This story about children with disabilities was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.
COLUMBUS, Ohio — When Selina Likely became director of the Edwards Creative Learning Center six years ago, she knew there was one longstanding practice that she wanted to change. For as long as she had taught at the thriving child care center, it had turned away many children with disabilities such as autism and Down syndrome. The practice was even encoded in the center’s handbook as policy.
Likely, the parent of a child with a disability, wanted to stop telling families no, but she knew that to do that she and her staff would need more support. “I said, ‘Let’s start getting training and see what we can do.’”
Not too long after, her effort received a big boost from a state-funded initiative in Ohio to strengthen child care teachers’ knowledge and confidence in working with young kids with disabilities and developmental delays. That program, Ohio PROMISE, offers free online training for child care workers in everything from the benefits of kids of all abilities learning and playing together to the kinds of classroom materials most helpful to have on hand. It also offers as-needed mentorship and support from trained coaches across the state.
Related: Young children have unique needs, and providing the right care can be a challenge. Our free early childhood education newsletter tracks the issues.
Child care providers across the country — including large, established centers and tiny home-based programs — struggle to meet the needs of children with disabilities, according to a 2024 report from the U.S. Government Accountability Office. More than a quarter of parents of children with disabilities said they had a lot of difficulty finding appropriate care for their kids. And even those who do find a spot regularly encounter challenges, like having their children excluded from extracurricular activities such as field trips and even academic instruction.
“It’s really hard to find child care for this population, we heard that loud and clear,” said Elizabeth Curda, a director on the GAO’s Education, Workforce and Income Security team and a coauthor of the report. Even the most well-resourced centers report that they struggle to meet the needs of children with disabilities, according to Curda.
There’s a lot of desire at the grassroots level to change that. Ohio PROMISE and a few other recent initiatives provide models for how to expand the capacity — and the will — of child care centers to serve the more than 2 million U.S. children age 5 or below who have a disability or developmental delay.
In Vermont, for instance, officials hope to soon unveil a free, on-demand training program aimed at helping child care teachers have more inclusive classrooms. And officials in Ohio’s Summit County, home to Akron, report growing interest from other counties in creating programs based on Summit’s more than decade-old model that provides in-person training for child care operators in inclusion of children with disabilities.
“We’re helping to create child care centers that feel they can handle whatever comes their way, especially when it comes to significant behavior concerns,” said Yolanda Mahoney, the early childhood center support supervisor for Summit County’s disabilities board.
The federal government until recently encouraged the creation of such models. In 2023, the federal Department of Education and Department of Health and Human Services issued a joint statement urging states to take steps to support inclusion in early childhood settings, including strengthening training and accountability.
Also, a year-old provision of the Child Care and Development Fund, the primary federal funding source for child care, requires that states increase the availability of child care for children with disabilities as a prerequisite for receiving funds. (However, 43 states have received waivers allowing them to delay implementation of that provision.)
Under the current president, federal momentum on the issue has largely stalled. While the administration of President Donald Trump hasn’t directly attacked inclusion in the context of special education, the president has criticized the term more broadly — especially when it comes to diversity, equity and inclusion. That can create uncertainty and a chilling effect on advocates of inclusion efforts of all kinds.
Funding for some inclusion efforts is also in jeopardy. States rely on Medicaid, which faces nearly $1 trillion in cuts over the next decade, to pay for early intervention programs for children birth to age 3 with developmental delays and disabilities. Trump has also proposed eliminating Preschool Development Grants, which states such as Vermont and Illinois have used to expand support of young children with disabilities.
That means over the next few years, progress on inclusion in child care settings could hinge largely on state and local investment. It helps that there’s a “real desire” among providers to enroll more children with disabilities, said Kristen Jones, an assistant director on the GAO’s education, workforce and income security team, who also worked on the report. “But there’s also a concern that currently they can’t do that in a safe way” because of a lack of training and resources.
Related: For kids with disabilities, child care options are worse than ever
In Ohio, the idea for Ohio PROMISE came after an appeal in 2022 from Republican Gov. Mike DeWine. He reported that families were coming to him saying they couldn’t find child care for their kids with disabilities.
“He said, ‘Come to me with ideas to solve that problem,’” recalled Wendy Grove, a senior adviser in the Ohio Department of Children and Youth who spearheaded development of the program.
