by Bianca Vázquez Toness, The Hechinger Report
November 18, 2025
This story was produced by the Associated Press and reprinted with permission.
ATLANTA — It was the worst summer in years. Sechita McNair’s family took no vacations. Her younger boys didn’t go to camp. Her van was repossessed, and her family nearly got evicted — again.
But she accomplished the one thing she wanted most. A few weeks before school started, McNair, an out-of-work film industry veteran barely getting by driving for Uber, signed a lease in the right Atlanta neighborhood so her eldest son could stay at his high school.
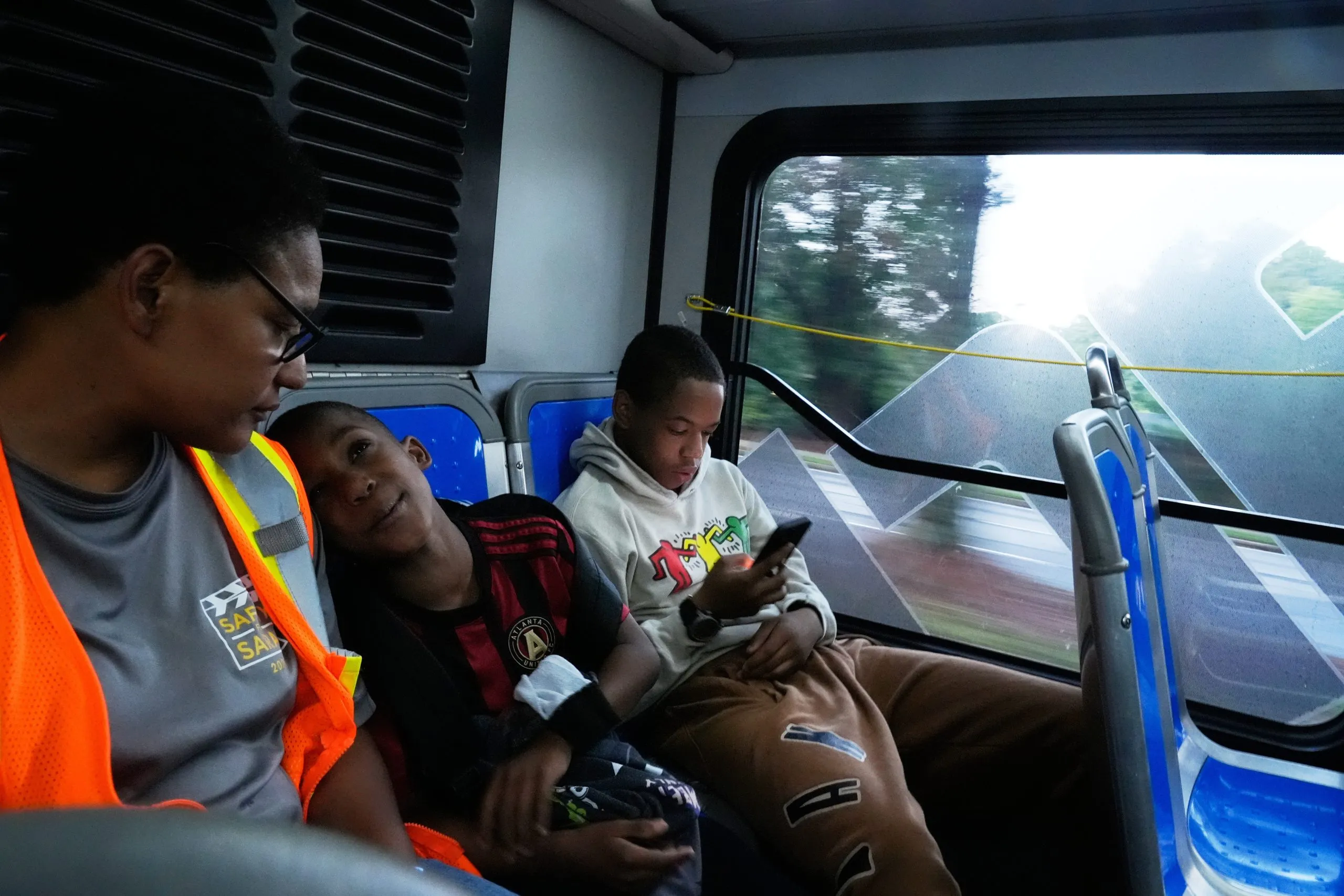
As she pulled up outside the school on the first day, Elias, 15, stepped onto the curb in his new basketball shoes and cargo pants. She inspected his face, noticed wax in his ears and grabbed a package of baby wipes from her rental car. She wasn’t about to let her eldest, with his young Denzel Washington looks, go to school looking “gross.”
He grimaced and broke away.
“No kiss? No hugs?” she called out.
Elias waved and kept walking. Just ahead of him, at least for the moment, sat something his mother had fought relentlessly for: a better education.
The link between where you live and where you learn
Last year, McNair and her three kids were evicted from their beloved apartment in the rapidly gentrifying Old Fourth Ward neighborhood of Atlanta. Like many evicted families, they went from living in a school district that spends more money on students to one that spends less.
Thanks to federal laws protecting homeless and evicted students, her kids were able to keep attending their Atlanta schools, even though the only housing available to them was in another county 40 minutes away. They also had the right to free transportation to those schools, but McNair says the district didn’t tell her about that until the school year ended. Their eligibility to remain in those schools expired at the end of last school year.
Still wounded by the death of his father and multiple housing displacements, Elias failed two classes last year, his freshman year. Switching schools now, McNair fears, would jeopardize any chance he has of recovering his academic life. “I need this child to be stable,” she says.
Related: Become a lifelong learner. Subscribe to our free weekly newsletter featuring the most important stories in education.
With just one week before school started, McNair drove extra Uber hours, borrowed money, secured rental assistance and ignored concerns about the apartment to rent a three-bedroom in the Old Fourth Ward. At $2,200 a month, it was the only “semi-affordable” apartment in the rapidly gentrifying ward that would rent to a single mom with a fresh eviction on her record.
On Zillow, the second-floor apartment, built in 2005, looked like a middle-class dream with its granite countertops, crown molding and polished wood floors. But up close, the apartment looked abused and held secrets McNair was only beginning to uncover.
The first sign something was wrong came early. When she first toured the apartment, it felt rushed, like the agent didn’t want her to look too closely. Then, even as they told her she was accepted, the landlord and real estate agent wouldn’t send her a “welcome letter” laying out the agreement, the rent and deposit she would pay. It seemed like they didn’t want to put anything in writing.
When the lease came, it was full of errors. She signed it anyway. “We’re back in the neighborhood!” she said. Elias could return to Midtown High School.
But even in their triumph, no one in the family could relax. Too many things were uncertain. And it fell to McNair — and only McNair — to figure it out.
The first day back
Midtown is a high school so coveted that school administrators investigate student residency throughout the year to keep out kids from other parts of Atlanta and beyond. For McNair, the day Elias returned to the high school was a momentous one.
“Freedom!” McNair declared after Elias disappeared into the building. Without child care over the summer, McNair had struggled to find time to work enough to make ends meet. Now that the kids were back in class, McNair could spend school hours making money and resolving some of the unsettled issues with her new apartment.
McNair, the first person in her family to attend college, studied theater management. Her job rigging stage sets was lucrative until the writers’ and actors’ strike and other changes paralyzed the film industry in 2023. The scarcity of work on movie sets, combined with her tendency to take in family and non-family alike, wrecked her home economy.
The family was evicted last fall when McNair fell behind on rent because of funeral expenses for her foster daughter. The teen girl died from an epileptic seizure while McNair and everyone else slept. Elias found her body.
McNair attributes some of Elias’s lack of motivation at school to personal trauma. His father died after a heart attack in 2023, on the sidelines of Elias’s basketball practice.
On his first day back at school this August, Elias appeared excited but tentative. He watched as the seniors swanned into school wearing gold cardboard crowns, a Midtown back-to-school tradition, and scanned the sidewalk for anyone familiar.
If Elias had his way, his mom would homeschool him. She’s done it before. But now that he’s a teenager, it’s harder to get Elias to follow her instructions. As the only breadwinner supporting three kids and her disabled uncle, she has to work.
Elias hid from the crowds and called up a friend: “Where you at?” The friend, another sophomore, was still en route. Over the phone, they compared outfits, traded gossip about who got a new hairdo or transferred. When Elias’s friend declared this would be the year he’d get a girlfriend, Elias laughed.
When it was time to go in, Elias drifted toward the door with his head down as other students flooded past.
The after-school pickup
Hours later, he emerged. Despite everything McNair had done to help it go well — securing the apartment, even spending hundreds of dollars on new clothes for him — Elias slumped into the backseat when she picked him up after class.
“School was so boring,” he said.
“What happened?” McNair asked.
“Nothing, bro. That was the problem,” Elias said. “I thought I was going to be happy when school started, since summer was so horrible.”
