A review of the University of Canberra’s (UC) management said governing body members should be held more accountable after staff felt ‘shut down‘ and shunned from decision making.
Please login below to view content or subscribe now.
Membership Login

A review of the University of Canberra’s (UC) management said governing body members should be held more accountable after staff felt ‘shut down‘ and shunned from decision making.
Please login below to view content or subscribe now.

It is clear that existing inequity can inhibit engagement with higher education careers support, creating a vicious cycle where the students with the greatest need for these services may not take up valuable opportunities. Given the wider lack of diversity in professional services leadership and staffing, there is also a risk that higher education policy and practice will continue failing to incorporate the lived experience and diverse voices that can help to drive change.
Leena Dattani-Demirci’s current doctoral studies explore the experiences of ethnically minoritised staff within university career services, an area comparatively underexplored despite extensive research on inequalities experienced by academic staff. Her research aims to address that gap, giving voice to the lived realities of those working to support students’ career aspirations. Claire is the author of What Happens Next?, the latest report in a long-running series from AGCAS that identifies and explores disabled graduates’ employment outcomes.
Early findings from Leena’s research highlight persistent challenges faced by ethnically minoritised staff. Drawing on 37 hours of interviews over eight months, this study explored the experiences of 21 ethnically minoritised career professionals in UK higher education. Participants worked in a wide variety of institutions, and most came from working-class backgrounds, with diverse ethnicities, faiths, and, in some cases, experiences of disability. These research participants reported exhaustion, career bottlenecks, and felt forced to leave their institutions to progress. The emotional labour of supporting minoritised students disproportionately fell on minoritised staff. Many staff felt immense pressure, particularly where the diversity of careers teams did not reflect the diversity of the student body. Career professionals described feelings of guilt for not being able to meet the demand for support from minoritised students.
Microaggressions remain commonplace: Participants described mocking of accents dismissed as “jokes” and being labelled “too sensitive” when raising concerns. “People say things and don’t think about the impact on those of us from BAME families; it stays with us,” one participant noted. Others described ill-equipped managers, promoted through time served, resulting in poor trust and under-reporting of inappropriate comments.
Performative inclusion is common: initial support for Black Lives Matter faded, and universities responded swiftly to Ukraine but remained silent on Gaza, revealing that, for many, inclusion feels conditional. One research participant highlighted how inclusion and diversity are part of the conversation around students, but not staff, “We’ve had team days where diversity and recruitment have come up for students, but if the topic moves onto our teams, it’s always shut down. People get defensive.”
Yet compassionate leaders and allies do exist. “When my manager asked me ‘Are you okay?’ during the summer riots, it meant the world to me,” shared one participant in Leena’s research. There is also excellent work happening across higher education, such as staff/student partnerships at the Open University that integrate the lived experiences of marginalised groups in curriculum design, and collaboration to ensure inclusive language across graduate attributes at Bath Spa University. However, default systems and cultures continue to shape staff progression and team structures. As one of Leena’s research participants explained, ‘I felt excluded because a lot of the candidates who did get the roles fit the mould of what managers had in their heads. I’ll never be that”.
Addressing oversights and inequity within careers services requires accurate data on staff demographics. Gathering the data on who works inside HE careers services is a crucial first step towards meaningful change. AGCAS recently came together with other higher education sector membership bodies to highlight why professional services staff should be included in the HESA staff record; this would support better understanding at a sector level, and lead the way for institutions.
The AGCAS “What Happens Next?” report underscores the complexity of student identities and outcomes, revealing how intersectional disadvantage can further compound employment challenges for many individuals. This year, the report included outcome evaluations incorporating ethnic background and gender alongside disability status and type. The report showed that while disabled graduates have lower rates of full-time employment than graduates with no known disability across all ethnic backgrounds, White disabled graduates are more likely to be in full-time employment than disabled graduates from any other ethnic background.
The need for joined-up approaches to careers and employability delivered by a diverse staff team is clear. We need to recognise that each individual’s identity is complex and multi-faceted, and to model equity and inclusion for students.
AGCAS has been working with careers professionals in their Equality, Diversity and Inclusion Working Party, Disability Task Group, and Social Mobility, Widening Participation and Regional Inequality Working Party to develop provision that supports genuine sector-wide action in this space. A recent positive action toolkit for members offers clear insights into relevant legislation across the UK and Ireland, including practical examples of how universities and careers services can apply positive action principles. Upcoming drop-in networking sessions support AGCAS members who identify as having Black, Asian and Ethnic heritage to build contacts and develop their network. AGCAS are keen to encourage members and wider higher education stakeholders to be part of our work towards much-needed change, whilst also championing and supporting individual projects like Leena’s that move the conversation forward.

