This story is part of Hechinger’s ongoing coverage about rethinking high school. Read about high school apprenticeships in Indiana, a new diploma in Alabama that trades chemistry for carpentry, and “career education for all” in Kentucky.
ELKHART, Ind. — The numbers were discouraging, and in some cases getting worse. Nearly 30 percent of Indiana’s high schoolers were chronically absent in 2022. Only about 52 percent of students in the state enrolled in college in 2023, a 12-percentage-point drop in seven years. Fewer students were pursuing other paths, too: The share of students enlisting in the military, for example, declined by 41 percent from 2018 to 2022.
When Katie Jenner toured the state after becoming education secretary in 2021, she heard from many students who said they simply didn’t value high school or see how it would help them. “That was really hard to hear,” Jenner said. “We had to look in the mirror and say, ‘OK, this is the reality. Let’s do better.’”
Jenner and her team began redesigning what high school looks like in Indiana, in an effort to make it more relevant to young people’s futures and help them gain a better grasp of career paths. For too long, she and others argued, kids had been pushed to plan for four-year college, yet only about half of seniors actually enrolled, and those who did go often dropped out before graduating.
When a draft of the plan was released in early 2024, it drew fierce protest from many parents and educators who worried the state was prioritizing workforce learning over academics. Jenner and her staff reworked the proposal, eventually crafting a plan that alleviated some, though not all, of the concerns.
The “New Indiana Diploma” — which was signed into law in April and goes into effect for all incoming first-year students this academic year — gives students the option to earn different “seals” in addition to a basic diploma, depending on whether they plan to attend college, go straight to work or serve in the military. Jenner describes it as an effort to tailor the diploma to students’ interests, expose students to careers and recognize different forms of student achievement.
Experts said the template is something of a model nationally, at a time when more states are reconsidering how to help students prepare for careers and the federal government is also pushing alternatives to four-year college. Elements of that effort have earned bipartisan support: Presidents from both parties have advocated for expanding work-based learning, and President Donald Trump recently called for the creation of 1 million new apprenticeships.
“The basic architecture of American high school is being questioned and challenged,” said Timothy Knowles, president of the Carnegie Foundation.* Indiana is at the forefront of an effort to incorporate more experiential learning instead of restricting education to school buildings, he said: “Indiana is really breaking ground.”
Related: A lot goes on in classrooms from kindergarten to high school. Keep up with our free weekly newsletter on K-12 education.
The initial proposal Jenner’s agency drafted would have created two high school diplomas, “Graduates Prepared to Succeed” and “Graduates Prepared to Succeed Plus.” Both would have scaled back math and science requirements and loosened recommendations for world languages and other electives. Meanwhile, they would have encouraged all students to participate in work-based learning in apprenticeships, internships or job shadowing, with at least 75 hours in such activities required for the “plus” diploma.
In 2024, the state board of education held dozens of meetings to gather feedback on the proposal for the revamped diplomas — and the backlash was intense. Leaders of higher education institutions, including the state’s flagship schools, Indiana and Purdue universities, said students graduating under the new system would not meet minimum requirements for admission. Purdue’s president, Mung Chiang, wrote a letter to Jenner showing that the proposed diploma system required too few credits in every subject except English.
Hoosier parents were furious that their children might have to sacrifice more challenging courses to fulfill the mandatory work experience requirement under the “plus” option. At an Indiana Department of Education hearing in June 2024, parent Michelae Hill was among dozens who criticized the proposal, calling it “intentionally dumbing down our population” and warning that “what will happen is that we are ensuring a permanent underclass, we are ensuring cheap workers.” There were also questions about the logistics of workplace learning, including transportation and possible safety issues on job sites.
State education policy makers went back to the drawing board. The revised version, adopted last December, establishes one basic diploma that all graduates earn, plus the seals students can pursue depending on their post-high-school plans. Even within each seal, students have several ways of meeting the requirements.
For example, to receive the “enrollment” seal — meant primarily for college-bound students — high schoolers can choose from more advanced classes in math, science, social studies and world languages, and may earn additional credits in Advanced Placement, International Baccalaureate or other such college-level courses. An “enrollment honors plus” seal requires that students concurrently obtain a credential such as an associate’s degree or technical certificate and complete 75 hours of work-based learning in apprenticeships, internships or other such programs.
“We wanted rigor and flexibility and less cookie cutter,” said Jenner.
Related: Apprenticeships for high schoolers are touted as the next big thing. One state leads the way
Even the updated system has critics, though. For the basic diploma, students must earn a minimum of 42 credits, two more than before. But how students reach that threshold is different: Economics, geometry and Algebra II are no longer required, while courses in financial literacy and communication are. Physical education is one credit instead of two, and world languages and fine arts are no longer recommended electives.
