The Higher Education Inquirer has approached artificial intelligence not as a speculative future but as a present reality already reshaping higher education. Long before university leaders and consultants embraced Artificial Intelligence (AI) as an abstract promise, HEI was using these tools directly while documenting how they were being embedded into academic institutions. What has become increasingly clear is that AI is not merely an educational technology. It is a structural force accelerating corporatization, automation, and mass surveillance within higher education.
Artificial intelligence enters the university through the language of efficiency and personalization. Administrators speak of innovation, student success, and institutional competitiveness. Yet beneath this language lies a deeper transformation. Teaching, advising, grading, counseling, and evaluation are increasingly reduced to measurable functions rather than human relationships. Once learning is fragmented into functions, it becomes easily automated, monitored, outsourced, and scaled.
This shift has long been visible in for-profit and online institutions, where scripted instruction, learning management systems, predictive analytics, and automated advising have replaced meaningful faculty engagement. What is new is that nonprofit and elite universities are now adopting similar systems, enhanced by powerful AI tools and vast data collection infrastructures. The result is the emergence of the robocollege, an institution optimized for credential production, labor reduction, and data extraction rather than intellectual growth.
Students are told that AI-driven education will prepare them for the future economy. In reality, many are being trained for an economy defined by automation, precarity, and diminished human agency. Rather than empowering students to challenge technological power, institutions increasingly socialize them to adapt to it. Compliance, constant assessment, and algorithmic feedback replace intellectual risk-taking and critical inquiry.
These developments reinforce and intensify inequality. Working-class students, student loan debtors, and marginalized populations are disproportionately enrolled in institutions where AI-mediated education and automated oversight are most aggressively deployed. Meanwhile, elite students continue to receive human mentorship, small seminars, and insulation from constant monitoring. Artificial intelligence thus deepens a two-tier system of higher education, one human and one surveilled.
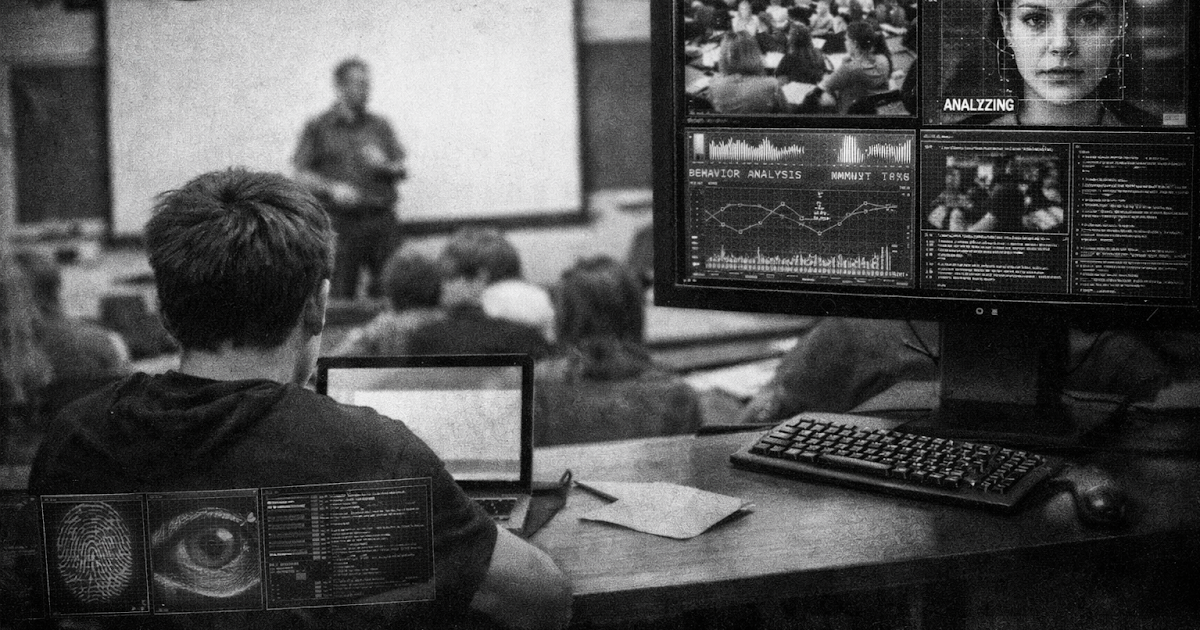
Mass surveillance is no longer peripheral to higher education. It is central to how AI operates on campus. Predictive analytics flag students as “at risk” before they fail, often without transparency or consent. Proctoring software monitors faces, eye movements, living spaces, and biometric data. Engagement dashboards track clicks, keystrokes, time spent on screens, and behavioral patterns. These systems claim to support learning while normalizing constant observation.
Students are increasingly treated as data subjects rather than citizens in a learning community. Faculty are pressured to comply with opaque systems they did not design and cannot audit. The data harvested through these platforms flows upward to administrators, vendors, private equity-backed education companies, and, in some cases, government and security-linked entities. Higher education becomes a testing ground for surveillance technologies later deployed across workplaces and society at large.
At the top of the academic hierarchy, a small group of elite universities dominates global AI research. These institutions maintain close relationships with Big Tech firms, defense contractors, and venture capital interests. They shape not only innovation but ideology, presenting AI development as inevitable and benevolent while supplying talent and legitimacy to systems of automation, surveillance, and control. Ethics initiatives and AI principles proliferate even as accountability remains elusive.
Cultural warnings about technological obsolescence no longer feel theoretical. Faculty are told to adapt or be replaced by automated systems. Students are told to compete with algorithms while being monitored by them. Administrators frame automation and surveillance as unavoidable. What is absent from these conversations is moral courage. Higher education rarely asks whether it should participate in building systems that render human judgment, privacy, and dignity increasingly expendable.
Artificial intelligence does not have to dehumanize higher education, but resisting that outcome requires choices institutions have largely avoided. It requires valuing human labor over scalability, privacy over control, and education as a public good rather than a data pipeline. It requires democratic governance instead of technocratic management and surveillance by default.
For years, the Higher Education Inquirer has examined artificial intelligence not as a neutral tool or a distant threat, but as a technology shaped by power, profit, and institutional priorities. The future of higher education is not being determined by machines alone. It is being determined by decisions made by university leaders, technology firms, and policymakers who choose surveillance and efficiency over humanity.
The question is no longer whether AI will reshape higher education.
The question is whether higher education will resist becoming a fully surveilled system that trains students to accept a monitored, automated, and diminished future.
Sources
Higher Education Inquirer, AI-Robot Capitalists Will Destroy the Human Economy (Randall Collins)
Higher Education Inquirer, University of Phoenix: Training Folks for Robowork