Just 44 days before duties on it go live, but some 389 days since it closed a consultation on it, the Office for Students (OfS) has finally published Regulatory advice 24 – its guidance to universities and colleges in England on freedom of speech that flows from the Higher Education (Freedom of Speech) Act (HEFoSA).
The timings matter partly because it’s mid-June, there won’t be many (if any) big committee meetings left (let alone processes designed to engage with people on policy development ahead of approval), and it was OfS itself that fined the University of Sussex partly over the proper approval of some of its policies.
And it’s not as if there are only minor drafting changes. An 11,773 word draft has become a 23,526 word final, and the list of 30 illustrative examples has grown to 52 – despite the fact that this new version omits all the duties on students unions (which the government announced last year it intends to repeal), and is now also silent on the free speech complaints scheme.
All the detailed and prescriptive expectations in the original draft over how that should be promoted have gone – largely because we’re all waiting for Parliament to debate (sensible) changes that will cause students to have to use the Office of the Independent Adjudicator (OIA), rather than OfS, to resolve any complaints in this area.
Alongside, there’s surely a record-breaking 788 paragraph analysis of responses and decisions off the back of the eleven question consultation, some alarming-sounding polling that will likely be making the news, and some short guides for students and staff.
A lot of the new version of the guidance adds more detail into the examples – many are now more realistic, plenty are better at signalling the differences between “good ideas” and minimum expectations, and a whole host of them are now more accurately qualified with reference to key legal principles or tests, many of which have been emerging in case law since OfS started its consultation.
That said, some are still so preposterous as to be useless. If there really is a college somewhere that requires students to seek written permission a month in advance to hand out leaflets or post flyers, where those flyers must be posted on a single designated noticeboard which is both small and on a campus where flyers may not be posted anywhere else, I’ll eat my hat – or maybe my pudding at the formal dinner at whichever Oxbridge college authors were reminiscing about when Example 38 was drafted.
As there are 52 of them, this initial article doesn’t dive into all of the vignettes comprehensively – although doubtless a number of them (not least because of the judicious use of qualifiers like “depending on the facts of the case”) will continue to cause readers to cry “yeah but what about…” – which is presumably why OfS initially attempted to let lessons unfurl from the casework rather than publish guidance. And we may well end up looking at some of them in more detail in the coming days and weeks.
What I have tried to do here is look at the major ways in which the guidance has developed, how it’s handling some of the bigger questions that both universities and their SUs were raising in responses during the process, and what this all tells us about OfS’ intended approach to regulation in this area as of August.
As a reminder, we’re talking here about the duty to “secure” freedom of speech on campus (A1 in HEFoSA), and the expectations that OfS has around the requirements for a souped up Code of Practice (A2) for each provider. There’s no guidance (yet) over the “promote” duty (A3), and to the extent to which the previous version strayed into those areas, they’ve largely been removed.
If we were to identify one theme that has dominated discussion and debate over the Free Speech Bill ever since then universities minister Michelle Donelan stumbled, live on Radio 4, into an apparent contradiction, it would be where free speech (to be protected and promoted) crosses the line into harassment – which of course, under a separate heavy new duty as of August 1st, is something to be actively prevented and prosecuted by universities. Middle grounds are no longer available.
The good news is that the section on reconciling free speech duties with equality law, anti-harassment provisions, and other legal requirements is better than anything else OfS has published to date on the interactions and fine lines. So detailed, for example, are many of the sections that deal with harassment on campus that at times, it’s a lot more helpful than the material in the actual guidance on registration condition E5 (Harassment and Sexual Misconduct).
People often, for example, find others’ conduct to be unpleasant or disagreeable – Para 47 reminds us that the concept of harassment in the Protection from Harassment Act 1997 is linked to a course of conduct which amounts to it, that a course of conduct has comprise two or more occasions, that the conduct must be “oppressive and unacceptable” rather than just “unattractive or unreasonable”, and must be of sufficient seriousness to also amount to a criminal offence.
Similarly, the judgement of harassment isn’t purely subjective – it applies an objective test based on what a reasonable person would think, which helps provide a consistent standard rather than relying solely on individual perceptions.
Hence in Example 1, a student publishes repeated comments on social media attacking another student based on lawful views, including “tagging” them in posts and encouraging others to “pile on”. The student’s speech is so “extreme, oppressive and distressing” that their course of conduct may amount to harassment – and so carrying out an investigation into the student based on a policy that bans harassment would not breach the “secure” duty.
Much of that flows from a newly reworked version of what counts as free speech within the law that translates some of the case law and principles set by the ECHR and the UK High Court in cases like Higgs v Farmor’s School. As such, while there’s still lines in there like “The Act protects free speech within the law – it does not protect unlawful speech”, there’s now much more helpful material on the different ways in which free speech might be curtailed or interfered with given other duties.
To get there it outlines a three step test (with some wild flowchart graphics):
There’s no doubt that it’s a more nuanced and balanced reflection of the legal position than we saw in the draft – albeit that it switches between “what to do in practice” and “what to say to students and staff in theory” in ways that are sometimes unhelpful.
The problem is that the closer it gets to necessary complexity, the further away it gets from something that’s easy to understand by the very staff and students whose day to day conduct and confidence (what we might call the “culture” on campus) is supposed to be being influenced by the new duties.
More importantly, as the examples unfurl, it’s both possible to spot numerous ways in which “it’s a balance” turns into Kafka’s cake and eat it, and to see how the “reasonably practicable steps” duty turns into something genuinely hard to understand in practice.
One thing that’s not gone is a tendency in the examples to signal to the outside world that the new rules will tackle the things they’ve read about in the Times and the Telegraph – until you realise that they won’t.
That Example 1 discussed above (highlighted in the accompanying press release) is a classic of the genre. On the surface it looks like OfS is tackling “mobbing”. But in reality, the whole point about pile-ons is that they’re almost never about one big evil ringleader engaging in conduct that is so “extreme, oppressive and distressing” that their course of conduct may amount to harassment.
It’s more often than not a hundred micro-oppressions having the cumulative effect of making the target feel terrible. Even if you argue that aspects of social media culture are within the influence (if not control) of a provider, in other parts of the guidance OfS seems to be saying that because each micro-act isn’t harassment, you shouldn’t be trying to meddle in the culture of the campus.
That problem becomes amplified in the section on microaggressions. In 2019, the Equality and Human Rights Commission (EHRC) found microaggressive acts to be a key component of a culture of racism on campus – and both argued that they could have an impact on equality of opportunity and good relations between different groups, and that universities must not ignore microaggressions that do not meet the definition of harassment in the Equality Act 2010 because of the cumulative impacts of repetition.
But as soon as universities started to tackle microaggressions by, for example, encouraging their reporting, various anti-EDI culture warriors started to raise concerns. Discussing a scheme launched by Sheffield SU to have their halls reps understand the concept, Spiked’s Joanna Williams argued:
They will need an odd combination of extreme sensitivity to offence – alongside a high degree of insensitivity to interrupting conversations – to point out exactly where the speakers went wrong. Presumably, candidates will also have to sit some kind of test to prove their own thought purity on all matters concerned with race and ethnicity.
The Command Paper that led to HEFoSA was also worried:
Schemes have been established in which students are paid to report others for perceived offences.
And as Report+Support tools started to open up avenues for students to raise issues such that universities could spot patterns, academics – among them a fairly obscure Cambridge philosopher called Arif Ahmed – started to complain:
The encouragement to report ‘inappropriate’ or ‘offensive’ behaviour amounts to a snitches’s charter. Any risk-averse white person will simply not engage with anyone from an ethnic minority, in case an innocent or well-meaning remark is overheard, misunderstood and reported. Whatever Downing College may think, being offensive is not an offence.
Several years on, Arif Ahmed is OfS’ Director for Freedom of Speech and Academic Freedom, asserting that his appointment and approach isn’t “political”, and launching actual regulation (Example 39) that says this:
University A promotes an anonymous reporting process. Students are encouraged to use a portal to submit anonymous reports to senior staff of “microaggressions”, which is not further defined. The portal includes free text boxes in which reporters may name or otherwise identify the individuals being accused. University A says that it may take action against named (or identifiable) individuals on the basis of any anonymous report that it receives.
…Depending on the circumstances, the existence of the reporting mechanism and portal may discourage open and lawful discussion of controversial topics, including political topics and matters of public interest.
…Reasonably practicable steps that A could now take may include remove the free text boxes from the anonymous reporting portal to be replaced with radio buttons that do not permit submission of any identifying data.
There is a legitimate, if contested, political view that structural racism is fictional, harmful or both – and that what flows from it is division via concepts like microaggressions. There’s another view that to tackle racism you need to interrogate and tackle not just skinheads hurling abuse and painting graffiti, but the insidious yet often unintended impact of stuff like this (EHRC again):
A recurring theme in our evidence was students and staff being dismissed as “oversensitive” and their experiences of microaggressions viewed as isolated incidents rather than a cumulative and alienating pattern of repeated slights and insults.
Many staff and students reported that racial harassment doesn’t only happen overtly. All too often, offensive comments were justified by perpetrators as “jokes” or “banter”. The damaging effect of repeated microaggressions is often made worse by a lack of empathy and understanding when individuals decide to speak up about their treatment.
In that “debate”, OfS has picked the side that we might have expected Arif Ahmed to pick. Whether he’s legally justified in doing so is one question – but let’s not pretend that the agenda is somehow apolitical.
All of this is possible because of a central conceit in the guidance that relates back to a long-running theme in the rhetoric surrounding culture on campus – what we might call a “maximalist” approach to describing free speech, and a “minimalist “ (specific, legal thresholds) approach to harm and harassment.
Anything goes unless it specifically breaks this specific law, and if you pretend otherwise you might end up “chilling” free speech.
You might. But while insisting on an objective test to determine whether harassment has happened is a central feature, no such test of objectivity is then applied to whether a chilling effect has occurred – it becomes, in effect, about “potential” and feelings. Hence in its Sussex investigation, OfS said:
…a chilling effect arose as a result of the Trans and Non-Binary Equality Policy Statement and the resulting breach of condition E1. By “chilling effect”, the OfS means the potential for staff and students to self-censor and not speak about or express certain lawful views. Staff and students may have self-censored as a result of the policy because they were concerned about being in breach of the policy and potentially facing disciplinary action for expressing lawful views.
So having established that “harassment” has to amount to something objectively criminal, while “chilling” is in the eye of the Director, OfS is able to get away with railing against another newspaper favourite – by all but outlawing requiring academic staff to issue trigger warnings. Example 50:
Depending on the facts, issuing a “content note” (informing attendees about sensitive material) in advance of this event may not be a reasonably practicable step for A to take. A standing requirement to use content notes may encourage more intrusive investigation of the content of seminars, readings or speaker events. An expectation of content notes may also discourage academics from exposing students to new controversial material (so as not to risk wrongly including no, or the wrong type of, content note).
You could of course just as easily argue that failing to issue “content notes” could have a chilling effect on some students’ active participation. Alternatively, you could double down and chuck in a minimalist little qualifier for cover:
However, there may be occasions when the use of specific content notes may be helpful to enable students to access material, if there is evidence that they are in fact helpful.
The point isn’t to debate whether they work or not – the point is that OfS suddenly gets to pick and choose what it thinks could chill, while demanding that rules reflect specificity and extremity over individual conduct for harassment. It’s culture war politics shoehorned into regulation, with the law lingering around in the background.
You might remember a major news story in 2021 when a student at Abertay was investigated after other students complained that she made “hateful, discriminatory, sexist, racist and transphobic” remarks during an online seminar on gender politics.
Following an investigation, it was determined that Lisa Keogh had a case to answer in relation to “making inappropriate comments” which “could be construed as discriminatory” – but after a panel reviewed recordings made available from the seminar, it found no evidence of discrimination:
As a result, the board found there was insufficient evidence to support the allegations made against you on your behaviour in class and, therefore, decided to not uphold the charge of misconduct.
Keogh’s argument was that she should never have been subject to formal processes in the first place – and so sued.
Her case was basically that the university acted in breach of the Equality Act 2010 by pursuing her for “expressing her gender critical beliefs” and caused “stress at the most crucial part of my university career” – but Dundee Sheriff Court dismissed her case, with Sheriff Gregor Murray saying that university was entitled to take steps to investigate complaints:
The number, nature and timing of the allegations, and the involvement of at least three final year students who were about to sit examinations, all placed the university in exactly the type of “tricky territory” that entitled it to investigate immediately.
The defender was entitled to take steps to investigate complaints. It could not be guilty of discrimination simply because it did so. Following investigation in this case, the complaint against the pursuer was not upheld.
Cases like that then get mangled into examples like Example 40 in the guidance. In the vignette, a professor expresses views that upset some students – they bring a complaint, there is a lengthy investigation process, and at the end of the process the university finds that there is no case to answer.
This should have been clear to investigators at the outset, but the university was concerned that closing the investigation quickly would further offend the students who complained. The prospect of a lengthy investigation with an uncertain outcome may deter students and staff from putting forward unpopular views on controversial topics.
