by Meredith Kolodner, The Hechinger Report
December 19, 2025
LUBBOCK, Texas — The meeting of the local NAACP chapter began with a prayer — and then the litany of injustices came pouring out.
A Black high school football player was called a “b—h-ass” n-word during a game by white players in September with no consequence, his mom said. A Black 12-year-old boy, falsely accused last December of touching a white girl’s breast, was threatened and interrogated by a police officer at school without his parents and sentenced to a disciplinary alternative school for a month, his grandfather recounted. A Black honors student was wrongly accused by a white teacher of having a vape (it was a pencil sharpener) and sentenced to the alternative school for a month this fall, her mom said.
“They’re breaking people,” said Phyllis Gant, a longtime leader of the NAACP chapter in this northwest Texas city, referring to local schools’ treatment of Black children. “It’s just open season on our students.”
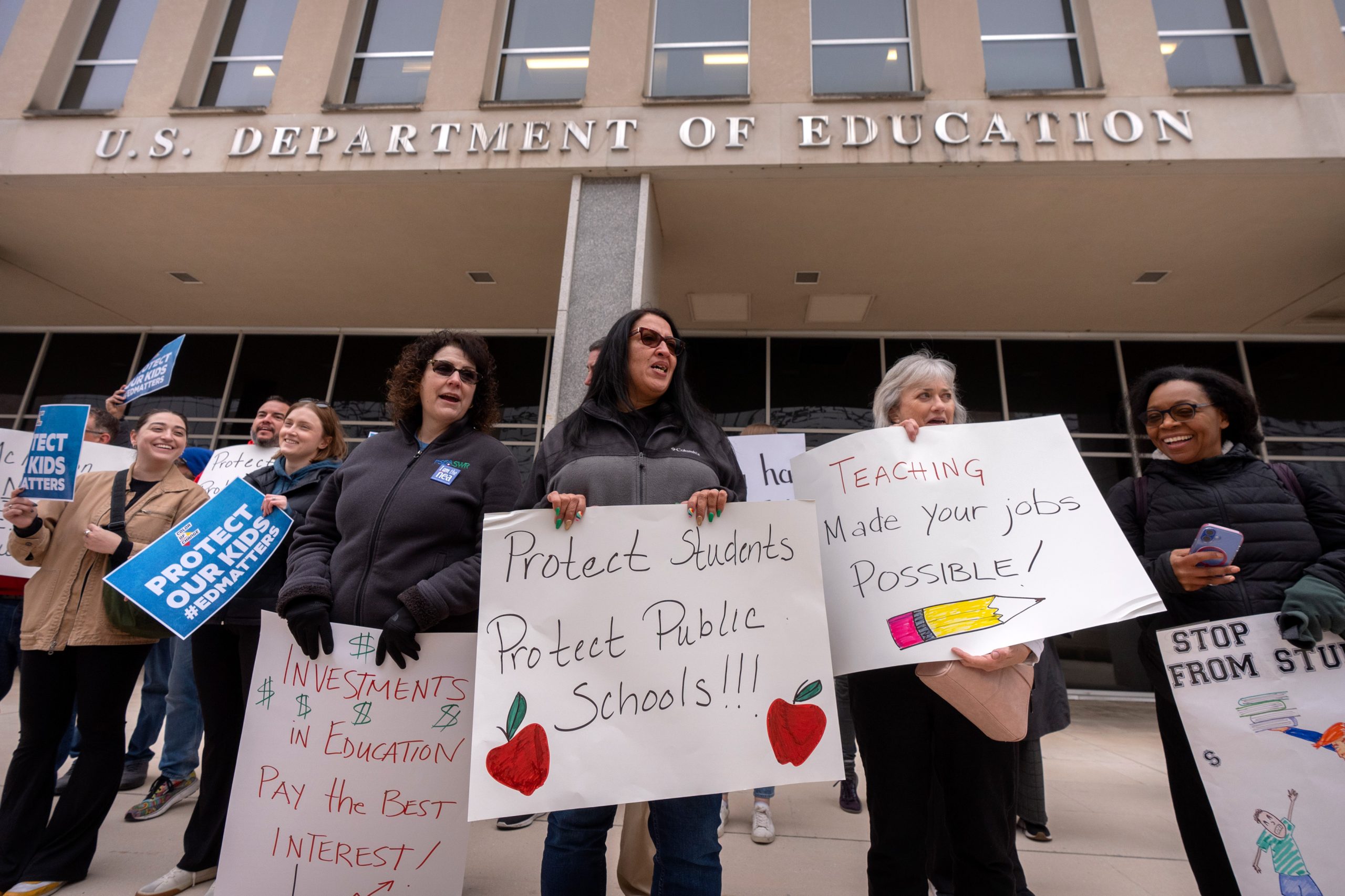
Just last year, there was hope that the racial climate at Lubbock-area schools might improve. The federal government had launched civil rights investigations after several alleged incidents of racial bullying shocked the community and made national headlines. In fall 2024, a resolution seemed to be in sight: An investigator from the Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights was planning to visit the area, community members said, for what they hoped would be a final round of interviews before the agency put in place a set of protections negotiated with the Lubbock-Cooper school district.
Then the 2024 presidential election happened — and the visit didn’t. In March, the Trump administration closed seven of the Education Department’s 12 regional civil rights enforcement offices, including the one in Dallas, which had been investigating complaints about Lubbock. Emails from the lawyer representing the families to the federal investigator bounced back — like hundreds of other OCR employees, she had been terminated.
Since then, race relations in school districts in and around Lubbock have taken a turn for the worse, many parents and educators say. Black residents — who make up about 8 percent of Lubbock County — didn’t expect the federal government to bring a halt to racist incidents, but the possibility of an agreement between the government and school districts provided a sense of accountability. Now, parents and students say racial epithets are more common in public, and Black teachers fear drawing attention to themselves. Gant says the NAACP chapter fields frequent calls from parents seeking help in addressing racial incidents they no longer bother to report to the Education Department.
Since President Donald Trump took office, the agency has not publicly announced a single investigation into racial discrimination against Black students, instead prioritizing investigations into alleged anti-white discrimination, antisemitism complaints and policies regarding transgender students.
All told this year, the Education Department under Trump has dismissed thousands of civil rights investigations. During the first six months of this year, OCR required schools to make changes and agree to federal monitoring in just 59 cases, compared with 336 during the same period last year, a Washington Post analysis found.
“In many of our communities where people feel isolated and like they didn’t have anyone to turn to, OCR mattered and gave people a sense of hope,” said Paige Duggins-Clay, a lawyer at the Intercultural Development Research Association, an education policy and legal advocacy group that helped file some of the OCR complaints against Lubbock schools. “And it matters that they’ve essentially destroyed it.”
In an email, Julie Hartman, press secretary for legal affairs for the Department of Education, wrote, “These complaints of racial bullying were filed in 2022 and 2023, meaning that the Biden Administration had more time to investigate this than the Trump Administration has even been in office. The Trump Administration’s OCR will continue vigorously enforcing the law to uphold all Americans’ civil rights.” She did not respond to a question about whether the agency had opened any investigations into discrimination against Black students.
Related: Become a lifelong learner. Subscribe to our free weekly newsletter featuring the most important stories in education.
Some white residents have noticed the change too. Lubbock County, located at the bottom of the Panhandle, is home to more than a quarter million people. It is the urban seat for a sprawling county that encompasses several suburban and rural school districts and hosts Texas Tech University at its center.
Tracey Benefield — who has two children in Hutchinson Middle School in the Lubbock Independent School District, which borders the Lubbock-Cooper district — is from a family that has lived in the area for generations. She says her son has witnessed multiple incidents of racial bullying over the past year.
“My son was walking down the hall with his friend who’s Black, and some kid shoulder-checked him and called him the n-word. That’s been one of many,” she said. “Things have absolutely gotten worse. The attitudes have always been there, but people acting on their attitudes is completely different.” Lubbock district officials did not directly respond to questions about Benefield’s assertions.
She thinks OCR’s retreat, among other changes within the federal government, has had an impact. “People are more emboldened,” she said. “People have always had racist ideas, but now there’s no consequences for being racist.”
Prior to Trump’s election, the concerns of parents and civil rights groups were quite different: Many were frustrated that Office for Civil Rights cases could linger for years as overworked investigators tracked down details and testimonies. Some were starting to advocate for more OCR staff and speedier resolutions. The outcry from residents, along with the media attention, prompted the Lubbock-Cooper and nearby Slaton school districts — where Black students make up about 3 percent and 5 percent of the student bodies, respectively — to adopt policies of mandatory in-school suspension for students caught making racial slurs and spurred training for staff.
But for many, the changes weren’t coming quickly enough.
Related: Under Trump, protecting students’ civil rights looks very different
In 2022, Tracy Kemp’s eldest son, Brady, then an eighth grader, was one of nine Black students whose pictures were put on an Instagram page called “LBMS Monkeys,” which stood for “Laura Bush Middle School Monkeys.” (Brady is being referred to by his nickname and his last name is being withheld to protect his privacy.) Kemp was part of a group of parents in the Lubbock-Cooper school district who filed OCR complaints that August over what they said was a toxic racial atmosphere that subjected their children to repeated racial bullying. White students would sometimes play whipping noises on their phones when Black students walked through the halls, according to the complaints. Despite a school district investigation that included reaching out to the FBI, those responsible were never caught.
Lubbock-Cooper officials said via email that they “responded swiftly and appropriately” to the 2022 incident at Laura Bush Middle School. “Efforts of the district to ensure all students feel valued, supported, and a sense of belonging have contributed to the positive, nurturing environment our campuses strive to maintain,” wrote Sadie Alderson, the district’s executive director of public information.
Kemp stayed in the Lubbock-Cooper district for another year, but even though the page was taken down, the taunting and bullying didn’t let up, she says. Her middle son was in sixth grade at LBMS that year and was called racial epithets on the school bus and in the hallways. (His name is being withheld to protect his privacy.) When Brady, who had graduated from the middle school and started at Lubbock-Cooper High School, tried to start a Black Student Union there, she says, a white student ripped the page with signatures from his notebook. Kemp says the principal told her there was nothing he could do. The final straw came one day when the ninth grader didn’t stand for the Pledge of Allegiance. The teacher told him he was a criminal who was breaking the law, Kemp says, and the harassment started up again, this time on Snapchat, with the same language as the “monkeys” Instagram page.
In July 2023, Kemp moved with her family to New Mexico and commuted 75 miles each way until she found a job closer to her new home. Leaving Lubbock-Cooper, she said, was life-changing for her kids’ mental health.
“In eighth grade, you’re going through puberty, you’re learning about yourself, you’re growing and you have all these different feelings. And now you add into the mix, ‘These people don’t like me because of my color’ — that’s a whole different type of aspect to have to deal with,” said Kemp. “And on the flip side of that, I also have to encourage my child that not every white person feels this way, because I don’t want to teach my child hate either.”
Brady, now a 12th grader, also says he’s happy the family moved. “Honestly, it’s a lot easier,” he said. “There’s no arguments, there’s nothing to worry about, really. I just focus on school more than anything.”
Related: What’s happened since Texas killed in-state tuition for undocumented students
Others who have stayed say they’ve paid a price. Last December, Ja’Maury, a then-12-year-old whose last name is being withheld to protect his privacy, learned of rumors that he’d touched a white girl’s breast during school. He went straight to administrators at the school, Commander William C. McCool Academy, to tell them the truth. But the assistant principal believed the girl’s story and radioed a police officer, who interrogated him and threatened him with jail unless he confessed, according to Ja’Maury and his grandfather, Mike Anzley. Alone in a room of adults, Ja’Maury broke down and admitted to something he says never happened.
“He was yelling and threatening to send me to juvie if I didn’t say I did it. I was scared,” Ja’Maury recalled in an interview. “It was a white person’s word against a Black person’s word.”
Ja’Maury was assigned 30 days at Priority Intervention Academy, Lubbock Independent School District’s detention school, where children are sent for offenses determined to be too severe for in-school suspension. Constantly anxious, he reverted to sleeping in his grandfather’s bed like he did as a toddler. At the detention school, he said, he was so afraid of defying adults that he twice wet his pants rather than challenge a teacher who said he couldn’t leave class to use the bathroom.
