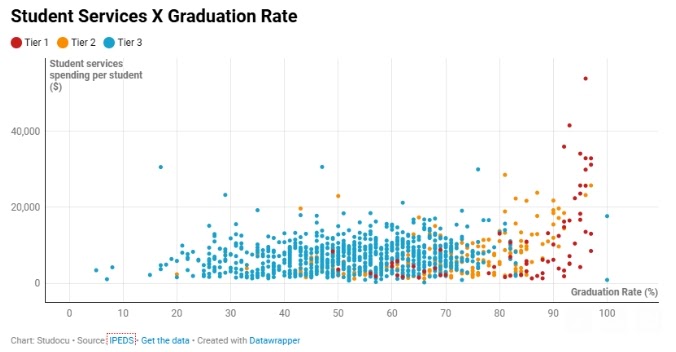
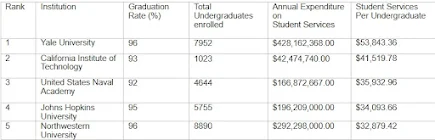
When hackers hit a school district, they can expose Social Security numbers, home addresses, and even disability and disciplinary records. Now, cybersecurity advocates warn that the Trump administration’s budget and personnel cuts, along with rule changes, are stripping away key defenses that schools need.
“Cyberattacks on schools are escalating and just when we need federal support the most, it’s being pulled away,” said Keith Krueger, chief executive officer of the Consortium for School Networking, an association of technology officials in K-12 schools.
Related: Our free weekly newsletter alerts you to what research says about schools and classrooms.
The stakes are high. Schools are a top target in ransomware attacks, and cyber criminals have sometimes succeeded in shutting down whole school districts. The largest such incident occurred in December, when hackers stole personal student and teacher data from PowerSchool, a company that runs student information systems and stores report cards. The theft included data from more than 60 million students and almost 10 million teachers. PowerSchool paid an undisclosed ransom, but the criminals didn’t stop. Now, in a second round of extortion, the same cyber criminals are demanding ransoms from school districts.
The federal government has been stepping up efforts to help schools, particularly since a 2022 cyberattack on the Los Angeles Unified School District, the nation’s second-largest. Now this urgently needed assistance is under threat.
Warning service
Of chief concern is a cybersecurity service known as MS-ISAC, which stands for Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center. It warns more than 5,700 schools around the country that have signed up for the service about malware and other threats and recommends security patches. This technical service is free to schools, but is funded by an annual congressional appropriation of $27 million through the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), an agency within the Department of Homeland Security.
On March 6, the Trump administration announced a $10 million funding cut as part of broader budget and staffing cuts throughout CISA. That was ultimately negotiated down to $8.3 million, but the service still lost more than half of its remaining $15.7 budget for the year. The non-profit organization that runs it, the Center for Internet Services, is digging into its reserves to keep it operating. But those funds are expected to run out in the coming weeks, and it is unclear how the service will continue operating without charging user fees to schools.
“Many districts don’t have the budget or resources to do this themselves, so not having access to the no cost services we offer is a big issue,” said Kelly Lynch Wyland, a spokeswoman for the Center for Internet Services.
Sharing threat information
Another concern is the effective disbanding of the Government Coordinating Council, which helps schools address ransomware attacks and other threats through policy advice, including how to respond to ransom requests, whom to inform when an attack happens and good practices for preventing attacks. This coordinating council was formed only a year ago by the Department of Education and CISA. It brings together 13 nonprofit school organizations representing superintendents, state education leaders, technology officers and others. The council met frequently after the PowerSchool data breach to share information.
Now, amid the second round of extortions, school leaders have not been able to meet because of a change in rules governing open meetings. The group was originally exempt from meeting publicly because it was discussing critical infrastructure threats. But the Department of Homeland Security, under the Trump administration, reinstated open meeting rules for certain advisory committees, including this one. That makes it difficult to speak frankly about efforts to thwart criminal activity.
Non-governmental organizations are working to resurrect the council, but it would be in a diminished form without government participation.
“The FBI really comes in when there’s been an incident to find out who did it, and they have advice on whether you should pay or not pay your ransom,” said Krueger of the school network consortium.
A federal role
A third concern is the elimination in March of the education Department’s Office of Educational Technology. This seven-person office dealt with education technology policies — including cybersecurity. It issued cybersecurity guidance to schools and held webinars and meetings to explain how schools could improve and shore up their defenses. It also ran a biweekly meeting to talk about K-12 cybersecurity across the Education Department, including offices that serve students with disabilities and English learners.
Eliminating this office has hampered efforts to decide which security controls, such as encryption or multi-factor authentication, should be in educational software and student information systems.
Many educators worry that without this federal coordination, student privacy is at risk. “My biggest concern is all the data that’s up in the cloud,” said Steve Smith, the founder of the Student Data Privacy Consortium and the former chief information officer for Cambridge Public Schools in Massachusetts. “Probably 80 to 90 percent of student data isn’t on school-district controlled services. It’s being shared with ed tech providers and hosted on their information systems.”
Security controls
“How do we ensure that those third-party providers are providing adequate security against breaches and cyber attacks?” said Smith. “The office of ed tech was trying to bring people together to move toward an agreed upon national standard. They weren’t going to mandate a data standard, but there were efforts to bring people together and start having conversations about the expected minimum controls.”
That federal effort ended, Smith said, with the new administration. But his consortium is still working on it.
In an era when policymakers are seeking to decrease the federal government’s involvement in education, arguing for a centralized, federal role may not be popular. But there’s long been a federal role for student data privacy, including making sure that school employees don’t mishandle and accidentally expose students’ personal information. The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act, commonly known as FERPA, protects student data. The Education Department continues to provide technical assistance to schools to comply with this law. Advocates for school cybersecurity say that the same assistance is needed to help schools prevent and defend against cyber crimes.
“We don’t expect every town to stand up their own army to protect themselves against China or Russia,” said Michael Klein, senior director for preparedness and response at the Institute for Security and Technology, a nonpartisan think tank. Klein was a senior advisor for cybersecurity in the Education Department during the previous administration. “In the same way, I don’t think we should expect every school district to stand up their own cyber-defense army to protect themselves against ransomware attacks from major criminal groups.”
And it’s not financially practical. According to the school network consortium only a third of school districts have a full-time employee or the equivalent dedicated to cybersecurity.
Budget storms ahead
Some federal programs to help schools with cybersecurity are still running. The Federal Communications Commission launched a $200 million pilot program to support cybersecurity efforts by schools and libraries. FEMA funds cybersecurity for state and local governments, which includes public schools. Through these funds, schools can obtain phishing training and malware detection. But with budget battles ahead, many educators fear these programs could also be cut.
Perhaps the biggest risk is the end to the entire E-Rate program that helps schools pay for the internet access. The Supreme Court is slated to decide this term on whether the funding structure is an unconstitutional tax.
“If that money goes away, they’re going to have to pull money from somewhere,” said Smith of the Student Data Privacy Consortium. “They’re going to try to preserve teaching and learning, as they should. Cybersecurity budgets are things that are probably more likely to get cut.
“It’s taken a long time to get to the point where we see privacy and cybersecurity as critical pieces,” Smith said. “I would hate for us to go back a few years and not be giving them the attention they should.”
Contact staff writer Jill Barshay at 212-678-3595, jillbarshay.35 on Signal, or [email protected].
This story about student cybersecurity was written by Jill Barshay and produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for Proof Points and other Hechinger newsletters.
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn’t mean it’s free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.