Again, you can just as easily argue that rapidly dismissing students’ genuinely held concerns would have a chilling effect on their confidence to complain, and that students making formal complaints of this sort is so rare that a university would be wise to carefully investigate whether there’s an underlying fire accompanying the smoke.
But as above, OfS seems to be saying “if students weren’t describing specific behaviours that would meet the harassment test, don’t even investigate” – applying a specific and objective test to harassment while being speculative and partial over its chilling test.
The original draft was fairly silent on antisemitism – an obvious issue given the high-profile nature of the coverage and political commentary on it, not least in the context of protests surrounding the war in Gaza.
Notwithstanding the specific stuff on “time, place and manner” (see below and here) and what OfS might be counting as an “essential function” of a university (again, see below), what I would say is that if there’s a debate about whether action A, protest B or leaflet C amounts to antisemitism, it’s pretty obvious that those advocating the adoption of the IHRA definition are seeking to have it used when making a judgement.
Some will argue (like Arif Ahmed once did) that universities should not adopt the definition:
This “definition” is nothing of the kind; adopting it obstructs perfectly legitimate defence of Palestinian rights. As such it chills free speech on a matter of the first importance. I hope the Secretary of State reconsiders the need for it; but these new free speech duties ought to rule it out in any case.
We’ve covered his mysterious conversion before – and wondered how that might manifest in any final guidance. It doesn’t, at all – but what we do get in the consultation commentary is this astonishing paragraph:
We do not comment in this guidance on the IHRA definition of antisemitism or on any other proposed non-legally binding definition that a provider or constituent institution may wish to adopt. Nonetheless, we have adopted the IHRA definition because we believe that it is a useful tool for understanding how antisemitism manifests itself in the 21st century. The IHRA definition does not affect the legal definition of racial discrimination, so does not change our approach to implementing our regulatory duties, including our regulatory expectations of registered providers. A provider that adopts any definition (of anything) must do so in a way that has particular regard to, and places significant weight on, the importance of freedom of speech within the law, academic freedom and tolerance for controversial views in an educational context or environment.
Some will argue that adoption – either by OfS or providers – has precisely the kind of chilling effects that are railed against at length throughout the guidance. Others will argue that adoption as a kind of interesting window dressing without using it to make judgements about things is pointless, raises expectations that can’t later be met, and allows antisemitism to go unchecked.
I’d argue that this is another classic case of Kafka’s cake and eat it – which dumps a deep set of contradictions on universities and requires attention and leadership from regulators and politicians. We are still not there.
As well as that central thread, there are various other issues in the guidance worthy of initial note.
A major concern from mission groups was the way in which the new duty might play out over transnational branch campuses – especially those with rather more oppressive legal regimes over expression than here.
We might have expected OfS to use some sort of “what’s practicable relates to the law in the country you’re delivering in” qualifier, but it has somehow managed to square the circle by simply stating, with no further qualification (P13) that:
HERA does not require providers or constituent institutions to take steps to secure freedom of speech in respect of their activities outside England.
It’s an… interesting reading, which is maybe related to the usual territorial extent qualifiers in legislation – the consultation commentary is similarly (and uncharacteristically) silent – but what it does appear to do is contradict the usual prescription that it’s about where the main base of the provider is, not where it’s provision is, that sets the duties.
Even if some legal workaround has been found, it does start to call into question how or why OfS can regulate the quality of your provision in Dubai while not worrying about freedom of speech.
Another section with a mysteriously short sentence is one on the original Donelan conundrum:
The OfS will not protect Holocaust denial (by visiting speakers or anyone else).
That’s a carefully worded sentence which seems to be more about OfS making choices about its time than an explanatory legal position. Unlike in many other countries, holocaust denial is not in and of itself illegal in the UK – although in the weigh up, Article 17 of the ECHR removes protection from speech that is contrary to fundamental convention values, and cases in the UK have tended to be prosecuted under other legislation such as section 127 of the Communications Act 2003 when the content is deemed “grossly offensive”.
Quite why OfS has not chosen to explain that is unclear – unless it’s worried about revealing that all sorts of other types of grossly offensive stuff might fall under the balancing provision. And more to the point, as I’ve often said on the site, most holocaust deniers don’t announce that the title of their talk in Room 4b On Tuesday evening will be “the holocaust is a fiction” – which opens up the question of whether or not it’s OK to outlaw holocaust deniers who may or may not engage in actual holocaust denial when they turn up.
The sole example in the guidance on the weigh-ups over external speakers and extremism is one where the proposed speaker is a self-professed member of a proscribed group. It’s easy to say “well it’s fine to ban them” – what we don’t have here is anything meaningfully helpful on the real cases being handled every year.
And some of the media’s hardy perennials – universities doing things like signing up to charters with contested “values” or engaging in contested work like decolonisation – are also either carefully contorted or preposterous.
Hence Example 51 describes a university that [overtly] requires that all teaching materials on British history will represent Britain in a positive light – one of the many not as clever as the authors think they are inversions of the allegations often thrown at woke, UK history hating academics.
Meanwhile Example 52 nudges and winks at the Stonewall Charter by describing a department of a university that applies for accreditation to a charter body with links to the fossil fuel industry, where the accreditation process requires it to sign up to a set of principles that include:
Fossil fuel exploration is the best way to meet our future energy needs.
The text underneath is fascinating. Once you’ve got the “depending on the circumstances” qualifier out of the way, we learn that “institutional endorsement of this principle may discourage expression of legally expressible views”. That’s your “chilling” allegation again.
But rather than warning against signing it, we merely get:
…not implementing the provisions of any accreditation that risks undermining free speech and academic freedom is likely to be a reasonably practicable step that university B should now take.
Replace that with the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance (IHRA) definition of antisemitism, and you can see why the fudge above will satisfy no-one.
I’ve read the para in the guidance several times now, and each time I read it I resolve different things. Either the university can take a position on contested ideas as long as these aren’t imposed on staff, or it can’t because taking the position on contested ideas would chill staff. Flip a coin.
It’s that sort of thing that makes the otherwise helpful section that clarifies that you can have a code of conduct for staff and students so silly. Codes of conduct are fine as long as any restrictions on speech reference a legal rule or regime which authorises the interference, that the student, member, member of staff or visiting speaker who is affected by the interference has adequate access to the rule, and if the rule is:
…formulated with sufficient precision to enable the student, member of staff or
visiting speaker to foresee the circumstances in which the law would or might be applied, and the likely consequences that might follow.
I’d tentatively suggest that while that makes sense, OfS’ own guidance represents a set of rules where forseeing how it might respond to a scenario, and the likely consequences that might follow, are clear as mud.
To clear up protest and disruption rights, OfS stresses viewpoint neutrality, uses its “time, place and manner” confection we first saw last year, and also has a new oft-repeated “essential functions” of higher education qualifier of:
…learning, teaching, research and the administrative functions and the provider’s or constituent institution’s resources necessary for the above.
I can’t really call whether OfS thinks the sports hall counts, or whether it thinks the encampment is OK there, but not in a seminar room. Either way, it’s another of those vague definitions that feels open to abuse and interpretation by all sides of a dispute and by OfS itself.
Another allegation thrown at universities is often about EDI training – Example 53 sets up the idea that an online EDI induction asks if white people are complicit in the structural racism pervading British society, where the only answer marked correct is “True” – a candidate who ticks “False” is required to re-take the test until they have explicitly assented to “True”.
Maybe I’m being naive, but if that’s grounded in a real example I’d be more worried about that provider’s wider approaches to teaching and assessment than its approach to free speech.
A few other fun bits. Fans of reputation management will be disappointed to learn at Example 22 that a social media policy requiring staff to not to post material that is “unnecessarily critical”, coupled with a strong but lawful pop at the provider’s employment practices in a public post on social media, would represent a “protect” policy breach and a “protect” practice breach if the staff member ends up with a warning.
Meanwhile, notwithstanding the silence over whether full-time SU officers are members or students of a provider, Example 23 has a student representative posting unfavourable commentary on university management on the SU’s website, along with some student testimonials describing students’ experiences of accommodation:
University Z requires the student to remove this post on the grounds that if the post is reported more widely in the media, this would threaten University Z’s recruitment plans.
That that would be a breach may feel like a problem for the small number of universities whose senior managers directly threatened SU officers over TEF student submission drafts.
But more broadly, like so many other examples in the guidance, neither the staff nor the student example get at broader culture issues.
You might argue that “reasonably practicable steps” in both cases might involve specific commitments to enable dissent, or more explicit encouragement of public discussion over controversial issues.
You could certainly argue that much of the committee discussion marked “confidential” should be nothing of the sort, and that non-disclosure agreements imposed on settled-with complainants outside of the specific ban on those in sexual misconduct cases should be outlawed.
You could also argue that in both cases, fears over future funding – your salary for the staff member, your block grant for the SU officer – are classic chillers that need specific steps to be taken. Alas, none of that sort of “why” stuff appears.
There’s also still a whole bunch of headscratchers. What happens when three different providers have three different sets of policies and codes and all franchise their provision to a fourth provider? Should providers be inspecting the reputation rules in the employment contracts of their degree apprentices or other credit-based work based learning? Now the requirement to tell all new students about all this has been softened, isn’t there still a need to include a lot of FoS material in the still compulsory training to be offered as per E5? And so on.
In the complaints scheme consultation, there was some controversy over the definition of visiting speakers – including when an invitation manifested as an actual invitation and who was capable of extending one. On this, OfS has actually decided to expand its definition – but neatly sidesteps the Amber Rudd dilemma, namely that while it’s easy to expect people in power to not cancel things because some object, it’s a lot harder to make a volunteer student society run an event that it changes its mind about, regardless of the reason.
And when the guidance says that OfS would “generally” expect providers to reject public campaigns to punish a student or member of staff for lawful expression of an idea or viewpoint that does not violate any lawful internal regulations, we are still stuck in a situation where some basic principles of democracy for anyone elected on campus – staff, but more often than not, students – come into direct conflict with that expectation even if they are “organised petitions or open letters, an accumulation of spontaneous or organised social media posts, or long-running, focused media campaigns”.
There may well be plenty more to spot in here – legal eagles will certainly be pouring over the document, expectations on all sides may need to be reset, and all in a context of very tight timescales – not least because much of the material implies a need for a much wider review of related policies than just “write a compliant Code”.
Everyone should also think carefully about the YouGov polling. There are some important caveats to be attached the results and some of the splits based on wording, assumptions and whether it’s even reasonable to expect someone teaching something highly technical to be wading into the sex and gender debate. And whether you’re teaching, researching or otherwise supporting, it must be the case that not all subject areas include as much scope for controversy and “debate” than others.
But even if you quibble over the N equalling 184, when 24 per cent of those who do not feel free in their teaching cite fear of physical attack, there is a problem that needs urgent interrogation and resolution.
(Thanks as ever to DK for the visualisation of the YouGov polling – sample size 1234 adults and weighted for teaching staff in England, by age, gender, region, and contract type)
We also still have the debate over the partial repeal of the Act to come too, some additional complexity over complaints to resolve, and as I note above, huge questions like “so can we adopt the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance (IHRA) definition of antisemitism or not” remain unanswered – as well as a set of inevitable conflicts to come over the practical application of the Supreme Court ruling on the meaning of “woman” in EA2010.
I should also say that I’ve not had time to properly interrogate the research aspects in the guidance – but we’ll get to that with my colleague James Coe in the coming days.
What I’m mainly struck by – other than the ways in which a particular set of (contested) views on campus culture have been represented as apolitical – is the way in which, ultimately, much of the material comes down to the regulatory realities of expecting authority to behave.
In some senses, that’s not unreasonable – governors and leaders hold considerable influence and power over students and staff, and what they ban, or punish, or encourage or celebrate can have important impacts that can be positive for some, and negative for others.
But to the extent to which there really is a problem with free speech (and academic freedom) on campus, much of it feels much wider and organic than the hermetically sealed campus community assumptions at play in documents of this sort.
I won’t repeat so many of the things I’ve said on the site over the past few years about confidence being key to a lot of this – suffice to say that the freedom ideal at play in here feels like something that is easier to experience when steps have been taken to improve people’s security, given them time and space to interact meaningfully with each other, and act specifically to boost their bravery.
Not only should some of the solutions be about resolving conflicts and integrating the concerns into a more stable definition of what it is to be a member of staff or a student, of all the agendas in higher education, it strikes me that this area remains one where solutions and sticks and games of blame abound, but causal analysis feels hopelessly weak.
In the absence of alternative guidance on the “promote” duty, if I was high up in a university, I’d be resolving to interrogate more carefully and listen more closely before I pretended that my shiny new Code of Practice will do anything other than tick the boxes while making matters worse.