Professor Michael Hicks, who runs the Center for Business and Economic Research at Ball State University in Indiana, said he worries about the reduced mathematics rigor in particular. While most states do not require Algebra II for graduation, the class is often seen as a necessity for admission to selective colleges and for certain careers. Hicks said high-achieving, well-resourced students may benefit from the flexibility of the new diploma, as could students committed to the military. But many other students could be harmed, he said, if they are left with the impression that the basic diploma alone will prepare them well for college when it does not.
“It is essentially funneling children away from academic opportunity very early at a time when we really needed to have more kids pushed into the academic options that would get them into college,” he said, arguing that people with college degrees outearn those with only a high school education and have also fueled the state’s and country’s economic growth of the past several decades. “This curriculum will cause the Indiana economy to stall and potentially go into reverse.”
At public meetings last winter, some parents and educators raised concerns that the new system amounted to an unfunded mandate for school districts and would put a huge burden in particular on counselors, who would be working closely with students to help chart their diploma paths. Critics also objected to the de-emphasis of other classes like music and foreign languages. Megan Worcester, the president of the Indiana Foreign Language Teachers Association, said the reduced emphasis on foreign language would hurt the state’s economy; she cited a study in which nearly 1 in 4 employers surveyed said they had lost or couldn’t pursue a business opportunity because of language barriers.
Jenner, a former high school teacher, said the new diploma allows students greater flexibility to choose electives depending on their goals, which could include language and music study. While Algebra II is no longer required, students must take four math credits beyond the required Algebra I and personal finance, she said. Jenner also said the state had allocated a portion of $50 million in discretionary funding to train counselors in helping students navigate the new diploma system. In addition, it dedicated up to $10 million in grants to help students pay for transportation, equipment and certifications related to work-based learning, and also provided financial assistance to companies that take on apprentices. Each school that offers work-based learning will receive an extra $500 per participating student.
The new plan eventually quieted the concerns of many education leaders. Several universities, including Indiana and Purdue, released letters of support. “We appreciate the thoughtful adjustments to the work based learning requirements, AP testing and transferability of dual credits,” wrote Pamela Whitten, president of Indiana University. (Neither university agreed to an interview with its leaders.) All major education groups in the state, including the Indiana State Teachers Association, Indiana School Boards Association and the Indiana Association of Public School Superintendents, endorsed the plan.

In April, Gov. Mike Braun announced that beginning this year, students who earn the state’s “enrollment honors plus” seal will be automatically accepted into the state’s public colleges and universities, including Purdue and Indiana, potentially persuading more students to enroll.
Parent Chantee Eldridge said she believes the new diploma will make higher education more affordable and help students sharpen their career plans at an earlier age. Her son, Micah, is a 16-year-old senior at Brownsburg High School, near Indianapolis, and has already taken dual credit courses through a partnership with Vincennes University. College credits can be expensive, she said, so earning them at no cost in high school can be a big money saver.
Micah, who has a 3.7 GPA and plays semi pro soccer, said he’s always enjoyed challenging classes and plans to go to college. “When things get repeated, that’s when I get bored and start to tap out mentally,” he said. In college, he anticipates studying psychology — a surprise to his mother, who expected him to pursue math or physics, two topics he’s always excelled in. She likes the idea of him doing an internship with a psychologist, so he can learn more about the field and gain practical work experience before he goes to college; that’s the sort of opportunity that will become more common under this new diploma system.
“Very rarely do you know exactly what you want to do between 16 and 18,” Eldridge said. “That will help students and their families make an informed decision.”
Related: Schools push career education ‘for all,’ even kids heading to college
For students who want to go straight into the workforce, the employment seals are designed to provide exposure to career options and work experience that boost students more quickly into higher-paying roles. Under the “employment honors” seal, students must: take coursework or earn a credential aligned to a specific occupation; complete 150 hours of work-based learning; and demonstrate communication, collaboration and work ethic skills. The “employment honors plus” seal requires that students also earn an associate’s degree or advanced industry certificate and complete 650 hours of work-based learning.
Matt Mindrum, president and CEO of the Indy Chamber, said that most of the 150,000 vacant jobs in Indiana right now don’t require a four-year degree. “And yet 100 percent of our high school students are pushed through a college preparatory path. That makes no sense,” he said. He believes an alternate path is critical for driving economic growth in the state, by helping to fill existing jobs and attract new businesses.
