|
||||
|

|
||||
|

This week on the podcast we examine the OfS penalty imposed on Leeds Trinity over subcontractual partnerships oversight. What does the £115,000 fine and a new proposed code of “ethical” governance tell us about decision-making at the top?
Plus we discuss the government’s decision to axe level 7 apprenticeships from levy funding, and explore incoming OfS chair Edward Peck’s ten trends shaping the future of campus universities.
With Alex Stanley, Vice President for Higher Education at the National Union of Students, Pam Macpherson Barrett, Head of Policy and Regulation at the University of Leeds, David Kernohan, Associate Editor at Wonkhe and presented by Mark Leach, Editor-in-Chief at Wonkhe.
Poor quality teaching and student outcomes. But where?
The new OfS chair identifies ten trends
A code of ethical university governance is overdue
Should governance reform be horizontal or vertical?

The Class of 2025 is prioritizing location, job stability and benefits when considering their first job postgraduation.
SDI Productions/E+/Getty Images
Commencement season brings excitement to college campuses as community members look to celebrate the accomplishments of the graduating class and usher them into their next chapter of life.
The Class of 2025, however, is gearing up to enter a challenging environment, whether that’s a competitive application cycle for gaining admission to graduate school or a tighter job market compared to previous years.
Inside Higher Ed compiled 25 data points regarding the Class of 2025 and the workforce they will enter, including levels of career preparedness, challenges in the workplace and the value of higher education in reaching career goals.
We bet your colleague would like this article, too. Send them this link to subscribe to our newsletter on Student Success.

Here I look into the past month of Trump’s actions and see how they might shape long-term trends. Specifically I touch on demographics, climate change, populism, technology, and a bit more. It’s a weird way to celebrate my birthday, but hopefully a productive one.

What does academic freedom mean in 2025?
We will explore this vital question with the help of Jeremy C. Young, the Freedom to Learn program director at PEN America (and excellent 2023 Forum guest).