Nearly six thousand current and former staff at Griffith University have been underpaid more than $6m over the past decade and will receive more than $8m in back-pay.
Please login below to view content or subscribe now.

New York, NY – Counslr, a leading B2B mental health and wellness platform, announced today that it has expanded its footprint into the State of Texas starting with a partnership with Colorado Independent School District (ISD) in Colorado City, TX. This partnership will empower students and staff to prioritize their mental health by enabling them to access unlimited live texting sessions with Counslr’s licensed and vetted mental health support professionals, who are available on-demand, 24/7/365 and also utilize the app’s robust and curated wellness resources. By increasing accessibility to Counslr’s round-the-clock support, Colorado ISD aims to empower those silent sufferers who previously did not or could not access care, whether due to cost, inconvenience, or stigma.
Texas is facing a critical mental health care crisis, with over 95% of its counties officially designated as Mental Health Professional Shortage Areas. This alarming statistic underscores the severe lack of access to mental health services across the state, particularly in rural, border, and frontier communities. This resource scarcity underscores the urgent need for additional resources and innovative solutions to bridge this critical care gap for school communities.
“We’re excited to partner with Counslr to bring innovative, accessible mental health resources to our school community,” said Alison Alvarez, Family and Community Engagement Coordinator, of Colorado ISD. “This partnership empowers our 6-12 grade students and staff with the support they need to thrive—both in and out of the classroom.”
As factors such as academic pressures, social media influence, burnout and world events contribute to an increase in mental health challenges for young people, schools throughout the country are recognizing the growing need to offer more accessible, prevention-focused resources. A recent study found that digital mental health apps like Counslr can play an important role in expanding access to mental health support, especially for school communities. Most users turned to Counslr through on-demand sessions, showing just how valuable it is to have someone available in the moment when support is needed most. Interestingly, more than 80% of sessions happened between 7 PM and 5 AM, a time when traditional counseling services are usually unavailable. This suggests that Counslr helps fill a critical gap, offering students and school community members a reliable way to talk to licensed counselors around the clock. The app was also used for a wide range of concerns, highlighting its potential to meet diverse mental health needs through both immediate and scheduled support.
“As we expand across the country, we’re proud to partner with new school communities to ensure that every student, regardless of location or background, has access to the mental health support they deserve,” said Josh Liss, Counslr CEO. Adding that, “With most of Counslr’s users being first-time care seekers, we’re excited to help reach those traditionally unreachable, who need help but do not or cannot access it, no matter where they are located.”
ABOUT COUNSLR
Counslr is a text-based mental health support application that provides unlimited access to robust wellness resources and live texting sessions with licensed professionals, 24/7/365. Users can access support on-demand within two minutes of opening the app, or by scheduled appointment. Through real-time texting, users enjoy one-on-one, private communication with a licensed counselor that can be conducted anytime, anywhere. Counslr was designed to help individuals deal with life’s day-to-day issues, empowering individuals to address concerns while they are “small” to help ensure that they stay “small”. Counslr partners with organizations of all shapes and sizes (companies, unions, nonprofits, universities/colleges, high schools, etc) so that these entities can provide Counslr’s services to their employees/members/students at no direct cost. For more information, please visit www.counslr.com.

