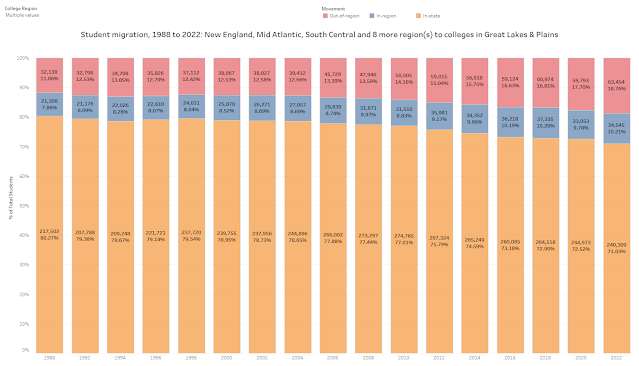
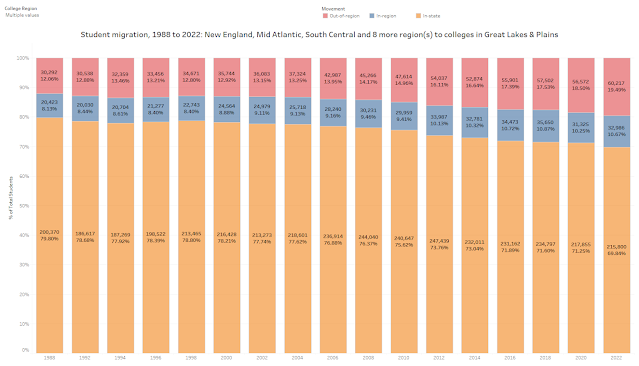
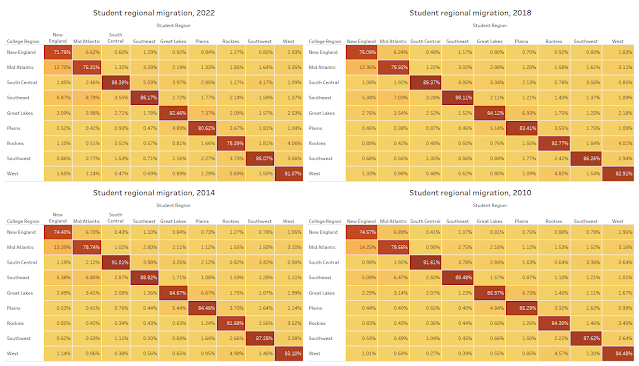
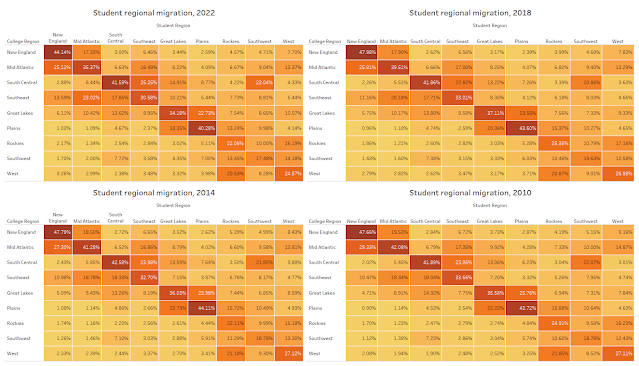
Miami – Achieve Miami, a nonprofit dedicated to equalizing educational opportunities for students throughout Miami-Dade County, has received $2.4 million from multiple philanthropic organizations and leaders, including a leadership gift of $2 million from Kenneth C. Griffin, founder and CEO of Citadel and founder of Griffin Catalyst. The funding, awarded over the past year, will further expand Achieve Miami’s transformative programs, reaching thousands of K-12 students through initiatives including Achieve Scholars, which prepares high schoolers for college success; Achieve Summer, a dynamic program combating learning loss through hands-on academics and enrichment; and the Teacher Accelerator Program (TAP), a groundbreaking effort to address Miami-Dade’s urgent teacher shortage.
