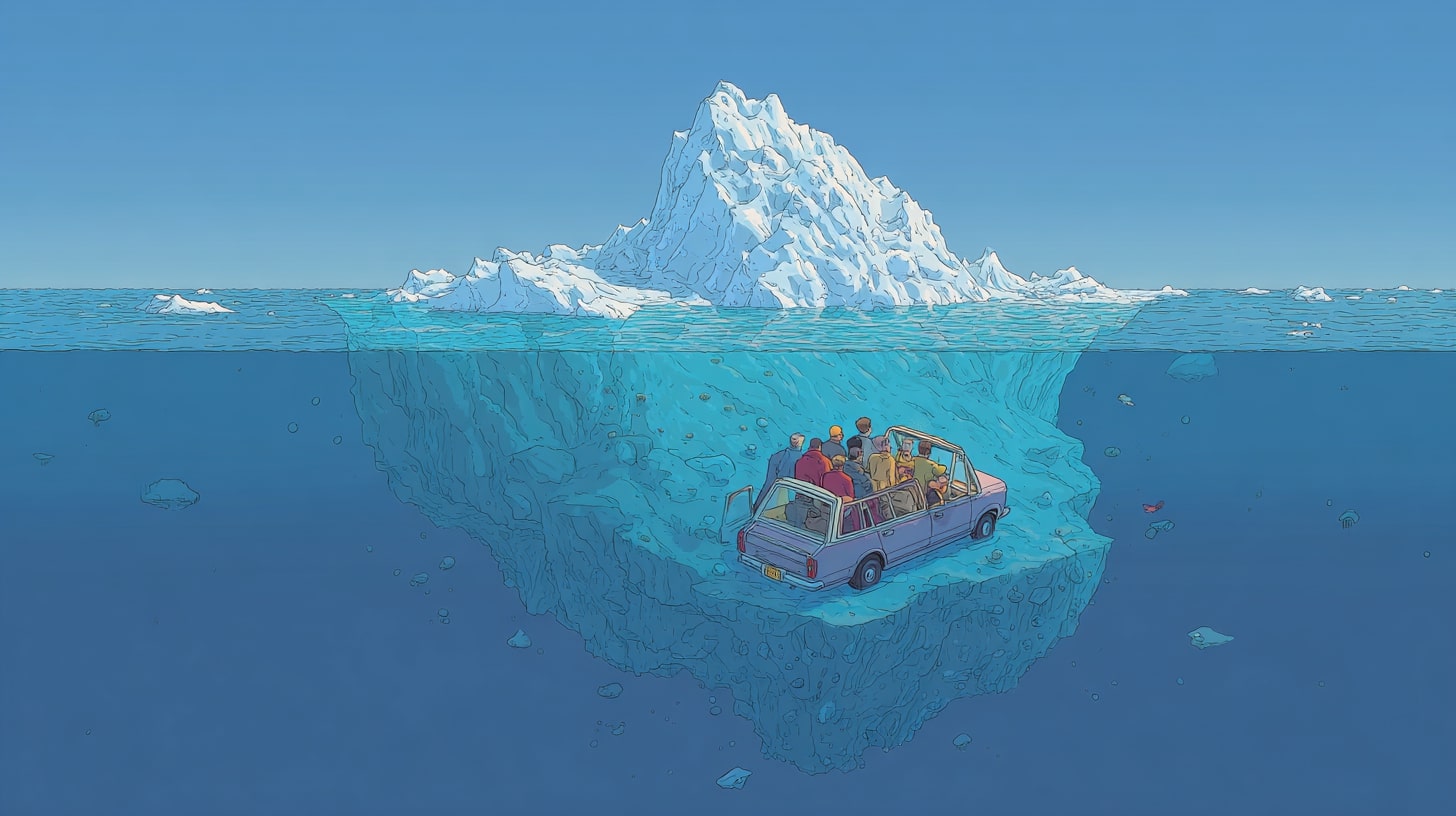
If you’re a proper Eurovision Song Contest loser like me, you look forward each year to the crowdsourced fansourced compilation of the season’s Iceberg.
On the surface is the stuff you figure that “normal” casual Saturday night viewers will notice – like the considerable coverage afforded to Malta’s entry this year, which involved its artist Miriana Conte attempting to argue that her song “Serving Kant” really meant “serving song”.
Then several layers below sea level there’s things like the news that Sasha Bognibov – who has entered the Moldovan selection several times with a series of increasingly creepy entries – had died of a heart attack, only to come back alive a few days later.
“Icebergs of ignorance”, as they’re officially known, were originally invented by a Japanese management consultant in the 80s. Sidney Yoshida’s keynote at the 1989 International Quality Symposium in Mexico had described his research on a car manufacturer named Calsonic – where he’d found that senior managers at the firm only saw about 4 percent of the issues, with the bulk hidden at lower levels.
And like an iceberg, most of the danger lies beneath the surface – with supervisors and frontline staff far more aware of the everyday challenges. In theory it all highlights the need for stuff like open communication, feedback loops and genuine staff voice – so decision-makers aren’t steering blind.
Under the surface
I’ve long been fascinated by the way the concept might apply in a university. Plenty of senior leaders might take the view that the cultural (and now regulatory/legal) protection afforded to academic staff saying critical things on social media on everything from workload to the travel booking system means very little is below the surface – but my guess is that that can breed complacency about the things that people don’t say out loud.
From a higher education sector and public perception point of view, we might interpret new research from the Policy Institute at King’s and HEPI in a similar way – an iceberg of misunderstanding where the surface-level chatter obscures the submerged reality.
The public apparently overestimate graduate regret, assumes that nearly half of graduates feel crushed by debt when only 16 per cent say so, and underestimate higher education’s economic heft. And like Yoshida’s managers, the danger isn’t so much ignorance of the big headlines as it is the quiet accumulation of false assumptions beneath the surface – gaps in knowledge that, if unchallenged, steer the national conversation off course.
But it’s the big financial crisis in the sector where I keep thinking most about the Iceberg. Above the surface, to the extent to which the issue is “cutting through”, it’s the prospect of a provider going under that the press seem really keen to report on. Every other day one of us at Team Wonkhe will get a message from journo or other asking us who might be on the brink, presumably because stories like this in the i Paper (“At least six unis at risk of going bust before 2025 freshers finish their degrees”) get clicks.
Just below the surface (for me at least) is what’s happening to student demand (or, more accurately, supply) – a process that seems to be converting “high”, “medium” and “low” tariff group categories into “medium”, “low” and “has a pulse” as each day of Clearing 2025 goes on.
The next level down for me is redundancy rounds and telegraphed cuts. They definitely sound bad – especially if a course closes. But if they result in 24 hour library becoming a 15 hour one, or the optional electives on an undergraduate degree being slashed, they seem be harder to pin down and understand – and often aren’t being picked up and protected by consumer law, complaints or Student “Protection” Plans.
The worst of all of that, at least so far, has been down the bottom end of the league tables – although journos hoping for an actual collapse may find that the realities of processes like endless cost-cutting remain buried at the bottom of the iceberg because of the amount of debt that everyone’s in.
A small provider like Spurgeon’s can fall over because the banks aren’t expecting millions to be repaid on shiny buildings – big universities extended in that way are likely to be able to renegotiate because banks like being paid back, albeit in a way that effectively surrenders the already shaky illusion that the Board of Governors is in control to a shadow board of bankers insisting on deeper and deeper cuts to students with the least social capital and confidence to complain about them.
We need a shrink
What then manifests is the scourge of shrinkflation. You know the idea – when the Quality Street tubs appear in the supermarket in September, you’re only minutes away from a national newspaper pointing out that there’s two fewer toffee pennies in this year’s tub of 525g than last year. I mean have you seen how small a Freddo is these days?
The problem for students is that this stuff is hard to spot and even harder to enforce rights over. It is simply not possible to lose the number of academic staff that the sector has lost over the past two years and for providers to not be in breach of contract – promises have either been broken, or the contract itself gives a university too wide a discretion to vary, or it doesn’t and the risks of not making the cuts are greater than the risks of a handful of students having the energy to complain.
And when the big red flags from the Office for “Students” are about financial sustainability with the odd askance murmur about finding efficiencies in a way that protects the student experience, it’s not as if the regulatory environment is doing anything other than egging on the shrinkflation. You’re only going to get inspected on the provision by OfS if your outcomes are terrible, and it seems to have all but given up doing inspections anyway.
Will a student enrolling onto a three year degree get the course they were promised in two years time? I’ve no idea, and all OfS can offer in protection terms is “let’s hope you paid your fees on a credit card because you might be able to get the credit card company to do a chargeback”.
Every year I get taken in by a fresh promise that OfS will actually enforce the stuff about broken promises. Almost a year ago to the day Director for Fair Access and Participation John Blake turned up at an SU staff conference to declare that he’d heard students worried about being promised one thing and getting another loud and clear. What he didn’t say was that a full year on, its new definitions of “fairness” will only apply to students in newly registered providers – with no sense of when “fairness” might be a thing for everyone else.
