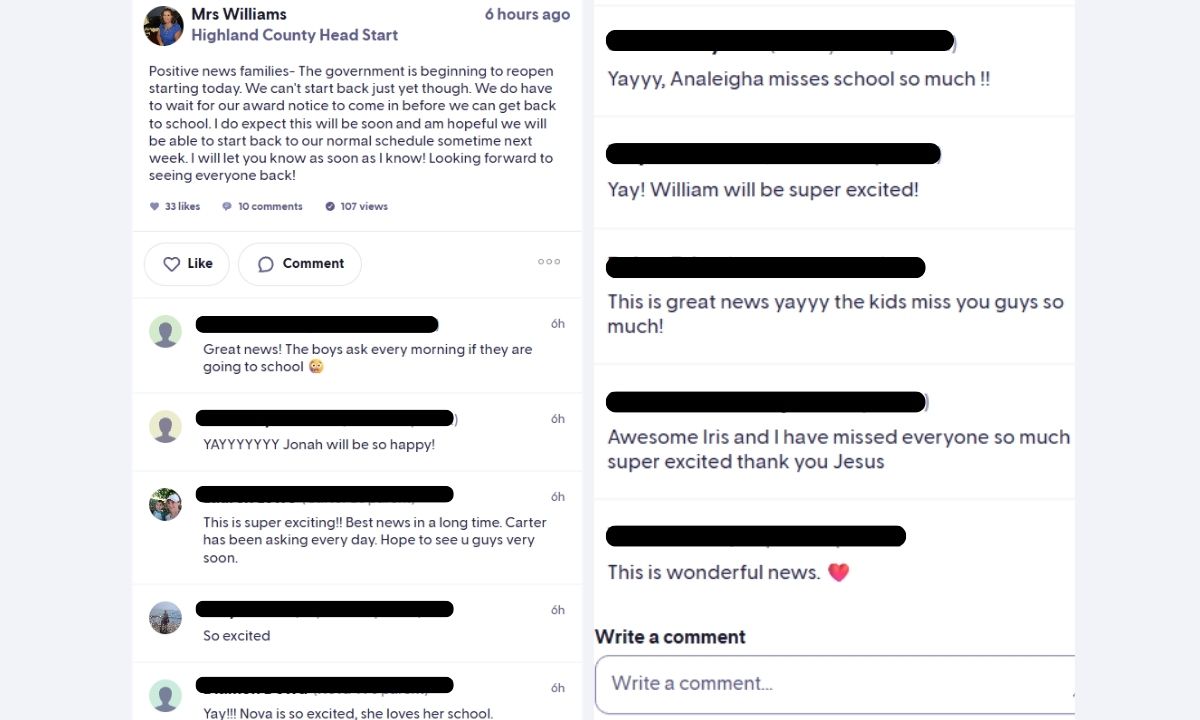
In polls and focus groups across the country, Reform voters have been singing from the same hymn sheet. They share a deep sense of national and local decline. They view the country through a lens of crumbling high streets, strained public services, and an economy seemingly trapped in a doom loop.
In this environment, they have developed a corrosive scepticism towards the modern university model, judging it a failed investment that saddles their children with debt for a degree that is only good for getting through graduate recruiters’ first sift of CVs. They demand contraction, utility, and accountability for a system they believe serves neither the student nor the economy.
To delve into these views, Public First conducted focus groups with those who currently intend to vote Reform UK in university towns in England. This revealed a surprising chink of light in an otherwise very gloomy outlook on universities: focus group participants were broadly very positive about international students.
Foreign subsidy as necessary evil
This needs to come with a heavy caveat: when we polled Reform voters, we found that 63 per cent agree that the UK government should restrict international student numbers in order to cut net migration. Cutting net migration remains a top priority for these voters, and for many, it appears that this should be done by any means necessary.
However, when confronted with the economics, Reform voters we have spoken to reveal a sophisticated and transactional view of international student recruitment. For them, students from overseas are not a problem to be solved, but a “great business.”
As polling has consistently demonstrated, the typical Reform voter is highly sceptical of mass, unmanaged immigration. Yet, when asked about foreign students, the response of those who live in university towns was not hostility, but economic pragmatism.
They see international recruitment as a clear, contained, and mutually beneficial transaction: the UK offers a world-class education (a product) and, in return, receives a higher rate of tuition fee (a profitable revenue stream). The students come to study, they contribute economically, and then – the crucial expectation – they either contribute to the UK economy or they leave.
This isn’t merely tolerance; it’s a qualified acceptance rooted in financial necessity. In these voters’ minds, these lucrative international fees act as the foreign subsidy that keeps the entire system afloat. As one participant noted, “If universities can’t stay open because they haven’t got any foreign students, then that is a detriment to UK students.” The implication is clear: to maintain a domestic higher education offering, the international revenue stream must be protected.
The conditions for goodwill
This surprising goodwill, however, is fragile and rests on extremely strict conditions. Voters grant the sector a licence to recruit internationally only as long as two core boundaries are strictly maintained.
No back doors: The arrangement must remain a transactional exchange, not a migration loophole. Support instantly evaporates when student visas are perceived as a “back door” into the country, particularly when students bring dependents or “disappear” into the country during the degree programme, or after graduation. The transaction is valid only if the purpose is learning, not permanent residency. “If you’re coming to learn, then you come to learn. You don’t bring your family, your dog, your cat and your goldfish,” argued one voter.
No crowding out: Crucially, if voters feel that their children are being denied places in favour of higher-paying overseas customers, the economic argument collapses under the weight of perceived injustice.
Despite the conditional acceptance of international fees, the core challenge for universities remains their perceived lack of utility to their students, and in their local communities. While Reform voters are pragmatic about international revenue streams, they are profoundly sceptical about the value of many domestic degrees that this income subsidises, and they see very little economic spillover in their towns: “…the areas outside of the city centre, I can’t see what benefit [universities] have.”
The sector cannot win over these key voters – and thus cannot escape the threat of cuts from political parties who want their support – by simply defending the status quo. Making the case to this influential group of voters requires clearly showing how international students are paying for local resources and subsidising domestic places, while demonstrating robust checks that ensure the system is not abused.
More widely, universities need to move beyond abstract civic rhetoric and show tangible value, taking concerted action to ensure and evidence that all degree courses benefit the student, the community and/or the country at large.
The support for international students presents a unique opportunity. It is the one pillar of the current HE model that Reform voters’ economic logic allows them to broadly accept, even if this acceptance is currently secondary to the desire to cut net migration.
The sector must leverage this pragmatic lifeline to pave the way to a secure future, while not telling but showing voters that their domestic offering is part of the solution to the UK’s economic doom loop.