Kenneth C. Griffin’s $2 million leadership gift is specifically focused on supporting TAP in creating a pipeline of talent for the teaching profession through recruiting, preparing, and mentoring aspiring educators, including those who had not previously considered a career in education. This gift builds on Griffin’s $3.5 million gift to TAP in 2022, further strengthening Achieve Miami’s efforts to recruit and train qualified educators to teach in public, private and charter schools across Miami-Dade and close learning gaps in the city’s schools. Griffin has a longstanding commitment to improving education and has contributed more than $900 million to providing greater access to a high-quality education and pathways to success for students in Florida and across the country.
Additional grants include:
- $200,000 from the Bezos Family Foundation, which is a director’s gift supporting early and adolescent learning through grants and programs that advance the science of learning.
- $100,000 from the Panera Bread Foundation, as part of its national initiative to support nonprofits that provide educational access to underserved youth.
- $65,000 from Morgan Stanley, in support of Achieve Miami’s financial literacy and career readiness programs, which equip students in the organization’s Achieve Scholars program with essential money management skills for financial independence and future success. As part of its commitment, a team of Morgan Stanley employees guide students through financial literacy sessions across ten Miami-Dade County public schools, providing essential lessons on topics like budgeting, investing, entrepreneurship, savings, and credit.
- $50,000 from City National Bank of Florida, as part of its long-term partnership with Achieve Miami in support of the Achieve Scholars program. City National Bank is planning financial literacy programming for students over the summer.
“Every student deserves access to resources, mentors, and opportunities that can set them up for success,” said Leslie Miller Saiontz, Founder of Achieve Miami. “These generous grants, led by Ken Griffin, will enable us to expand our reach, empower more educators, and bridge opportunity gaps that are prevalent in Miami. By investing in students and teachers, we are building a stronger future for our community.”
“Each of us has a story of how a teacher has changed our lives,” said Ken Griffin in February 2023 alongside his initial gift to Achieve Miami. “I care deeply about bringing more high-quality educators into Miami classrooms to help ensure the children of Miami will continue to enjoy the impact of life-changing teachers.”
Despite being one of the fastest-growing states with the nation’s fourth-largest economy, Florida ranks #21 in per capita education funding. Achieve Miami’s initiatives aim to eliminate educational disparities by equipping students with the tools and support needed for success with a variety of diverse enrichment programs such as Achieve Scholars, Achieve Saturdays, and Achieve Music.
Achieve Miami’s impact to-date includes support for over 10,000 Miami-Dade County students, college and career readiness programming for Achieve Scholars across ten high school sites, providing internet access to over 106,000 homes through Miami Connected, and the recruitment and training of nearly 200 new teachers through the Teacher Accelerator Program (TAP) since the initiative’s launch in 2023.
ABOUT ACHIEVE MIAMI
Achieve Miami is a nonprofit organization that is dedicated to fostering a transformational education ecosystem in Miami. Since its founding in 2015, the organization has supported over 10,000 K-12 students, bolstered programming for 60+ local schools, and engaged thousands of volunteers. Together with partners from the public and private sector, Achieve Miami designs and manages programs that bring together members from various parts of the community to extend learning opportunities for students, teachers, and community leaders. Learn more at www.achievemiami.org.
ABOUT THE TEACHER ACCELERATOR PROGRAM
Teacher Accelerator Program (TAP) is a non-profit organization creating a pipeline of talent for the teaching profession through recruiting, preparing, and mentoring aspiring educators. TAP’s comprehensive and streamlined program equips college students and career changers with the skills, knowledge, and certification necessary to excel in the classroom. TAP addresses the nationwide teacher shortage crisis by providing a built-in path to teaching, inspiring a new generation of educators.
TAP participants take a one-semester course, followed by a six-week paid summer internship, earn a certificate to teach, and begin instructing in a Miami-Dade County public, private, or charter school classroom. TAP is an initiative of Achieve Miami, supported by Teach for America Miami-Dade, and is offered by the University of Miami, Florida International University and Miami-Dade College. Learn more at www.teacheraccelerator.org.