Grove and her colleagues had already been working on a related effort. In 2020, Ohio won a federal grant that included help exploring how well — or not — children with disabilities were being included in child care and early education settings. DeWine liked the idea Grove’s team presented of morphing that work into a state-led effort to strengthen training and support for child care teachers. They also proposed more direct support to families, including the extension of child care vouchers to families with incomes above the poverty level, with a higher reimbursement rate for children with disabilities.
The training, which debuted about two years ago, is provided in three levels. Jada Cutchall, a preschool teacher at Imaginative Beginnings, an early learning center just outside of Toledo, recently completed the third tier, which for her included customized coaching. Cutchall’s coach helped her create communication tools for a largely nonverbal student, she said, including a board with pictures children can point to if, for example, they want to go to the bathroom or try a different playground activity.
As a result, Cutchall said, she has watched kids with disabilities, including those with speech impairments and autism, engage much more directly with their classmates. “They have the courage to ask their peers to play with them — or at least not distance themselves as much as they usually would,” she said. All of the children in the classroom have benefited, she added, noting that kids without disabilities have taken an interest in learning sign language, strengthening their own communication skills and fostering empathy.
Child care programs where one teacher and one administrator have completed some of the training earn a special designation from the state, which may eventually be tied to the opportunity to get extra funding to serve children with disabilities. In Ohio PROMISE’s first year, 1,001 child care centers — about 10 percent of the total number in Ohio — earned that designation, according to Grove.

The effort costs a little over $1 million in state dollars each year, with most of that paying for several regional support personnel who work directly with centers as mentors and advisers. Over the last two years, Ohio has seen a 38 percent increase in the number of children in publicly funded centers who qualify for the higher voucher reimbursement rate for children with disabilities, which can be double the size of the standard voucher.
Grove hopes that ultimately the effort plays a role in narrowing a critical and stubborn gap in the state: about 27 percent of children without disabilities show readiness on state standards for kindergarten; only 14 percent of children with disabilities do. Since so few disabilities exhibited at that age are related to intellectual or cognitive functioning, “we shouldn’t see that gap,” said Grove. “There’s no real reason.”
One goal of the new efforts is to reduce the number of young children with disabilities who are expelled from or pushed out of care. Those children are frequently asked to leave for behaviors related to their disability, the GAO report found.
Several years ago, a child care center in Columbus expelled Meagan Severance’s 18-month-old son for biting a staff member. The boy has several special needs, including some related to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Severance brought him to Edwards Creative Learning Center, where not too long after Selina Likely shifted into the role of director. The boy also bit a staff member there — not uncommon behavior for toddlers, especially those with sensory sensitivities and communication challenges.
Likely was determined to work with the child, not expel him. “They put in time and effort,” said Severance. “The response wasn’t, ‘He bit someone, he’s gone.’”
Likely empathized. Decades earlier, her own daughter had been expelled from a child care center in her hometown of Mansfield, Ohio, for biting.
“I was so angry and mad at the time — how are you going to kick out a 1-year-old?” she said. The center director didn’t think at all about how to help her child, Likely recalled, instead asking Likely what might be happening at home to make the child want to bite. She said she got no notice or grace period to find a new placement. “That left me in a disheartened place,” she said. “I was like, ‘I still have to go to work.”
Seventeen years old at the time, she was inspired by the injustice of the situation to quit her job in a factory and apply to be an assistant in a child care program. She’s been in the industry ever since, gradually trying to make more space for children like her daughter, who was later diagnosed with autism.

As director, Likely displays the nameplate “chaos coordinator” on her desk. And she’s taken the stance that the center should at least try to work with every kid. She and some of her teachers have completed the first two tiers of the Ohio PROMISE training, as well as some related sessions available from the state. Likely estimates that about 10 percent of the children in her center have a diagnosed disability or developmental delay.
Liasun Meadows, whose son has Down syndrome, chose Edwards several years ago for her then 1-year-old over another program better known for its work with children with disabilities. She has not been disappointed.
Parents of kids with disabilities watch their children like a hawk, she said. “There are certain things you notice that you don’t expect others to notice, but they do at Edwards. They’ve been growing and learning alongside him.”