More than 300 NIH employees criticized their director, Jay Bhattacharya, in the letter published Monday.
Jim Watson/AFP/Getty Images
Hundreds of staff at the National Institutes of Health are publicly condemning the agency’s actions in recent months, including firing thousands of workers and canceling research grants for projects that don’t align with the Trump administration’s ideologies.
In a letter sent Monday morning to Jay Bhattacharya, the Trump-appointed NIH director who gained notoriety for his criticism of the NIH’s handling of the COVID-19 pandemic, more than 300 employees from across the agency called on him to deliver on his promise to embrace dissent, which he has called “the very essence of science.”
“We are compelled to speak up when our leadership prioritizes political momentum over human safety and faithful stewardship of public resources,” states the letter, titled the Bethesda Declaration (Bethesda, Md., is the location of the NIH’s main campus) and modeled after Bhattacharya’s own Great Barrington Declaration, which condemned the NIH in 2020 for ignoring his calls to mostly cease pandemic-related precautions.
“This censorship is incompatible with academic freedom, which should not be applied selectively based on political ideology.”
In addition to accusing Bhattacharya of politicizing research, the letter published Monday also criticized the agency for “undermining” peer review, unilaterally capping indirect costs and firing NIH staff.
Bhattacharya is scheduled to appear before the Senate appropriations subcommittee today to discuss Trump’s proposal to cut $18 billion or about 40 percent from the NIH’s budget.

