The biggest thing everyone is going to be talking about this year – barring another university doing a surprise Laurentian – is the set of federal cuts coming down the pike. They are big. And they are nasty. So, it’s worth understanding exactly the scale of what is heading in our direction. This is going to be a three-parter. Today, I will talk about the overall size of the cuts to come, and on Tuesday and Wednesday I will talk about how this will affect the two ministries that have the most to do with post-secondary education: Employment and Skills Development Canada (ESDC, tomorrow) and Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED, Wednesday).
So: we don’t know the exact scope of the budget cuts the government is contemplating. What we do know is the following:
Preliminary budget figures for Fiscal 2024-25 show that the government of Canada posted a budget deficit of $43.2 billion on revenues of $495B, program expenses of $480B, debt charges (that is, interest on existing debt) of $54B and actuarial losses of $4B. We didn’t have a budget this spring, but spending projections for 25-26 from the 2024-25 budget show a projected deficit of $39 billion on revenues of $515B, program expenses of $496B, debt charges of $55B and actuarial losses of $2B.
The Liberal Manifesto for election 2025 planned deficits of $60 billion or so right through to 2028-29. Its fiscal plan was basically i) existing spending commitments, ii) 30-odd billion in new spending and tax cuts and iii) tiny revenue changes, plus $20 Billion or so in counter-tariffs for 2025-26. (Yes, they also promised “savings from increased productivity” – otherwise known as “frantic handwaving” – of $6B, $9B and $13B in fiscal years ’27, ’28 and ’29. I am excluding them here but will return to them in a sec).
Figure 1: Government of Canada fiscal picture according to the Liberal manifesto, minus the handwaving, in Billions.
(The foregoing might all sound strange to those of you who recall Carney making pledges about balanced budgets. But, of course, as I pointed out back here, he never actually promised that. He promised balanced operating budgets, that is budgets with an only vaguely defined “capital spending” netted out. By a complete coincidence, the Liberal platform claimed the government spent roughly $50 billion in capital, so basically the government is already basically in balance. Neat trick, but not sure bondholders will see it that way. I digress.)
Since the election, a few things have happened. Counter-tariffs are not collecting anything like the $20 billion forecast, we ditched the Digital Services Tax in a futile attempt to get the Americans to be nicer to us, and, most importantly of all, the prime minister promised to up defense spending by about $18 billion over the next four years in order to reach 2% of GDP by 2028. That means the actual fiscal picture, before any handwaving about savings, looks like this:
Figure 2: Government of Canada fiscal picture, according to the Liberal Manifesto, minus the handwaving, including proposed spending and tariffs since April 28, in Billions.
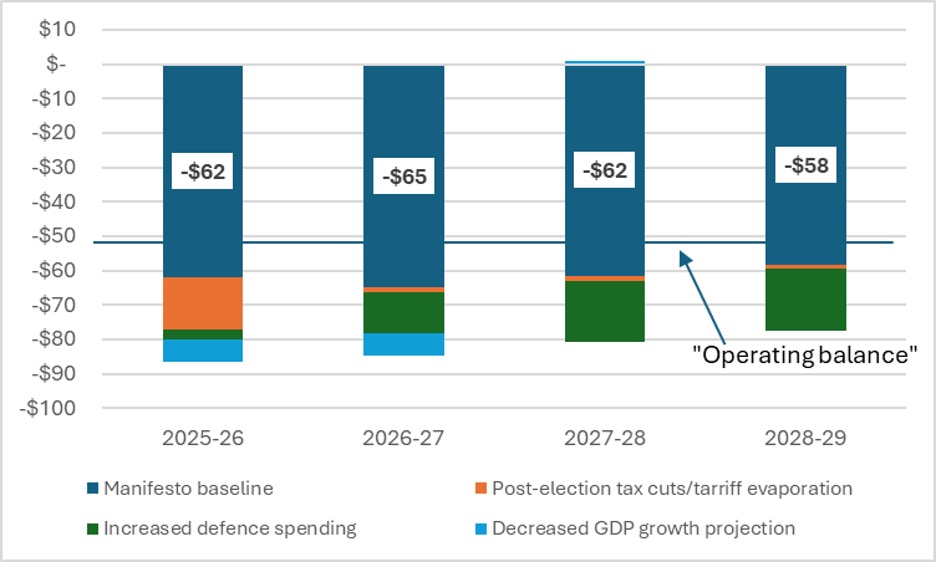
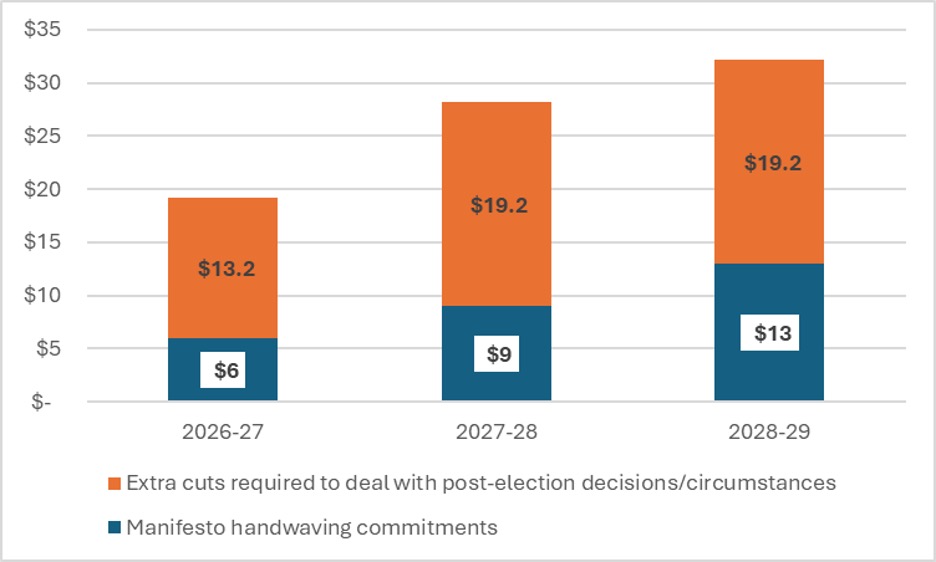
As you can see, we are a lot further away today from “operating balance” (i.e. a $50B deficit) than we were when Carney was elected. And this is where the handwaving/cuts come into play. So, let’s start thinking about how much money it would take to keep us at “operating balance”. In Figure 3, we see that by 2028-29, we are looking at about $32 Billion in cuts. The handwaving “efficiencies” in the Liberal manifesto were meant to cover just $13 billion of that, leaving another $19.2 billion or so to be made up, somewhere, somehow.
