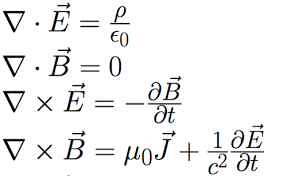Please follow and like us:
Einstein’s Explanation of the Unexplainable
In Maxwell’s mathematical formulation of electromagnetism, he defined light as a propagating electromagnetic wave created by the interaction of its electric and magnetic fields
While Einstein in his General Theory of Relativity defined the forces associated with gravity in terms of a geometric curvature or spatial displacement in space-time caused by its energy density.
Additionally, he showed that it was directed along the radius of the curvature in the two-dimensional plane that was parallel to it.
Therefore, to explain how Maxwells equations can be defined in terms of a space-time environment one must show how both the observable and mathematical properties of an electromagnetic: such as why its wave properties are created by the interaction of its electric and magnetic fields and why polarized light has a perpendicular orientation in terms of the geometry of space time.
Additionally, one must also show why its electrical and magnetic components are in phase, it’s the only form of energy that can move at the speed of light along with the defining the reason why it always appears as a photon when observed or interacts with its environment in terms of that same geometry.
As was just mentioned gravity’s force vector is along the radius of one of dimensional plains of three-dimensional space. However, that does not mean the other two plains of three-dimensional space cannot contribute to energy content of space.
The fact that light is polarized supports that assumption because it allows one to understand the mechanism responsible for its perpendicular orientation in terms light waves moving on the different dimensional plains that are perpendicular to each other.
However, one ALSO allow one to explain both the observations and Maxwell equations in terms of the dimensional prosperity of space if one assumes the electrical and magnetic are components of light are propagated by spatial displacements created by an energy wave moving on the surface of one of those two-dimensional plains.
(This assumption is supported by Einstein suggestion that spatial displacements in one of the three-dimensional plains of three-dimensional space is responsible for gravitational energy.
One can understand the mechanism responsible by using the analogy of how a wave on the two-dimensional surface of water causes a point on that surface to become displaced or rise above or below the equilibrium point that existed before the wave was present.
The science of wave mechanics tells us a force would be developed by those displacements which would result in the elevated and depressed portions of the water moving towards or becoming “attracted” to each other and the surface of the water.
Similarly, an energy wave on the “surface” on one of the two spatial dimensions that are perpendicular to the axis of gravitational forces would cause a point on that “surface” to become displaced or rise above and below the equilibrium point that existed before the wave was present.
Therefore, classical wave mechanics, if extrapolated to the properties of two of the three spatial dimensions of our universe that are perpendicular the one responsible for gravity tells us a force will be developed by the differential displacements of energy wave which will result in its elevated and depressed portions moving towards or become “attracted” to each other as the wave moves through space.
This would define the causality of the attractive electrical fields associated with an electromagnetic wave in terms of a force caused by the alternating displacements of a wave moving with respect to time on a “surface” of the two spatial dimensions which are perpendicular to the axis of gravitational forces.
However, it also provides a classical mechanism for understanding why similar electrical fields repel each other. This is because observations of waves show there is a direct relationship between the magnitude of a displacement in its “surface” to the magnitude of the force resisting that displacement.
Similarly, the magnitude of multiple displacements in a “surface” of a two-dimensional plain in space-time will be greater than that caused by a single one. Therefore, they will repel each other because the magnitude of the force resisting the displacement will be greater than it would be for a single one.
One can also derive the magnetic component of an electromagnetic wave in terms of the horizontal force developed along the axis that is perpendicular to the displacement caused by its peaks and troughs associated with the electric fields.
This would be analogous to how the perpendicular displacement of a mountain generates a horizontal force on the surface of the earth, which pulls matter horizontally towards the apex of that displacement.
This also explain why the electrical and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave are in phase or maximum at the same time in terms of the geometric properties of space time defined by Einstein
However, it also provides an explanation for why electromagnetic waves can transmit energy through space at the speed of light.
The observations and the science of wave mechanics tell us waves move energy through water, causing it to move in a circular motion therefore it does not actually travel with waves. In other words, waves transmit energy, not water, across the ocean and if not obstructed by anything, they have the potential to travel across an entire ocean basin.
Similarly, an electromagnetic wave will cause the geometry of space time to move in a circular motion and therefore the geometric components of space Einstein associated with mass do not move with respect to its velocity vector. Additionally, if not obstructed by anything, they have the potential to travel across an entire universe to the velocity of light.
As was just shown the speed of a wave on water is defined in part by the rate at which its particles interact.
Therefore, the speed of light would depend on the rate at which the electrical and magnetic components interact.
Therefore, its velocity is constant in free space with no obstacles to its motion because the rate at which its electrical and magnetic components interact is constant.
However, to understand how and why an electromagnetic wave evolves into photon one must connect its evolution to that environment.
One can accomplish this by using the science of wave mechanics and the properties of space-time as define by Einstein.
For example, an electromagnetic wave is observed to move continuously through space and time unless it is prevented from doing so by someone or something interacting with it. This would result in its energy being confined to three-dimensional space. The science of wave mechanics tells us the three-dimensional “walls” of this confinement will result in its energy being reflected back on itself thereby creating a resonant or standing wave in three-dimensional space. This would cause its wave energy to be concentrated at the point in space were a particle would be found.
Additionally, wave mechanics also tells us the energy of a resonant system, such as a standing wave can only take on the discrete or quantized values associated with its fundamental or a harmonic of its fundamental frequency.
This explains why an electromagnetic wave if it is prevented from moving through space-time either by being observed or encountering an object is reduced or “Collapses” to a form a standing wave that would define the quantized energy Quantum Mechanics associates with a particle.
However, this also provides a Classical mechanism in terms of Einstein theories for defining one of the core principals Quantum Mechanics in that when field properties light and all other forms of energy are prevented from moving through space either by being observed or encountering an object that energy will become quantized in the form of a particle.
This shows how one can define all of the mathematical of Maxwells equation in terms of the physical properties of space time
Please follow and like us: