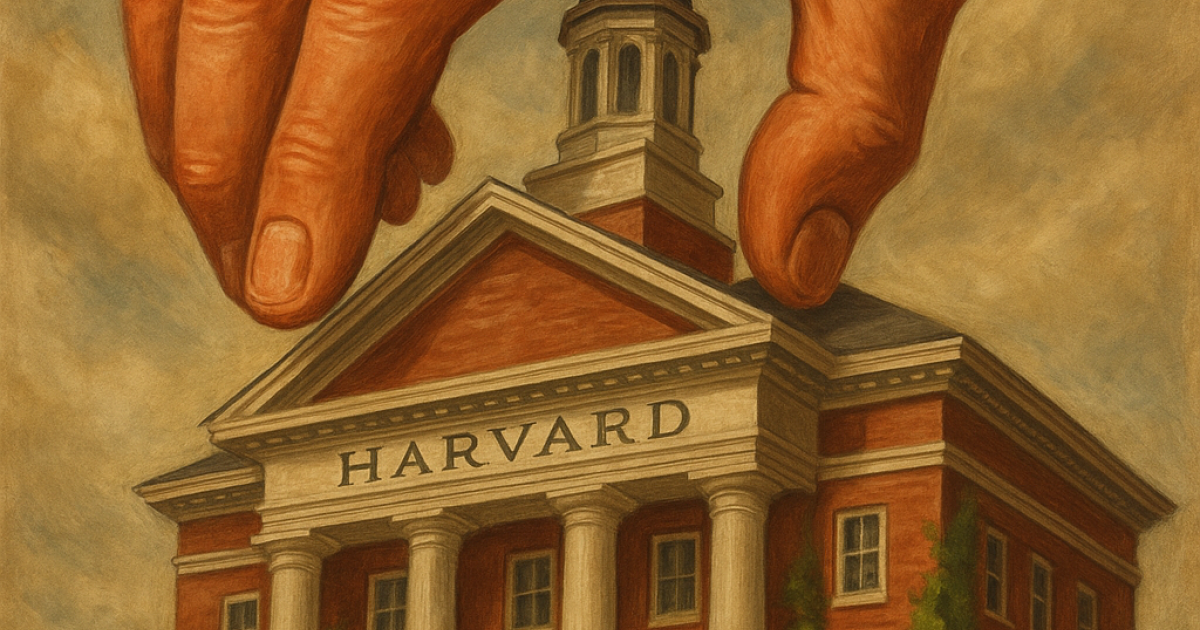
On April 21, 2025, Harvard University filed a lawsuit against the Trump administration after the federal government froze $2.2 billion in federal research funding with threats of more cuts to come. The administration claimed Harvard failed to address anti-Semitism on campus, especially in the aftermath of Hamas’ attack against Israel on Oct. 7, 2023, and issued a list of demands in exchange for lifting the freeze.
These demands included adopting an ideological litmus test for foreign students, a comprehensive mask ban, an audit of disfavored academic departments, mandated reforms to the university’s internal governance structure, and eliminating diversity programs. Harvard argued that these demands and the funding cuts that followed violated its institutional autonomy and constitutional right free speech and academic freedom. In the lawsuit, the university is asking the court to restore its funding and block the government from imposing such requirements in the future.
FIRE agrees that the Trump administration’s approach is unlawful. Below are answers to some common questions we have received about the situation.
Harvard isn’t entitled to federal funds. Why is FIRE defending it?
You’re right. Harvard isn’t entitled to federal funding. No institution is.
But Harvard — just like you (or FIRE, or any person or organization) — is entitled to a federal government that follows the law. And just as the law gives us certain protections, it also says the government can’t cancel funding on a whim, like the administration did last week.
Let’s take a closer look.
The vast majority of colleges and universities receive federal funds. These funds mostly consist of financial aid, like Pell grants, and grants for scientific and medical research. Of the $9 billion reportedly under review by the Trump administration, the Harvard Crimson estimates over $6 billion comes in the form of funding for five regional hospitals associated with the university, along with $2.7 billion in research funding at the university itself.