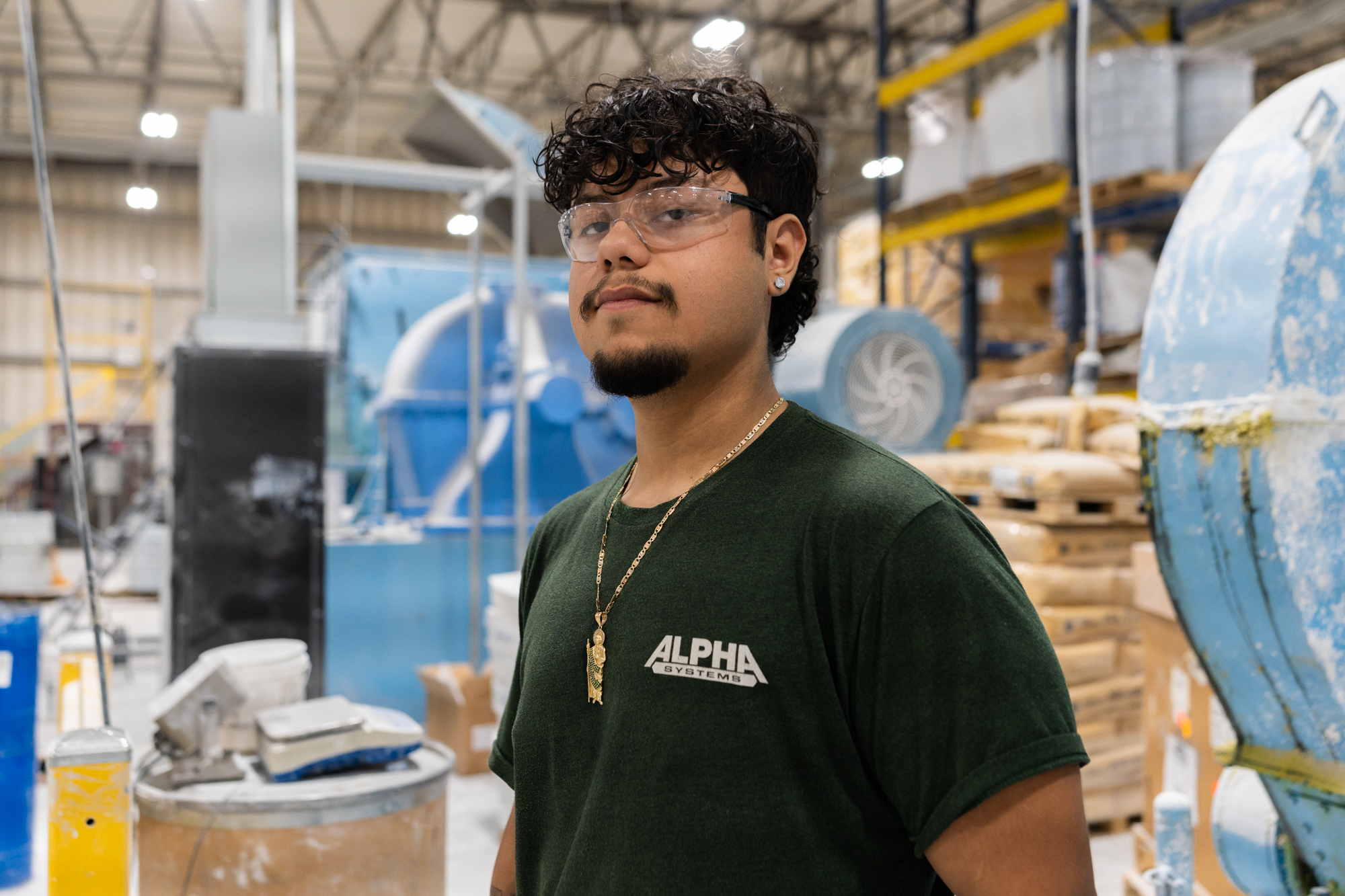
Edgar Soto, a senior at Concord High School in Elkhart, is the kind of student Mindrum has in mind. Soto said he has never wanted to attend a four-year college. To get workforce experience, he enrolled in an apprenticeship through his school and is up before dawn each morning to start work with manufacturing technology company Alpha Systems. “It’s something new every day. I love it,” he said. He earns $17 an hour and gives half his paycheck to his mom for family expenses. When school is in session, he spends his afternoons taking classes back at Concord High.
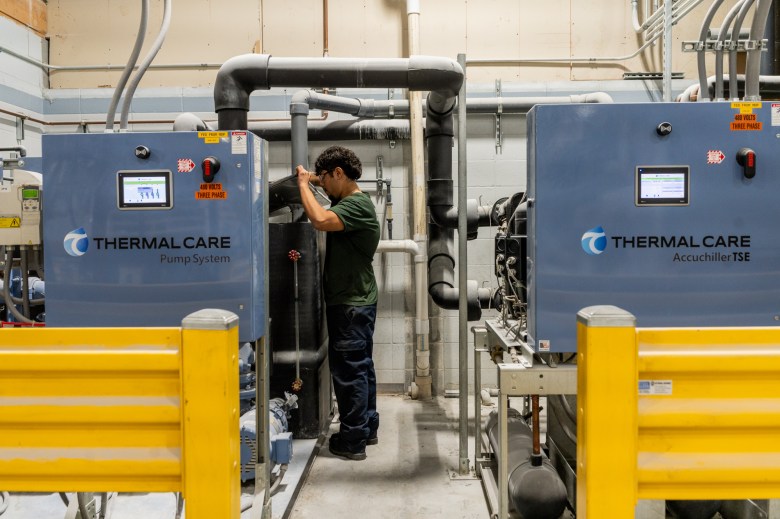

Working has motivated him to study harder at school, he said; he’s never cared for math, but when he realized it was important for his job, he began asking his teacher for extra help. “I got a taste of the real world and I want to be that type of person who does things right,” he said.
Alpha Systems pays for him to take classes in industrial systems through the state community college system, Ivy Tech, and has promised to pay for any further postsecondary education if he stays with the company. In just a few years, company executives said, he could easily make more than $40 an hour, approximately $80,000 a year.
Mindrum is working with employers around the state to try to increase work-based learning opportunities so they match student demand, a particular challenge in rural areas. Communities that have already made a commitment to work-based learning have had trouble recruiting enough employers: For example, in Elkhart County, only 1 in 3 high schoolers who apply for an apprenticeship gets one. Schools will also have to reorganize class schedules and overcome transportation challenges to ensure students can complete the necessary work-based learning under the various seals. The state has a goal of 50,000 apprenticeships by 2030. “It’s an aggressive but achievable target,” Mindrum said.
Related: A new kind of high school diploma trades chemistry for carpentry
Supporters hope the revamped diploma will also encourage more students to enlist in military service. Nationally, the military is struggling to recruit, and according to Army data, just 23 percent of 17- to 24-year-olds who apply to the U.S. military meet its medical fitness and academic requirements. In Indiana, the number of students enlisting in the National Guard dropped by 38 percent between 2018 and 2022, the sharpest decline of any state.
Retired Maj. Gen. Dale Lyles, who led the Indiana National Guard and helped create the “enlistment” seal criteria, said students often don’t know much about enlisting and the benefits of military service. In Indiana, for example, serving in the National Guard unlocks free tuition to state colleges.
The new diploma options are meant to fix that: Students in the “enlistment honors” and “enlistment honors plus” seals are taught about each branch of service, what it means to swear an oath to your country and the many different job opportunities available. They also must take a public service course or complete a year of Junior ROTC and receive a certain score on the military’s aptitude test, the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery, among other requirements. Students can receive coaching for the test and have the opportunity to visit Camp Atterbury-Muskatatuck, a nearly 35,000-acre military post, for hands-on learning opportunities.
“Today’s military is much different than it was even five years ago, just because of the high degree of technology,” said Lyles, citing the Indiana National Guard’s platoon that flies automated aerial drones and its cyber warfare battalion. “We are in a battle for talent.” He added that the pathway emphasizes that there are other ways to serve, including as a firefighter, as a police officer or in the Department of Homeland Security.
Nicholas Purdy, a 17-year-old from Marion, has three grandparents who served in the military and said he’s always been interested in enlisting. In his first year of high school, he signed up for JROTC, and he said he loves traveling to other states for competitions and leadership camps where students participate in activities such as rappelling, water operations and land navigation. “It doesn’t matter what your background is, how much money you have, your looks,” he said of the experience. “The only thing that matters is your character.”
His mother, Stephanie Purdy, said she’s seen his confidence deepen as a result of his experiences with JROTC. Nicolas has won ribbons and pins for marksmanship and leadership that he wears on his uniform, and he likes the idea that under the new seals, those accomplishments would be reflected on his high school transcript. Nicholas wants to become a combat medic in the army. “The training set me up for really good opportunities, and it’s all paid for,” he said.
Jenner’s work continues — with a pressing deadline, as schools roll out these changes for first-year students this year. Her office is working on an online advising tool, a pilot program to help communities identify solutions to transportation challenges, guidance for educators on the new diploma options and courses, and incentives for school districts to measure skills like communication, collaboration and work ethic, not just academic outcomes.
It’s a big task. “This is new terrain for our country when you think about the level of scale we’re trying to accomplish,” said Jenner. “We don’t have a model to just copy and paste, so we’re going to learn some lessons along the way.”
*Due to an editing error, an earlier version of this story included an inaccurate description of the Carnegie Foundation.
Contact editor Caroline Preston at 212-870-8965, via Signal at CarolineP.83 or on email at [email protected].
This story about work-based learning was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.