Deep down
But the temptation would be to assume that the harms of where we are are exclusively in those layers already mentioned. For me, right down at the bottom of the Iceberg – for the public, regulators and students themselves – is the sharing problem.
I often lament that being in a university library in certain weeks of the year is like being on a short-formed Cross Country train with no air con on a Bank Holiday Monday when the service before it has been cancelled. There’s nowhere to sit, everyone is very tense, and there’s a real sense that an actual fight might break out between two otherwise polite members of the public over a seat reservations issue.
There’s always an idiot with their bag on a seat, the catering trolley can’t get through, and the wheelchair user finds themselves yelling at those with suitcases because they’ve been plonked in the space for chairs at the end of the carriage. It’s carnage.
Over the years, I’ve often skim-read commentary from financial and management consultant types that “one less international PGT means needing to recruit two home students”, as if the only thing that matters is the overall financial target rather than having enough of everything for the students being recruited.
What I (almost certainly naively) never expected is that it pretty much is panning out like that at the top end of the tables – and while there’s debates to be had about acquisition costs, suitability for a course and/or culture, market instability and the loss of “local” options and choice, the thing that worries me most of all is the sharing thing.
Let’s imagine – hopelessly simplistically, I know – that some universities are indeed setting a financial target regardless of the number of students that would involve recruiting. As part of that, let’s imagine that these are universities more likely to recruit students living away from home. If 1 x PGT becomes 2 x UG, are there enough bed spaces in the city?
Enough is enough
Enough books in the library? Enough marking capacity to hit the 2 week turnaround pledge? Enough sockets for laptops when everyone’s in at once? Enough spaces in seminar rooms to avoid students sitting on the floor? Enough counselling staff to cope when that extra intake tips more students into crisis? Enough careers support to avoid queues that make the whole thing feel tokenistic rather than transformative?
Enough quiet corners for those who can’t concentrate in noisy shared flats or packed libraries? Enough placements to go around when professional courses all need them at the same time of year? Enough personal tutor appointments to avoid the system becoming decidedly impersonal? Enough contact with actual academics rather than a carousel of casualised staff? Enough eduroam bandwidth when every lecture, seminar, and social is streaming at once? Enough student housing that isn’t mouldy, miles away, or eye-wateringly expensive?
“Enough” is already pretty subjective – and itself subject to wild differences between subject areas on campus in a way that makes it hard to not always spot someone (probably an international PGT in the Business School) who’s worse off. Even if they knew they could and even if they were minded to, it’s pretty hard for a student to argue that something that is still there and was always shared is being stretched a little too thinly now.
And this sort of thing almost always manifests in conflict between students rather than pinning the blame tail on the university donkey – see our dismal debates about things like NHS access and immigration for a classic example.
It’s not even as if the regulator doesn’t understand. John Blake again, a year ago:
When the 2012 number controls were abolished, there are institutions that literally doubled in size overnight… I don’t know that the answer is us saying, no, you can’t have your students, or you have to do this. But I think there’s definitely scope for us thinking about what the obligation of institutions is to have discussions with their local community about where their students are going to go, because it’s clearly not sustainable for every institution to double itself overnight in small places.
See also everything else about a university experience that, by definition, involves sharing things.
Swear words
It remains the case that it’s almost as bad to sing the uncensored version of Miriana Conte’s Eurovision entry in a church as it is to even gently propose some student number controls. And even though one of the least publicly resisted immigration rules is not a cap but a “if you want more CAS, you have to think about whether you have the capacity” (maybe because it’s never been meaningfully or publicly enforced by UKVI), people even seem to be nervous about suggesting something like that for home students.
I’ve said it before and I’ll say it again – higher education is an endeavour that is profoundly unsuited to very rapid expansion and very rapid contraction at programme, subject and institutional level. But the biggest mistake of all would be to focus on the end of the league tables where the impacts of contraction are closest to the Iceberg’s surface.
Cramming tens of thousands more students into the cities of the (not so) high tariffs may well be just as damaging, all while the tone of their recruitment relationship – “you’re lucky to be here” – reduces the chances of students doing anything other than the HE equivalent of putting your head down, crouching next to the toilet and staring at your phone for three gruelling hours. Or, in HE’s case, years.
It’s really not hard this one. You want to expand your student numbers by more than 5 per cent in a subject area? Publicly consult on how you’ll do it – including the results of conversations with staff, students, the local community and local providers, and you’re on. Imagine suggesting out loud that doing some planning to ensure more students doesn’t mean a worse experience would represent a regulatory “burden”.