models, according to Rand.
In the 1980s and 1990s, policymakers and funders began demanding that after-school programs play a part in closing the academic gaps between wealthier and poorer kids. High-poverty schools began setting aside some of their Title I funds to provide after-school programs.
But it wasn’t until 1998 that the federal government offered targeted support to after-school programs, in the form of competitive grants awarded by the states through the newly created 21st Century Community Learning Centers Program. The first year, Congress appropriated $40 million for the program; by 2002, that number had swelled to $1 billion.
Today, the after-school sector is made up of a mix of programs providing academic support, enrichment (sports, theater and the like) or some combination. Their goals and funding streams vary, from public dollars to philanthropic and corporate gifts. Many survive by stitching together multiple sources of funding.
The 21st Century program remains the only dedicated federal funding stream for after-school and summer learning, providing $1.3 billion in support to 10,000 centers serving close to a fifth of students in 2023.
After-school programs are popular among parents, and demand for slots far exceeds the supply. For every child in an after-school program, there are three more who would participate if an affordable, accessible option was available to their families, according to surveys by the Afterschool Alliance.
Gina Warner, CEO of the National Afterschool Association, says afterschool is a space where kids can try new things and take risks they wouldn’t take at school, where the stakes are higher. “Afterschool is still a place where kids can fail” without consequence, she said.
The programs also connect students with positive adult role models who aren’t their teachers or caregivers, said Jodi Grant, executive director of the Afterschool Alliance. “Our biggest strength, when it gets down to it, is relationships,” Grant said.
But sustaining those connections can be difficult in a sector with low pay and limited opportunities for advancement. Turnover rates are high, and when staff don’t stick around, “You’re missing one of the best benefits of afterschool,” said Warner.

For a sector accustomed to scraping by, the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 was like a winning lottery ticket.
Over three years, after-school programs received roughly $10 billion in ARPA aid — money they used to add staff, improve pay and benefits and expand enrollment, according to the Afterschool Alliance. It estimates that programs were able to serve 5 million more kids as a result.
But the money has mostly been spent, and late last month, Education Secretary Linda McMahon told districts that their time to use any remaining funds was over. In Cleveland, which spent almost $28 million on out-of-school time programs between fiscal 2022 and 2024, Horizon and other nonprofits formed a coalition to try to convince the district to continue at least a portion of the aid. They held rallies, secured media coverage and brought parents to testify before the school board. But the district wouldn’t budge, said David Smith, Horizon’s executive director.
“There’s no opportunity to go back to the scale we were at during the pandemic, and we still have the same problems,” said Smith. “Kids are getting in trouble after school, and they still need the extra academic help.”
The Cleveland Metropolitan School District made significant gains under its last CEO, Eric Gordon, whose Cleveland Plan was credited with improved student outcomes, including a 25 percentage point increase in the high school graduation rate. But the pandemic erased some of those gains and Cleveland, like many districts, is still recovering.
Related: $1.5 billion in recovery funds goes to afterschool
The district’s new CEO, Warren Morgan, has defended his decision not to fund the nonprofit providers, noting that the district offers after-school sports and an arts program. But those extracurriculars vary by day and by school, and after-school advocates say many schools have been left without the consistent, comprehensive care working parents depend on.
“Our city is focused on workforce development without thinking about who cutting this care hurts,” said Black, of America Scores Cleveland.
Without continued support from the district, Black’s organization has had to dip into its rainy-day fund and drop fall soccer for middle schoolers. Serving elementary students feels more essential, she explained, since younger kids can’t stay home alone.
Other nonprofits have been harder hit. The Greater Cleveland Neighborhood Centers Association, or NCA, has closed half of its locations in the district, leaving programs in seven schools. The Boys and Girls Clubs of Northeast Ohio, which lost $3 million in pandemic relief dollars and other federal support this academic year, has shuttered 17 sites.
Dorothy Moulthrop, chief executive officer of Open Doors Academy, another nonprofit, thinks the losses might have been less severe if the after-school coalition had been able to show strong results for the federal money. Though individual programs handed over reams of data to the district, Moulthrop wasn’t able to get its leaders to share the data in a form that would allow providers to study their collective impact.
“We needed to be able to demonstrate our return on investment and we were not able to,” she said.