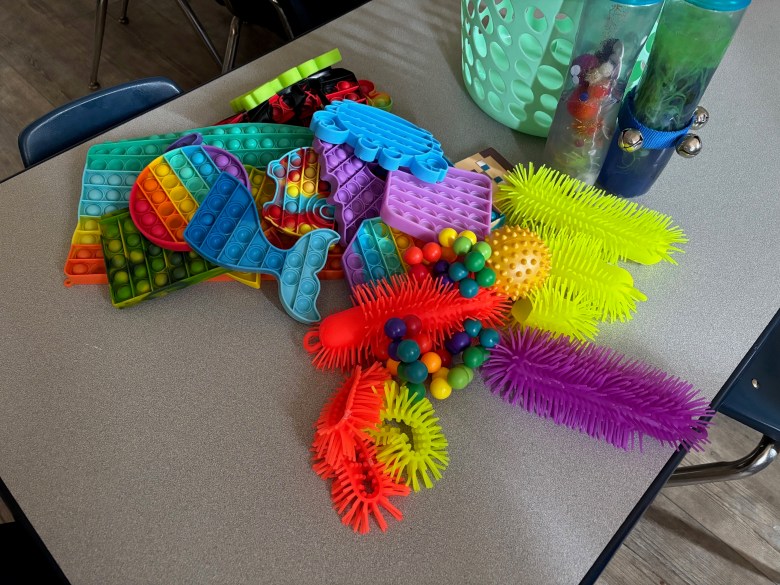
Severance, whose son is now 8, works at the center these days, leading the 3-year-old room, which includes two children who are largely nonverbal. She’s made the classroom more inclusive, adding fidget toys for children with sensory issues, rearranging the classroom to create calming areas, providing communication books to nonverbal children so they can more easily express needs and wants, and teaching everyone some sign language.
“For a while there was segregation in the classroom” between the kids with disabilities and those without, Severance said. But that’s lessened with the changes. “Inclusion has been good for the kids who are verbal — and nonverbal,” she said.
Related: Where do kids with disabilities go for child care?
As in Ohio, state officials in Vermont turned to online training to help ensure young children with disabilities aren’t denied quality care. The state should soon debut the first parts of a new training program, focusing on outreach to child care administrators and support for neurodivergent children. The state wanted to focus on center leaders first because “directors that are comfortable with inclusion lead programs that are comfortable with inclusion,” said Dawn Rouse, the director of statewide systems in Vermont’s Child Development Division.

Vermont also pumped millions of dollars into a separate program, known as the Special Accommodations Grant, that supports young children with disabilities. Since 2009 the state has set aside $300,000 a year that child care centers can tap to provide services for individual children with disabilities. It might help buy specialized equipment for a child with cerebral palsy, for instance, or be used to hire a full- or part-time aide.
The $300,000 has been maxed out every year, Rouse said. And after the pandemic, the need — and the number of applications — surged.
As a result, the state allocated some federal American Rescue Plan and Preschool Development Grant dollars to increase spending on the program by about sevenfold — to between $2 million and $2.5 million annually — an amount Rouse still describes as a “Band-Aid.” Without access to the grants, “we see a lot of children being asked to leave programs,” Rouse said. “That’s not good for any child, but for children with specialized developmental needs it’s particularly bad.”
Over time, Likely hopes, her Ohio center can play a small role in reducing that instability, although the center hasn’t yet been able to work with all such children it wants to. Likely recalls one toddler with a severe disability who climbed up anything he could. There wasn’t enough money to pay for what the child really needed: a full-time aide. “It’s hard when you know you’ve tried but still have to say no,” she said. “That breaks my heart more than anything.”
On one June morning, the center’s teachers acknowledged and celebrated several milestones in its work on inclusion, big and small. One child in the 3-year-old classroom with fine and gross motor challenges was drinking independently from a bottle. The preschool classroom held its first graduation ceremony, translated partly into sign language. All of the kids, no matter their challenges, were set to go on field trips to Dairy Queen and the zoo.
Likely dreams of someday running a center where about half of the children have a disability or delay. It may be years off, she said, but as with the milestones she sees scores of children at the center reach every day, “There’s a way — if there’s a will.”
Sarah Carr is a fellow at New America, focused on reporting on early childhood issues.
Contact contributing editor Sarah Carr at [email protected].
This story about children with disabilities was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.