“He had never been in trouble before,” said Anzley. He’d always taught Ja’Maury to trust adults, and said he was devastated by the adults at McCool betraying that trust. “I had to make him distinguish right from wrong in a whole new way.”
Anzley filed a formal grievance with the district and, according to a copy of the findings shared with The Hechinger Report, administrators agreed to wipe the incident from his discipline file, issue a formal apology and provide training in discipline and due process to both McCool administrators and the officer who interrogated him.
McCool administrators did not respond to requests for comment. Amanda Castro-Crist, executive director of communications and community relations for Lubbock ISD, wrote in an email that the district could not discuss individual students because of federal laws protecting student privacy, but that it “is proud to serve a diverse student body.”
Related: More first-generation students in Texas are applying to college
Gant, the 62-year-old NAACP leader, says that growing up in Lubbock she never experienced the kind of racism she sees now. An accountant who runs her own business, she got involved in community activism about 20 years ago after enduring identity theft and a costly, time-consuming effort to clear her name. “I’m a strong, faith-based woman,” said Gant. “Who else will someone call? Who will go to their meetings for free, come with the facts and the research and not make them feel like they owe anything?”
Gant noted changes the districts have made in the wake of the OCR investigation and parent activism, including the new suspension policies. Administrators in Lubbock-Cooper sometimes even proactively contact her about a parent concern, she said. In Lubbock ISD, Gant credits the director of student and parent resolution, Brian Ellyson, with listening to parents and helping them resolve conflicts in a principled manner.
Ellyson was one of two Lubbock school officials at the September NAACP meeting, held in an independent living center on the south side of town equidistant between Laura Bush Middle School and McCool Academy. Parent after parent described their children’s mistreatment.
Leshai Whitfield said her son was sent to a detention school after a teacher complained that he’d pushed her; she said her son was only trying to leave the classroom because of a fight between two other students. Naquelia Edwards said her son has been repeatedly called the n-word and disciplined for fights while white students went unpunished. Jessika Ogden, mother of the 11th grade honors student who was wrongly accused of having a vape, said she believes her daughter was racially profiled. She filed a grievance against Lubbock Independent School District’s Coronado High School to keep her daughter from being sent to the district’s detention school, which she says she eventually won. But her daughter missed school while the case was being resolved, Ogden said, as she refused to send her to the detention school. “Had I not fought for my daughter, she would have suffered that punishment, missing more class, more credits,” Ogden said.
In interviews, more than a dozen Black high school students in Lubbock said they regularly heard other students use the n-word. “Slurs happen all the time – it don’t matter what time of day it is,” said a 10th grader from Coronado High School, whose name is being withheld to protect her privacy.
Gant says the absence of an actual agreement between the federal government and any of the districts means the environment in schools hasn’t fundamentally changed. Those agreements come with teacher training, data collection and penalties for failing to comply. In-school suspension for racist behavior may keep some of it in check, but the changes are cosmetic, she and parents say.
Emails obtained by The Hechinger Report through public records requests show that Kulsoom Naqvi, the OCR investigator based in the Dallas office, conducted staff surveys, data requests and several rounds of interviews throughout much of 2024, but the work came to a halt that fall. Naqvi, who is not technically separated from the Education Department because of ongoing litigation over the mass firings at the Education Department, said she could not comment on the case.
“Given the pace that things were moving, I felt confident that we were going to get a resolution before the end of the year,” said Duggins-Clay, the lawyer who helped file some of the complaints. “Had the election not happened, we would have gotten to a negotiated resolution.”
Alderson, the spokesperson for Lubbock-Cooper, said that the investigation is still open, but the current superintendent, hired in June, was not aware of any communication from an OCR investigator. She said the district had sought mediation with OCR in spring 2024, but Naqvi had denied that request and had not given Lubbock-Cooper a timeline for resolving the complaints.