Questions about whether after-school programs are a good investment of public dollars have dogged the sector since the early 2000s, when Mathematica Policy Research began publishing the results of an evaluation that found the 21st Century program had little impact on student outcomes.
The study, which is often cited by politicians seeking to gut after-school spending, was controversial at the time, and remains so. Defenders of afterschool argue the evaluation was methodologically flawed and point to other research that found that students who regularly attended high-quality programs saw significant gains. But one of the study’s two authors, Susanne James-Burdumy, said in an interview that it was the most rigorous of its time.
In the 20 years since the Mathematica reports were published, hundreds of dissertations and program evaluations have added to the evidence base for both sides of the debate. But large-scale, rigorous evaluations of after-school programs remain rare, and their findings are mixed, James-Burdumy and other researchers say.
Though some analyses have found after-school programs can boost reading and math achievement, promote positive social behaviors and reduce negative ones, other studies have shown little growth in those and other areas.
Some of that inconsistency likely stems from differences in the quality of programs, researchers and advocates say. When funding is tight, after-school programs tend to focus their dollars on services, rather than professional development or program evaluation.
“Quality often feels like an extra,” said Jessie Kerr-Vanderslice, a consultant at the American Institutes for Research who focuses on out-of-school time programs.
Related: Tracking Trump: His actions to abolish the Education Department, and more
Advocates also note a misalignment between program goals and outcome measures: While after-school programs often prioritize relationships and social and emotional skill-building, their funders frequently focus on academic gains.
One variable that seems to matter in student outcomes is attendance: Studies have found that students who attend regularly reap greater benefits than those who show up sporadically.
Yet more than half of students who participated in programs paid for with 21st Century grants in 2022-23 attended for less than 90 hours, a program evaluation shows. That works out to just 30 days for a three-hour program.
At Clara E. Westropp Elementary in Cleveland, where Horizon Education Centers has been able to continue its after-school program with a 21st Century grant, 73 students are enrolled, but average daily attendance is less than half that.

On the other side of Lake Erie, at Detroit’s Downtown Boxing Gym, students are required to attend at least three days a week. To keep them coming, the program offers a huge range of activities, from cooking to coding (but ironically, not boxing).
Inside the large building that houses the program, there’s a lab with a flight simulator and 3D printer, and a music studio paid for and built by one of Eminem’s former producers.
Outside, on a turf field where the program plans to build an addition that will enable it to double enrollment, a group of middle school majorettes was preparing for an upcoming dance performance.
Debra Beal, who became the caregiver to her niece’s two young sons when she was in her 50s, says the program saved her life — and theirs. It kept the boys, now 19 and 20, off the streets while she worked, provided them with exercise and tutoring, and even served them dinner. The staff became like family, supporting her when she struggled as a parent and offering to pay for counseling when one son lost his father and uncle from fentanyl overdoses on the same day.
“What they’re doing is life-changing,” said Beal, whose long denim coat had the word “Blessed” written in sequins on the back.
Financially, the Downtown Boxing Gym is on surer footing than its counterparts in Cleveland. The Michigan Legislature has provided $50 million in funding for after-school programs in each of the last two years, and the program recently received $3 million in funds from the state.
That doesn’t mean the program isn’t being pinched by the Trump administration’s cost-cutting campaign and purge of diversity, equity and inclusion programs, said Jessica Hauser, its executive director. Corporations the program was counting on for seven-figure gifts for the addition and program expansion are reconsidering their pledges, and a promised federal earmark now seems unlikely.
Hauser is also worried about potential cuts to federal child nutrition programs and student aid, which the program depends on for meals and college student tutors.
Back in Cleveland, the coalition Smith formed to fight for after-school funding has expanded to include the city, the county and a local foundation, which hired a consultant to come up with the cost to deliver quality after-school programming. To longtime advocates like Smith and Allison Wallace, executive director of the NCA, it feels like the sector is having to prove itself, yet again.
“They’re revisiting conversations we had 15 years ago, around best practices and identifying quality,” Wallace said. “We keep going over the same things, and we’re not getting any traction.”
Things could get even tougher in the next couple years, as the district shifts the costs of providing security and custodial services for after-school programs onto the nonprofit providers. Wallace estimates that the change will cost providers tens of thousands per site.
And future federal funding is far from guaranteed. Though the 21st Century program enjoys bipartisan support in Congress, Trump sought to eliminate it in every budget proposal he issued in his first term and is expected to do so again.
For now, though, after-school programs are still providing kids in Cleveland with caring staff, a safe place to spend the hours after school, and engaging activities like gummy bear construction.
Related: After-school programs have either been abandoned or overworked
The teams had 10 minutes to build structures that could support a notebook. When the timer went off, the structure built by Zayden and Mia’s group resembled a two-story house with a caved-in roof. Zayden wasn’t feeling optimistic.
“I think it’s going to fall,” he said.
“Think positive,” said Kathy Thome, a program administrator who is helping the group.
Ian Welch, the program’s site coordinator for Clara E. Westropp, picked up a notebook and approached the table. He reminded the teams that failure is part of the scientific method. If their structures collapse, they can try again, he said.
“It’s going to squish down,” Mia predicted.
She was right. But the flattened structure still held the notebook aloft. The kids jumped up and down, and Zayden did a little boogie.
“We’re so happy — we did it!” he said.
Welch rewarded their effort with some fresh gummy bears, and the kids, proud and hopped up on sugar, waited for their parents to pick them up.
Contact editor Caroline Preston at 212-870-8965, on Signal at CarolineP.83 or via email at [email protected].
This story was produced with support from the Education Writers Association Reporting Fellowship program.
This story about afterschool was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.