Get stories like this delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter
LARAMIE—The Lab School is a family affair for Corelle Lotzer.
Not only did Lotzer enroll her daughter and son in the school, but she taught math here for over a decade. Her daughter, who thrived years ago as a student in the K-8 atmosphere, returned as an adult to work as a paraprofessional — just down the hall from her mom.
Because Lotzer took a year off to take care of an aging aunt, she lost tenure. So when the closure of the 138-year-old school became official this winter, she did not receive a contract with the district to continue working at one of its other schools.
Lotzer, who was raised in Laramie, instead accepted a position at Cheyenne East High School. In early May, she was still trying to figure out the logistics involved with working in Cheyenne while her other, younger kids continue their education in Laramie.
“It’s been tough,” Lotzer said in a second-story room in the Lab School. The shrieks and laughter of children at recess drifted in from an open window. “I would have rather stayed in Albany County.”
Lotzer is one of 11 Lab School teachers without tenure, Principal Brooke Fergon said. “That’s probably been the most difficult challenge, that our tenured teachers have been placed in other schools throughout the district, and our teachers who do not have tenure … were not initially placed in positions.”
It’s not the only pain point involved in closing a school that predates the state of Wyoming itself. Many people fought to keep the Lab School open, and the past year has been a rollercoaster of emotions for school staff, students and their families as hopes have been raised and dashed, Fergon said. The school, which sits on the University of Wyoming campus, started as an educational learning site for college students studying to be teachers. It’s beloved for its experiential and outdoor-based approach to learning and emphasis on inclusivity.
But the school’s future was thrown in doubt last summer as the university and Albany County School District 1 hit a stalemate over a lease agreement. School advocates pleaded to keep it open by some means and floated ideas that didn’t stick. The Lab School no longer served its former functions, university and district officials said, and issues from maintenance costs for the 75-year-old building to district-wide enrollment trends factored into closure talks.
The final Hail Mary came during the Wyoming Legislature. A bipartisan bill sponsored by Laramie Democrat Chris Rothfuss would have required UW and a coordinating district to operate a K-8 public lab school. The bill passed out of the Senate, but House lawmakers killed it in February, and that was pretty much that for the Lab School.
In the last year, Fergon said, “I think we’ve really been sitting in a place of uncertainty, just with all of the different avenues that could have kept the school going, and so that did feel kind of like a final door closing.”
And for her staff, she said, “even though we’re not happy to say goodbye to the school, and we didn’t want to see the school close, I think that having some certainty and a path forward … feels better than just sitting in limbo.”
With the school year ending Thursday, Lab School students will be saying goodbye to their classrooms and dispersing to other schools in the district. Some teachers will too, but others are starting new jobs or moving out of Laramie entirely. The school community spent the last couple of months bidding farewell, some with regret about how it ended.
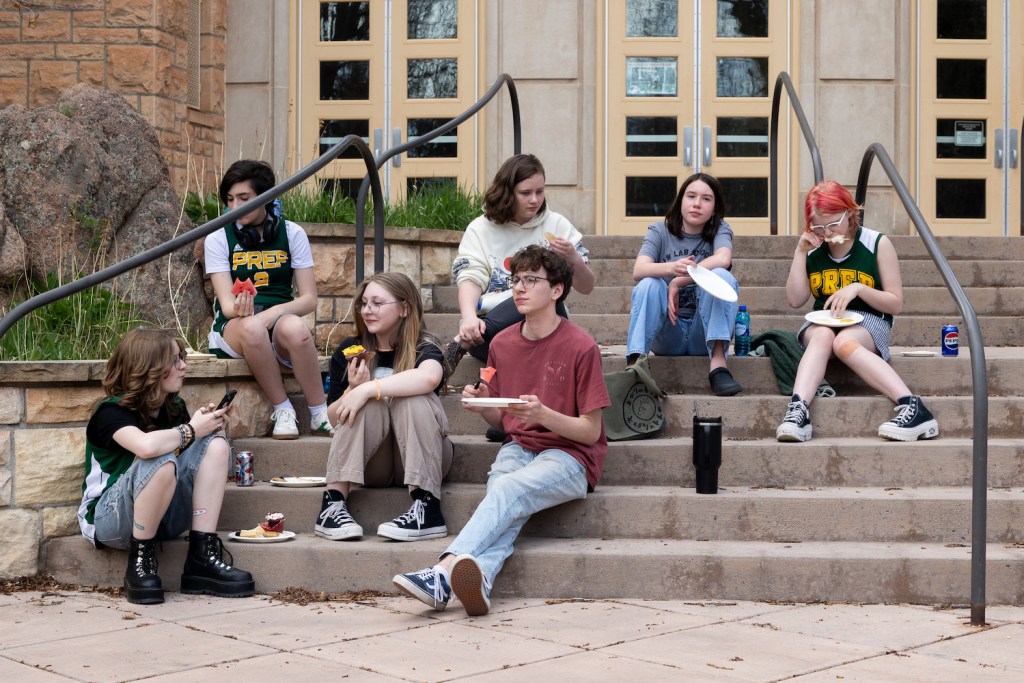
“We love the school,” said Lindsey Rettler, a parent with two elementary students in Lab. Rettler was experiencing a mixture of emotions, she said in May. “Surprise, a little bit of shock, really, really sad, super disappointed and honestly, quite betrayed by those who are supposed to be leading people based on what’s best for the people.”
The school was established in 1887 as the Preparatory School to serve secondary education students from counties without access to high school. In 1913, it transitioned to the Training Preparatory School, used as a learning laboratory by UW’s College of Education.
In 1999, the private school partnered with the Albany County School District to become a district public school. The Lab School then operated as a “school of choice,” meaning any district family could enter a lottery to enroll their kids.
College of Education students continued to train in its classrooms, but they also did so in classrooms across the district, state and beyond.
Historically, UW and the school district operated with a memorandum of understanding laying out terms of tenancy. Efforts to renew that MOU, however, failed to produce an updated agreement. Instead, the university announced last summer it was pursuing an extension only for the 2024-’25 school year, meaning the school would have to find a new home if it was to continue beyond that.

Among the major sticking points: whether the district or UW should pay for things like major maintenance in the aging building. UW also cited the fact that the school “no longer serves a significant role for teacher training in UW’s College of Education,” along with security challenges regarding having a school-district-operated facility located on university grounds; the Lab School’s incongruence with the state’s public funding model and the fact that the school district “has excess capacity in its existing facilities to accommodate current Lab School students.”
The Albany County School District Board of Trustees voted in December to close the Lab School after considering options to move it into another district building. Trustees expressed heartache but also a fiduciary obligation before making the decision.
Concerned residents bemoaned the decision, and Albany County state lawmakers took notice. Sen. Rothfuss’ bill was the product of that concern. The bill brought together strange bedfellows, with co-sponsors ranging from Freedom Caucus-aligned lawmakers like Ocean Andrew to Laramie Democrat Karlee Provenza. Both serve in the Wyoming House of Representatives.
The issue raised questions about the state’s role in local education and what constitutes a situation so exceptional that lawmakers should meddle. Lab School supporters argued its unique role as a teaching laboratory and its century-plus of education history made it a place worth saving.
“This legislation is not about saving a school,” Rep. Andrew, R-Laramie, said on the House floor on Feb. 28. “It is about protecting a legacy and educating future generations of Wyoming teachers.”