Figure 3: Cuts Required Just to Keep the Government of Canada at Operating Balance (i.e. a $50B deficit), By Source, in Billions.
I said “somewhere”, but there isn’t much mystery here. As Figure 4 shows, you divide government spending into four categories: debt charges (which the government has to pay regardless), transfers to provinces (which Carney has promised he won’t touch), transfers to individuals (ditto) and then “program spending”. As Figure 4 shows, the first three areas make up 58% of total spending. That means that the last area, program spending, is going to take up the entirety of these cuts. In 2025-26, program spending is estimated at $227 billion; a $32 billion cut to that equals an overall reduction in program spending of 14% by 2028. (Coincidentally, this was more or less exactly the size of the program cuts in the “savage” 1995 budget – $7 billion phased in over three years on a base budget of about $52 billion. Government grew back, as you can see.)
Figure 4: Government of Canada Expenditures by Category, 2025-26
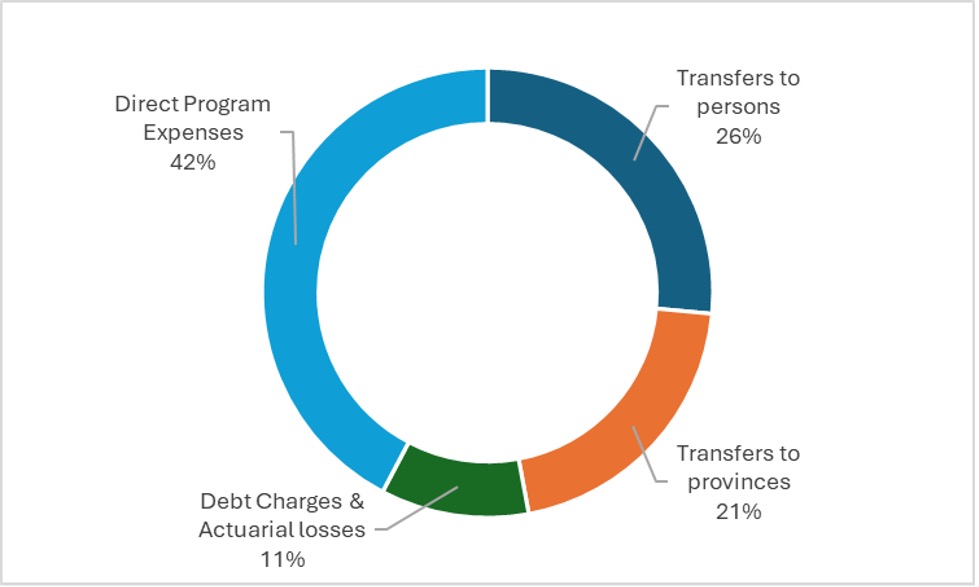
It’s worth being careful here. Overall program spending is $227 billion, but $46 billion of that is currently being spent on defense and housing, two areas that are almost certainly immune to cuts given the government’s overall priorities. Excluding these two fields from cuts means that the field of “cuttable” programs shrinks to $181 billion, and the size of the cuts required to meet the $50 billion target balloons to 17.7%.
This brings us to the program review that has been going on in Ottawa since July. Recall that Minsters were asked to bring forward scenarios that involved cuts of 7.5% for next year, 10% the year after that and 15% the year after that. Many thought initially that these numbers were deliberately overdone so that big cuts could be made in some departments so as to shield other departments from having to do the same. Now I am not so sure. That 15% target is awfully close to the 17% overall target the Liberals need to hit just to keep the deficit at $50 billion, and so I am starting to think that in fact the cuts might not be dispersed unequally between departments. They might really need 15% from everybody – and then some.
There are a couple of alternatives of course that could lessen the blow. For instance, while Carney promised not to cut transfers to provinces, to my knowledge he never ruled out cutting the rate of growth of transfer payments (currently about 5% per year, across CHT, CST and equalization combined). Slash that in half and you’ve got yourself another $8 billion to play with by 2028, thereby reducing by a quarter the required amount of program cuts. Something similar could be achieved by de-indexing pensions for a couple of years. Or, unlikely as it seems, the Government could actually increase taxes (elbows up requires some sacrifices, no?). But, absent those measures, I think we need to seriously brace for impact. These cuts are real, they are huge, and even if they don’t hit this fall (it’s not impossible that the alleged fall budget might actually just be the usual fall economic statement under another name), they are for sure going to hit in early 2026.
The question, really, is, what needs to be saved? What should the sectors’ priorities be? I’ll discuss that over the next two days.