Key points:
As we welcome a new year, educators and industry leaders are excited to discover the biggest education trends for 2025. The past few years have been characterized by fresh and innovative solutions for learning, as well as transformative, technology-forward approaches to education.
Each year, we like to look ahead and anticipate the biggest upcoming education trends. There are many topics education professionals can expect to be at the center of the conversation in 2025–from new perspectives on artificial intelligence for education to the emergence of nontraditional school models amid an increasingly competitive enrollment environment.
For 2025, schools and districts are focused on making learning more engaging for students, creating a more positive environment for educators, and transforming school culture to meet the diverse needs of the school community. As schools work to accomplish these goals, we expect to see an expansion of AI and other emerging technologies in the classroom, enhanced professional development and support for teachers, and more individualized learning opportunities for students.
Here are five of the biggest education trends for 2025:
1. Nontraditional school models
Everything from career opportunities, technology, and the world around us has changed significantly over the past decade, yet the traditional model of public schools in the U.S. has remained largely unchanged for generations. As this industrial-age school model persists, many students feel bored and disengaged with their learning.
When the COVID-19 pandemic caused school interruptions in 2020, many families decided it was time to pivot to new and nontraditional learning opportunities for their children. Since 2019, over 1 million students–the equivalent of one student from every class in the country–have left the conventional classroom to seek out different educational approaches and more innovative learning environments. The National Center for Education Statistics projects that public schools, including public charter schools, will lose an additional 2.4 million students by 2031.
Today’s students desire more individualized learning approaches, which empower them to use their creativity, explore their passions, and engage with their peers in more collaborative ways. In 2025, we will see a greater emergence of nontraditional school models that center student engagement, collaboration, and creativity, and prepare learners to graduate into a continually-evolving workforce.
Some of these emerging nontraditional education models include microschools, online and hybrid learning programs, and project-based or student-led schools, as well as long-established nontraditional school programs such as homeschooling, Montessori, and career and technical education schools. In 2025, we also anticipate that public schools will step up to meet the diverse needs of students through innovative approaches, mirroring some of the elements of these nontraditional school models in order to maintain enrollment, enhance engagement, and equip students with applicable career-ready skills.
2. Expanded use of AI in education
As we predicted last year, artificial intelligence (AI) has become prevalent in the educational space, and this emerging technology shows no sign of stopping its rapid growth as we make our way into 2025. This year, we expect the conversation around AI to shift, reflecting a more widespread acceptance of the technology as a beneficial tool to enhance education and productivity.
In 2025, schools will continue to integrate more AI into the curriculum, guiding students to use it appropriately to enhance their learning. Many schools and districts have already developed formal AI school policies and modified student codes of conduct to ensure safe, effective, and ethical use of AI tools in the classroom.
Furthermore, many educators are now taking the initiative to incorporate AI tools into their lesson plans to help students build familiarity with the technology. Introducing students to AI in a safe and controlled environment enables them to learn how to use it effectively and ethically. Equipping students with foundational skills in AI is already regarded as an essential skill set for college and many careers.
Because AI is a fairly new technology for everyone, including educators, we anticipate that more schools will implement AI professional development opportunities this year, enabling teachers to deliver more effective AI instruction. Some schools are also beginning to employ AI tools for administrative productivity, which will require training and guidance to ensure educators and staff can successfully integrate these tools into their work.
3. Targeted support for educators
Over the past five years, many districts have been focused on allocating Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) funding to implement new educational programs and tools, support student wellbeing, and overcome learning loss. Now that the final ESSER deadline has passed, 2025 will see schools and districts shift their attention to providing targeted support directly to educators.
With all of the new technology, refreshed learning spaces, and updated curriculum districts have recently introduced, professional development is essential to ensure effective implementation of these enhancements. In 2025, schools will incorporate new professional development programs that empower educators to foster engaged learners. By providing the tools and resources teachers need to be successful, schools can help educators improve their productivity and attain professional goals, while still keeping teacher wellbeing as a top priority.
Teachers are the primary influencers of the K-12 educational experience, so supporting educators is a holistic approach that benefits the entire school community. To address rising workloads, schools will implement new tools and strategies to support teacher efficacy and wellbeing. Some schools are even piloting automated and AI-powered technologies to take repetitive and administrative tasks off teachers’ plates, freeing up invaluable time for them to connect with students and focus on teaching.
Additionally, districts have begun to recognize the importance of a healthy work-life balance, as many teachers have left the profession over the past several years. In 2025, districts will continue to explore ways to cultivate a more positive job experience for teachers. Teachers want solutions for student behavioral issues, more attentive leadership teams, and more manageable workloads. Schools will work to improve these matters, while maintaining aspects of the job teachers value most, including school culture, opportunities for professional learning and certifications, and STEM and arts programs.
4. A focus on school and district culture
With a growing list of education options, students and their families are seeking out learning environments that not only provide high-quality curriculum and resources, but also align with their values and prioritize school-home communication. In this increasingly competitive enrollment environment, cultivating a positive culture and connected school community are the qualities that make schools stand out.
Funding and resources are directly related to the number of students at each school, so cultivating an inviting school culture is key. In 2025, schools and districts will take time to refine their school brand in order to attract and maintain students. School leaders will focus on creating more opportunities to engage with students and families, implementing new communications tools, initiatives, and events that bring the school community together.
In the past few years, some K-12 administrators have piloted mobile teaching stations to increase their visibility and daily impact throughout their school. We anticipate more school leaders will embrace this approach in 2025, enabling them to build stronger relationships with students and teachers. By working from mobile workstations, administrators can directly engage with students and staff, making face-to-face connections on a daily basis. Frequent positive interactions with school leadership help students, teachers, and families stay engaged with the school community, promoting a culture of connection and support.
5. Universal design for learning
Today’s students are making more choices about how and where they want to learn than ever before. Universal design for learning (UDL) promotes achievement among diverse student bodies by giving each student access to resources and environments that help them learn. Accessibility goes far beyond ADA compliance, and schools are recognizing this through the application of UDL across the learning experience. Understanding the diverse needs of students is crucial for creating learning experiences that are inclusive and supportive.
In 2025, UDL will be at the center of creating comfortable and engaging learning environments that accommodate all students’ needs. For instance, more schools are implementing sensory spaces, ensuring neurodiverse learners have a safe and comfortable space to self-regulate throughout the school day. These spaces don’t just serve neurodivergent students–all students benefit from having areas at school that are dedicated to supporting wellbeing.
As in previous years, accessibility and equity will continue to be prominent topics in 2025, but the conversation will pivot to focus on ways UDL can positively impact curriculum. UDL emphasizes providing students with multiple, flexible types of engagement, different ways of presenting information, and multiple ways to demonstrate their understanding in the classroom. This practice supports students who are neurodivergent and/or experience learning challenges, but also improves the learning experience for neurotypical students.