To be eligible to receive federal funding, institutions pledge to follow federal anti-discrimination laws. Those laws include Title VI, the federal law that prohibits colleges and universities from discriminating on the basis of race, color, and national origin. Since the George W. Bush administration, the federal government has interpreted Title VI as prohibiting anti-Semitic discrimination, too.
So far, so good. Colleges get government funding for students and research. The federal government in return gets (among other things) a commitment that those colleges won’t engage in or tolerate discrimination. That’s the deal.
And the deal has rules to protect colleges, the government, and the taxpayers who foot the bill from being negatively affected by arbitrary decisions. Before the federal government can pull funds from an institution, it has to take a series of steps.
First, the Department of Education must investigate complaints about discrimination. If it finds problems, ED is required to work with an institution to address those problems “by informal means whenever possible.” This is the most common process, where the department’s Office for Civil Rights enters into a “resolution agreement” with an institution to ensure compliance with Title VI.
If that doesn’t work, for whatever reason, here’s what happens next. In order to strip federal funding, the department must give notice to the institution again and provide an opportunity for an administrative hearing where the institution can challenge the determination. If the determination stands, ED then has to report this to Congress and give 30 days’ notice before it actually terminates funding to the affected programs. ED may also refer the matter to the Department of Justice for litigation.
In short, one way or another, the federal government is going to have to provide evidence and prove its case if it wants to pull out of the deal.
Those are a lot of steps, but they’re important. They protect students by making sure colleges live up to their obligations. And they protect colleges by making sure they have an opportunity to contest the allegations as well as a chance to make things right.
These rules are also important because they provide a safeguard against political bias, risk of error, and governmental overreach.
Even the federal government acknowledges the role of due process and following existing statute. In a federal court filing earlier this month, the government wrote, “But ED’s only power is to withhold funding from institutions receiving federal funding, after a robust process required by statute and aimed at ensuring compliance.” In that same court filing, the government reiterated that point, writing that “by statute and regulation, numerous steps aimed at ensuring compliance must occur before ED may withdraw funding.”
Without these rules, an administration could, for example, decide to dramatically expand the definition of “sexual harassment” to include core protected speech and to remove due process protections from sexual misconduct hearings, using the threat of federal funding to force schools to go along with it. That’s exactly what happened under President Obama — and FIRE fought back.
And without these rules, nothing prevents the federal government from arbitrarily declaring a university in violation of federal law, yanking federal funding, and demanding fealty and censorship.
That’s what President Trump is doing now. And again, FIRE is fighting back.
Is FIRE saying that what happened to Jewish students at Harvard and other colleges is OK?
No. As FIRE has consistently noted, some campus protests veered into violations of both campus rules and the law. Examples include when protesters took over buildings, blocked access and exit to and from areas of campus, disrupted classes, or committed acts of violence against Jewish students.
In responding to these incidents — or failing to respond — Harvard, Columbia, and other colleges may well have been in violation of their obligations under Title VI. If they refused to correct their mistakes as the process played out, revoking their funding might have been justified and legal.
But the process matters.
What FIRE is saying is that the law is important. Following it isn’t optional. It protects all of us — students, faculty, administrators, families, scientists, hospitals, and the entire country. The administration can’t just decide unilaterally to skip steps.
If you support President Trump — or just don’t like Harvard — remember this: Any power the president seizes to ignore the law now won’t magically disappear when he leaves office. It will be wielded by his successors, too. And this time, it might well target schools or other organizations you like.
Didn’t Harvard rank last for free speech on your list?
It sure did — two years in a row, in fact.
But one of the reasons we created our rankings was to give colleges and universities an incentive to do better. Protecting expressive rights on campus is a big part of our mission, and Harvard has a long way to go. Indeed, Harvard (like Columbia) makes a politically popular target precisely because so many people resent its years of engaging in the kind of behavior towards dissenting students and faculty that FIRE was founded to combat.
But lately Harvard has been making an effort, and we won’t succeed by writing schools off. And we definitely won’t succeed by allowing the federal government to take them over, trading one dominant ideology for another.
You can’t censor your way to free speech.