True local control reflects the wishes of the people in the community, he continued, “and in this case, the overwhelming support for keeping the Lab School open has been ignored. The people of Wyoming, the parents and the students have spoken, and they have been met with indifference by those in power.”
But others said the state should not interfere in a matter of local concern.
“This really feels like we’re being asked to micromanage a local school,” said Rep. Art Washut, R-Casper. “I don’t think this is the proper role of the state legislature.”
The body ultimately killed the measure on a 24-32 vote.
With that, school staff began the work of transition, making plans with its 145 students to help them figure out transfer schools and options, Fergon said.. The school counselor even brought in a “transition curriculum” to help students navigate and cope with the stress of such significant change.
There was also a staff of roughly 20 teachers along with employees like janitors and paraprofessionals. Many say they are sad to leave a school community that felt like family.
Some, like Fergon, are continuing to work in the district. She will be an assistant principal at another high school.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter

This story was originally published by Chalkbeat. Sign up for their newsletters at ckbe.at/newsletters.
A federal judge on May 22 issued a preliminary injunction blocking President Donald Trump’s executive order to shut down the U.S. Department of Education and said the agency must reinstate the employees who were fired as part of mass layoffs.
After U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon announced the agency’s plans in March to slash its workforce by roughly half, she called it a first step in getting rid of the agency. Trump followed days later with his executive order aiming to eliminate the department, a move he has long wanted.
But only Congress can actually eliminate the department, and the administration’s attempt at getting around that influenced U.S. District Judge Myong Joun’s Thursday ruling.
The Trump administration argued that they implemented agency layoffs to improve “efficiency” and “accountability,” the Massachusetts judge wrote, but then said: “The record abundantly reveals that [the administration’s] true intention is to effectively dismantle the Department without an authorizing statute.”
Joun added: “A department without enough employees to perform statutorily mandated functions is not a department at all. This court cannot be asked to cover its eyes while the Department’s employees are continuously fired and units are transferred out until the Department becomes a shell of itself.”
Within hours of the Joun’s ruling, the Trump administration filed an appeal.
“This ruling is not in the best interest of American students or families,” Madi Biedermann, Deputy Assistant Secretary for Communications, wrote in a statement.
Calls for the injunction came from lawsuits filed by the Somerville and Easthampton schools districts in Massachusetts along with the American Federation of Teachers, other education groups, and 21 Democratic attorneys general.
They argued that the gutting of the department rendered the agency incapable of performing many of its core functions required by Congress.
For example, all of the attorneys from the agency’s general counsel office who handle grants for K-12 schools and grants under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, or IDEA, had been fired. The dismantling of the Office for Civil Rights made it difficult to enforce civil rights protections. The department’s Financial Student Aid programs, which provide financial assistance to almost 12.9 million students across approximately 6,100 postsecondary educational institutions, were also hampered.
Trump’s executive order instructed McMahon to “take all necessary steps to facilitate the closure of the Department of Education and return authority over education to the States and local communities” to the “maximum extent appropriate and permitted by law.”
At the same time, the order said McMahon should ensure “the effective and uninterrupted delivery of services, programs, and benefits on which Americans rely.”
Trump said he would move the agency’s student loan portfolio to the Small Business Administration, and the Department of Health and Human Services would replace the Education Department’s role in “handling special needs.”
Before the layoffs, the Education Department was the smallest of the 15 cabinet-level departments in terms of staffing, according to the judge, with around 4,100 employees. And the plaintiffs said the agency was strained meeting its obligations even then.
The ruling was not based on the employees’ job rights, but rather how the agency was able to fulfill its obligations.
“It’s not about whether employees have a right to a job,” said Derek Black, a University of South Carolina law professor. “It’s about whether the department can fulfill its statutory obligations to the states and to students.”
The case made by former department employees, educational institutions, unions, and educators, Joun wrote, paints “stark picture of the irreparable harm that will result from financial uncertainty and delay, impeded access to vital knowledge on which students and educators rely, and loss of essential services for America’s most vulnerable student populations.”
American Federation of Teachers President Randi Weingarten heralded the judge’s ruling, calling it “a first step to reverse this war on knowledge and the undermining of broad-based opportunity.”
But Biedermann, from the Education Department, said the ruling was unfair to the Trump administration.
“Once again, a far-left Judge has dramatically overstepped his authority, based on a complaint from biased plaintiffs, and issued an injunction against the obviously lawful efforts to make the Department of Education more efficient and functional for the American people,” she said in a statement.
Chalkbeat national editor Erica Meltzer contributed reporting.
Chalkbeat is a nonprofit news site covering educational change in public schools.
For more news on federal policy, visit eSN’s Educational Leadership hub.
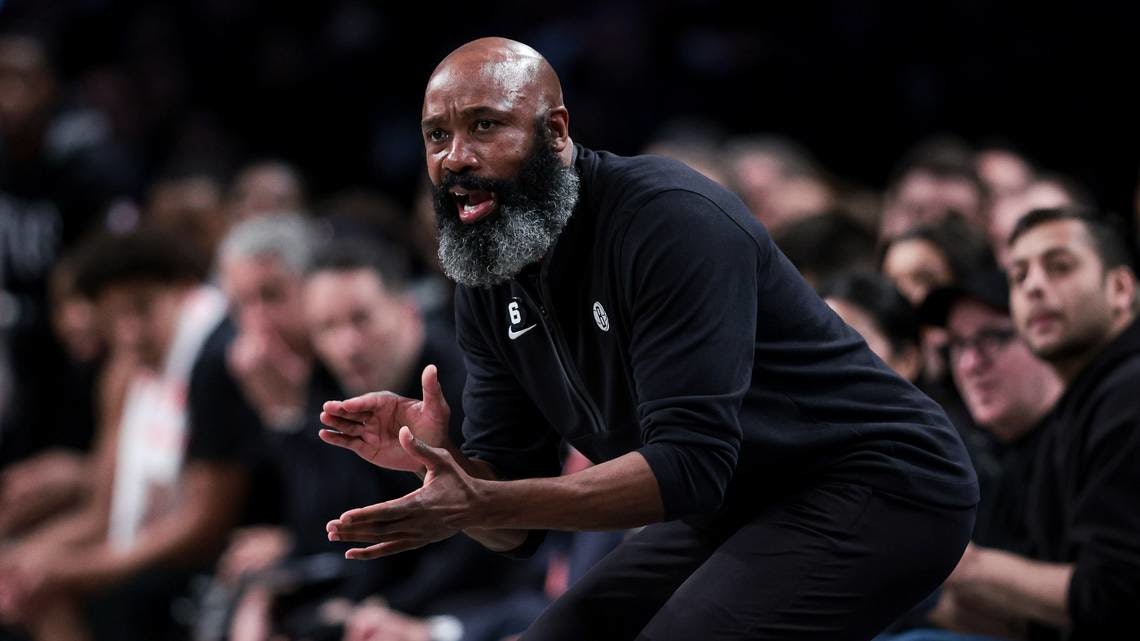