Of all of the classes he was taking — geometry, gym, French, world history, environmental science — only gym interested him. He wished he could take art classes, he said. Elias has acted in some commercials and television programs, but chose a science and math concentration, hoping to study finance someday.
After dinner at Chick-fil-A, the family visited the city library one block from their new apartment. While McNair spoke to the librarian, the boys explored the children’s section. Malachi, 6, watched a YouTube video on a library computer while Derrick, 7, flipped through a book. Elias sat in a corner, sharing video gaming tips with a stranger he met online.
Related: Schools confront a new reality: They can’t count on federal money
“Those people are learning Japanese,” said McNair, pointing to a group of adults sitting around a cluster of tables. “And this library lets you check out museum passes. This is why we have to be back in the city. Resources!”
McNair wants her children to go to well-resourced schools. Atlanta spends nearly $20,000 per student a year, $7,000 more than the district they moved to after the eviction. More money in schools means smaller classrooms and more psychologists, guidance counselors and other support.
But McNair, who grew up in New Jersey near New York City, also sees opportunities in the wider city of Atlanta. She wants to use its libraries, e-scooters, bike paths, hospitals, rental assistance agencies, Buy Nothing groups and food pantries.
“These are all resources that make it possible to raise a family when you don’t have support,” she said. “Wouldn’t anyone want that?”
Support is hard to come by
On the way home, the little boys fall asleep in the back seat. Elias asks, “So, is homeschooling off the table?”
McNair doesn’t hesitate. “Heck yeah. I’m not homeschooling you,” she says lightly. “Do you see how much of a financial bind I’m in?”’
McNair pulls into the driveway in Jonesboro, the suburb where the family landed after their eviction. Even though the family wants to live in Atlanta, their stuff is still here. It’s a neighborhood of brick colonials and manicured lawns. She realizes it’s the dream for some families, but not hers. “It’s a support desert.”
As they get out of the car, Elias takes over as parent-in-charge. “Get all of your things,” he directs Malachi and Derrick, who scowl as Elias seems to relish bossing them around. “Pick up your car seats, your food, those markers. I don’t want to see anything left behind.” Elias would be responsible for making the boys burritos, showering them and putting them to sleep.
McNair heads out to drive for Uber. That’s what is necessary to pay $450 a week to rent the car and earn enough to pay her rent and bills.
But while McNair is out, she can’t monitor Elias. And a few days after he starts school, Elias’s all-night gaming habit has already drawn teachers’ attention.
“I wanted to check in regarding Elias,” his geometry teacher writes during the first week of school. “He fell asleep multiple times during Geometry class this morning.”
Elias had told the teacher he went to bed around 4 a.m. the night before. “I understand that there may be various reasons for this, and I’d love to work together to support Elias so he can stay focused and successful in class.”
A few days later, McNair gets a similar email from his French teacher.
That night, McNair drives around Atlanta, trying to pick up enough Uber trips to keep her account active. But she can’t stop thinking about the emails. “I should be home making sure Elias gets to bed on time,” she says, crying. “But I have to work. I’m the only one paying the bills.”
Obstacles keep popping up
Ever since McNair rented the Atlanta apartment, her bills had doubled. She wasn’t sure when she’d feel safe giving up the house she’d been renting in Clayton County, given the problems with the Atlanta apartment. For starters, she was not even sure it was safe to spend the night there.
A week after school started in August, McNair dropped by the apartment to check whether the landlords had made repairs. At the very least, she wanted more smoke detectors.
She also wanted them to replace the door, which looked like someone had forced it open with a crowbar. She wanted a working fridge and oven. She wanted them to secure the back door to the adjoining empty apartment, which appeared to be open and made her wonder if there were pests or even people squatting there.
But on this day, her keys didn’t work.
She called 911. Had her new landlords deliberately locked her out?
When the police showed up outside the olive-green, Craftsman-style fourplex, McNair scrolled through her phone to find a copy of her lease. Then McNair and the officer eyed a man walking up to the property. “The building was sold in a short sale two weeks ago,” he told McNair. The police officer directed the man to give the new keys to McNair.
Related: The new reality with universal school vouchers: Homeschoolers, marketing, pupil churn
The next day, McNair started getting emails from an agent specializing in foreclosures, suggesting the new owners wanted McNair to leave. “The bank owns the property and now you are no longer a tenant of the previous owner,” she wrote. The new owner “might” offer relocation assistance if McNair agreed to leave.
McNair consulted attorneys, who reassured her: It might be uncomfortable, but she could stay. She needed to try to pay rent, even if the new owner didn’t accept it.
So McNair messaged the agent, asking where she should send the rent, and requested the company make necessary repairs. Eventually, the real estate agent stopped responding.
Some problems go away, but others emerge
Finally, McNair moved her kids and a few items from the Jonesboro house to the Atlanta apartment. She didn’t allow Elias to bring his video game console to Atlanta. He started going to bed around 11 p.m. most nights. But even as she solved that problem, others emerged.
It was at Midtown’s back-to-school night in September that McNair learned Elias was behind in most of his classes. Some teachers said maybe Midtown wasn’t the right school for Elias.
Perhaps they were right, McNair thought. She’d heard similar things before.
Elias also didn’t want to go to school. He skipped one day, then another. McNair panicked. In Georgia, parents can be sent to jail for truancy when their kids miss five unexcused days.
McNair started looking into a homeschooling program run by a mother she follows on Facebook. In the meantime, she emailed and called some Midtown staff for advice. She says she didn’t get a response. Finally, seven weeks after the family’s triumphant return to Midtown, McNair filed papers declaring her intention to homeschool Elias.
It quickly proved challenging. Elias wouldn’t do any schoolwork when he was home alone. And when the homeschooling group met twice a week, she discovered, they required parents to pick up their children afterward instead of allowing them to take public transit or e-scooters. That was untenable.
Elias wanted to stay at home and offered to take care of McNair’s uncle, who has dementia. “That was literally killing my soul the most,” said McNair. “That’s not a child’s job.”
Hell, no, she told him — you only get one chance at high school.
Then, one day, while she was loading the boys’ clothes into the washing machine at the Atlanta apartment, she received a call from an unknown Atlanta number. It was the woman who heads Atlanta Public Schools’ virtual program, telling her the roster was full.
McNair asked the woman for her opinion on Elias’s situation. Maybe she should abandon the Atlanta apartment and enroll him in the Jonesboro high school.
Let me stop you right there, the woman said. Is your son an athlete? If he transfers too many times, it can affect his ability to play basketball. And he’d probably lose credits and take longer to graduate. He needs to be in school — preferably Midtown — studying for midterms, she said. You need to put on your “big mama drawers” and take him back, she told McNair.
The next day, Elias and his mother pulled up to Midtown. Outside the school, Elias asked if he had to go inside. Yes, she told him. This is your fault as much as it’s mine.
Now, with Elias back in school every day, McNair can deliver food through Uber Eats without worrying about a police officer asking why her kid isn’t in school. If only she had pushed harder, sooner, for help with Elias, she thought. “I should have just gone down to the school and sat in their offices until they talked to me.”
But it was easy for her to explain why she hadn’t. “I was running around doing so many other things just so we have a place to live, or taking care of my uncle, that I didn’t put enough of my energy there.”
She wishes she could pay more attention to Elias. But so many things are pulling at her. And as fall marches toward winter, her struggle continues. After failing to keep up with the Jonesboro rent, she’s preparing to leave that house before the landlord sends people to haul her possessions to the curb.
As an Uber driver, she has picked up a few traumatized mothers with their children after they got evicted. She helped them load the few things they could fit into her van. As they drove off, onlookers scavenged the leftovers.
She has promised herself she’d never let that happen to her kids.
Bianca Vázquez Toness is an Associated Press reporter who writes about the continuing impact of the pandemic on young people and their education.
The Associated Press’ education coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.
This <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org/she-wanted-to-keep-her-son-in-his-school-district-it-was-more-challenging-than-it-seemed/”>article</a> first appeared on <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org”>The Hechinger Report</a> and is republished here under a <a target=”_blank” href=”https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/”>Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License</a>.<img src=”https://i0.wp.com/hechingerreport.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/cropped-favicon.jpg?fit=150%2C150&ssl=1″ style=”width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;”>
<img id=”republication-tracker-tool-source” src=”https://hechingerreport.org/?republication-pixel=true&post=113392&ga4=G-03KPHXDF3H” style=”width:1px;height:1px;”><script> PARSELY = { autotrack: false, onload: function() { PARSELY.beacon.trackPageView({ url: “https://hechingerreport.org/she-wanted-to-keep-her-son-in-his-school-district-it-was-more-challenging-than-it-seemed/”, urlref: window.location.href }); } } </script> <script id=”parsely-cfg” src=”//cdn.parsely.com/keys/hechingerreport.org/p.js”></script>