Related: ‘It was the most unfair thing’: Disobedience, discipline and racial disparity
Just over 20 miles away from downtown Lubbock, in the neighboring town of Slaton, which had its own series of racist incidents and ensuing complaints to OCR, residents say the racial atmosphere has deteriorated even further this year and the school administration has been completely unresponsive. School officials promised to work with local authorities to paint over part of a mural in the center of town that depicts Black men picking cotton under the watch of a white farmer, teachers say. But that never happened. Parents say the n-word is used regularly by white students without consequence in the district, where just 5 percent of students are Black.
“I’ve witnessed kids on my campus calling Black kids ‘monkeys,’” said a Slaton teacher who grew up in the town and spoke on condition of anonymity out of fear for her job. “I’m sorry to say that it’s gotten worse. I feel like more of the extremists have come out.”
Parents say their children continued to be bullied because of their race even after Slaton administrators pledged in 2022 to discipline students for slurs. One mom said her second grader was called an “African monkey” the next year by other kids in his class at Cathelene Thomas Elementary. She says she told the principal, who said, “‘Would you be offended if they called him a cat or something different?’” the mother recalled. “I got up and left. I didn’t even know what to say.”
After that she started homeschooling her kids. She asked to remain anonymous because her children still participate in community events and she is worried they will face retribution.
Cathelene Thomas Principal Margaret Francis did not respond to requests for comment. Superintendent Shelli Conkin said in an email that federal law prevented the district from discussing student-related matters and did not respond to additional questions. “Since I became superintendent in 2023, Slaton ISD has experienced many positive developments that highlight our commitment to students and staff,” she wrote, including facility upgrades, a district fundraising effort and a four-day school week.
Related: Which schools and colleges are being investigated by the Trump administration?
Anzley, meanwhile, is still fighting for justice for his grandson. After the district declined to discipline the girl for making the accusation, he said, and with OCR no longer seeming like an option for redress, he’s hoping to find a lawyer to file a civil rights lawsuit on behalf of his grandson.
The district’s apology and commitment to better train administrators did not undo the damage to Ja’Maury, he and his grandfather said. “People kept on messing with me about it, saying I was a pedophile, saying I was a pervert,” said the middle schooler. “After that I almost hated life, I didn’t even want to live no more after that. That was horrible.”
Last spring, four months after Ja’Maury had been back at McCool, he got into a fight with a boy who called him the n-word on the school bus, he said. This fall, Anzley decided to transfer Ja’Maury from the top-rated school he once loved — which is 9 percent Black — to Dunbar College Preparatory Academy, which is 45 percent Black and received an F rating this year from the Texas Education Agency. Ja’Maury says he feels safer there; Anzley says the move was necessary for his grandson’s mental health but that he preferred the learning opportunities at McCool.
“None of this is new, because the very name Lubbock is the name of a Confederate soldier,” said Gant. “It’s heartbreaking, but it doesn’t surprise me. The aggression of it has been heightened under the Trump administration.”
She added, “The districts know that OCR has been dismantled so there’s no urgency to fix these issues. It’s on the community, and it’s on the parents to be factual, vocal and not quit.”
Contact senior investigative reporter Meredith Kolodnerat 212-870-1063 or [email protected] or on Signal at merkolodner.04.
This story about federal investigations in schools was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter.
This <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org/probes-into-racism-in-schools-stall-under-trump/”>article</a> first appeared on <a target=”_blank” href=”https://hechingerreport.org”>The Hechinger Report</a> and is republished here under a <a target=”_blank” href=”https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/”>Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License</a>.<img src=”https://i0.wp.com/hechingerreport.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/cropped-favicon.jpg?fit=150%2C150&ssl=1″ style=”width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;”>
<img id=”republication-tracker-tool-source” src=”https://hechingerreport.org/?republication-pixel=true&post=114040&ga4=G-03KPHXDF3H” style=”width:1px;height:1px;”><script> PARSELY = { autotrack: false, onload: function() { PARSELY.beacon.trackPageView({ url: “https://hechingerreport.org/probes-into-racism-in-schools-stall-under-trump/”, urlref: window.location.href }); } } </script> <script id=”parsely-cfg” src=”//cdn.parsely.com/keys/hechingerreport.org/p.js”></script>