Vaughn returns to Kansas as an assistant coach under Bill Self, becoming the first former NBA head coach to join the Jayhawks’ coaching staff.
Vaughn brings more than 15 years of NBA coaching experience, having served as head coach for both the Orlando Magic and Brooklyn Nets. During his coaching tenure, he mentored NBA All-Stars including Kevin Durant, Kyrie Irving, and Ben Simmons, as well as former Kansas players Markieff Morris and Jalen Wilson.
“We’re very excited to welcome Jacque and Laura into the fold,” Self said. “I’ve known Jacque from a distance for several years now and have always admired how he has conducted himself professionally and how he has treated people.”
Vaughn’s Kansas career from 1993-97 established him as one of the program’s most exceptional student-athletes. He concluded his collegiate career as the Big Eight Conference’s all-time assists leader with 804 assists, earning second-team All-American honors during his senior season under Roy Williams while maintaining extraordinary academic standards.
His scholarly achievements were equally impressive, earning Academic All-American First Team selections in both 1996 and 1997. Most notably, Vaughn received the 1997 Academic All-American of the Year award, joining Cole Aldrich as the only Kansas players to earn this prestigious national recognition. Additionally, he was honored by Diverse with the Arthur Ashe Jr. Scholar-Athlete Award in 1996, cementing his status as a role model for student-athletes nationwide.
Following his collegiate career, Vaughn was drafted 27th overall by the Utah Jazz in 1997 and enjoyed a 12-season NBA playing career that included stops with five teams and culminated in an NBA Championship with the San Antonio Spurs in 2007. He transitioned to coaching as an assistant with San Antonio before becoming head coach of the Orlando Magic in 2012, later leading the Brooklyn Nets to playoff appearances in 2020 and 2023.
“I’m truly honored and overwhelmed with excitement to return to my alma mater,” Vaughn said. “I couldn’t pass up the opportunity to bring those experiences back to the school that means so much to me.”
Vaughn replaces Norm Roberts, who recently retired, representing a powerful example of how academic excellence and athletic achievement can create pathways for continued leadership in higher education.
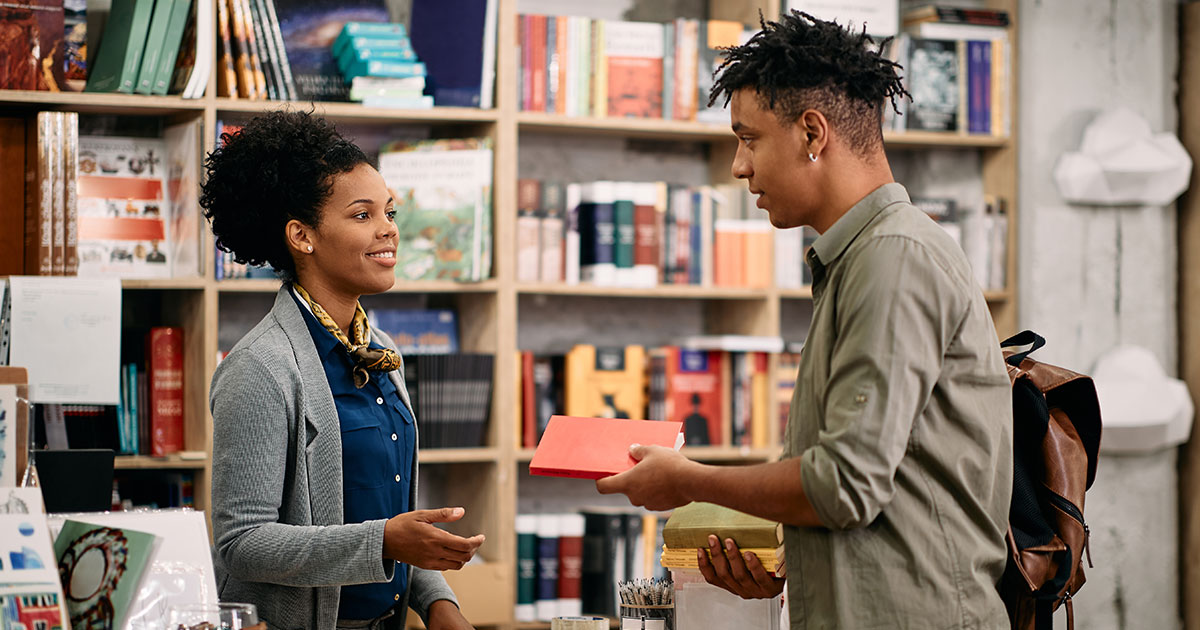

By knowing about and engaging with these key figures on campus, you can make the most of your college experience and set yourself up for success.

Director, National Resource Center for the First-Year Experience and Students in Transition, University of South Carolina

Associate Director for Faculty Development and Resources, University 101 Programs, University of South Carolina
Congratulations! You’ve made it to your first day of classes! You are excited by the opportunities before you…and overwhelmed. Colleges and universities employ a host of staff and faculty whose primary role is to support your success. Part of your tuition and fees go to support these folks — you should use them! Meet the 10 people you need to maximize your college experience.
You’re surely familiar with the folks teaching your courses. Use office hours to get to know your instructors. Ask them how they got into their fields and why they love their work. You might be interested in a similar topic, land yourself a research opportunity, or find yourself a new mentor!
Course registration should not be the last time you speak with your academic advisor! Academic advisers help anytime you are thinking about your course of study, whether you want to drop a class, change your major, add a minor, take a summer class, or figure out how to work a study abroad program into your plan.
Librarians have magical skills to make your classwork so much easier. Okay, it’s not really magic, but they can help you find awesome sources for class papers and teach you about technical resources like citation management software to make your work a lot easier!
Is chemistry or calculus stressing you out? Your institution has a student success center or a tutoring center to help. Our advice: Get help as soon as you start feeling overwhelmed. Don’t wait until you’re really behind!
You have probably already received your financial aid package, but life happens. If your financial situation changes, the financial aid office is your first call. They might adjust your aid package and/or connect you to additional financial resources.
You probably know to go to the health center if you sprain an ankle or have a sinus infection, but the medical and counseling team can help with a lot more. If you are feeling overwhelmed or are struggling, schedule an appointment to gain access to counseling sessions, support groups, and workshops to help you feel your best (all things which are included in your tuition and fees).

Whether you have mapped out a career plan or have no clue what you want to do, your career center staff can help! It’s not just for seniors — career centers help with career exploration, internships, resume development, and interview skills. They might even be able to help you find an on-campus job so you can build career skills and start earning money while you’re a student.
If you received accommodations in high school, be sure to register with disability services on your campus, as those do not automatically roll over. These may be related to dietary restrictions, learning disabilities, or mental health conditions. They can work with you to ensure you have what you need to be successful!
You didn’t just come to college to study and work, right? Join a student organization, attend fun events, play on an intramural sports team, or take a group exercise class! Besides having a good time, you’ll grow your leadership, teamwork, and communication skills and make friends.
Decades of research on college student success tell us that your fellow students, or your peers, are key to your success. Many of the campus offices employ student staff members, often called peer mentors. By getting involved on campus, you will make friends who support and encourage you.
The folks outlined here can help you get the most out of your college experience. Don’t ever hesitate to ask someone a question, introduce yourself, or try a new resource; it can only help! These amazing people will help find the opportunities that will shape your future. As you build connections with them, you will find friends and mentors to last a lifetime.