As I reviewed the new IPEDS data release last week, I was looking for the data and intelligence that would be most helpful for online enrollment leaders to have in hand to underpin and inform this year’s success. These points, in combination with key trends that became clear in other sources I reviewed late last year will enable online leaders to succeed this year as well as plan for the future.
Note that I am not discussing changes that may emerge after January 20, but I will be doing so after a long talk I have scheduled with Cheryl Dowd from WCET who tracks online regulations and with whom I will be co-presenting at the RNL National Conference this summer.
So, what do you need to know?
Four years after the pandemic, more students each year are continuing to decide to enroll in either fully or partially online study. While year-over-year change in every post-pandemic year has seen some “return to the classroom,” when compared with pre-pandemic enrollment (2019), 2.3 million more undergraduates and 450k more graduate students are choosing fully or partially online study. Perhaps more important, 3.2 million fewer undergraduates and 288k fewer graduate students are choosing classroom-only programs. Institutions seeking to grow enrollment must develop processes to quickly determine the best online programs to offer and get them “to market” within 12 months.
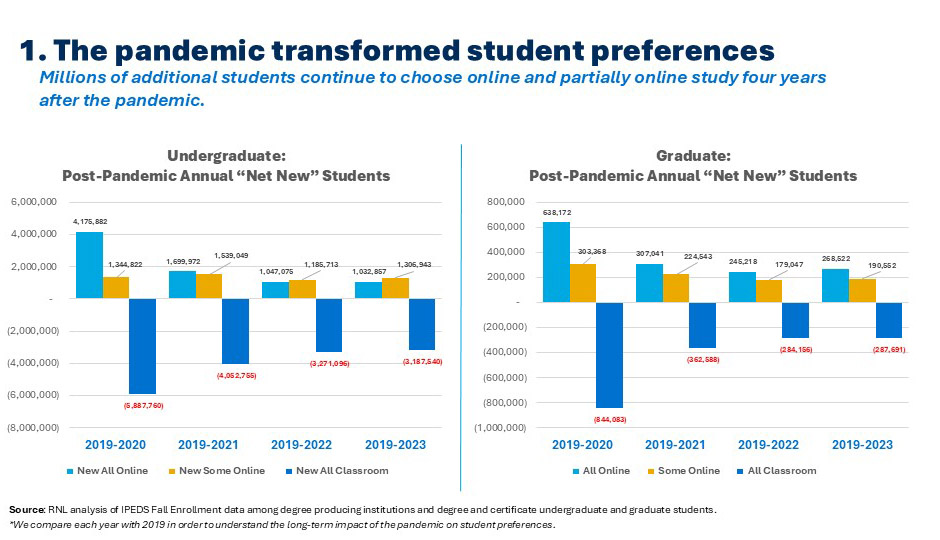
As recently as five years ago, your strongest competition came from for-profit institutions. In some ways, these institutions were easy to beat (excepting their huge marketing budgets). They had taken a beating in the press to the extent that students knew about it, and they were far away and unknown. Today, institutions face no less of a competitive environment, but the institutions dominating the scene – and most likely a students’ search results – are national non-profits. These institutions are, of course, not local so they aren’t well known, but they have not been through the scrutiny which eroded interest in the for-profits. Student search engine results are also now filled with ambitious public and private institutions seeking to “diversity their revenue streams.” As such, institutional marketers need to adjust their strategies focused on successfully positioning their programs in a crowded market, knowing that they can “win” the student over the national online providers if they ensure that they rise to the top of search results.
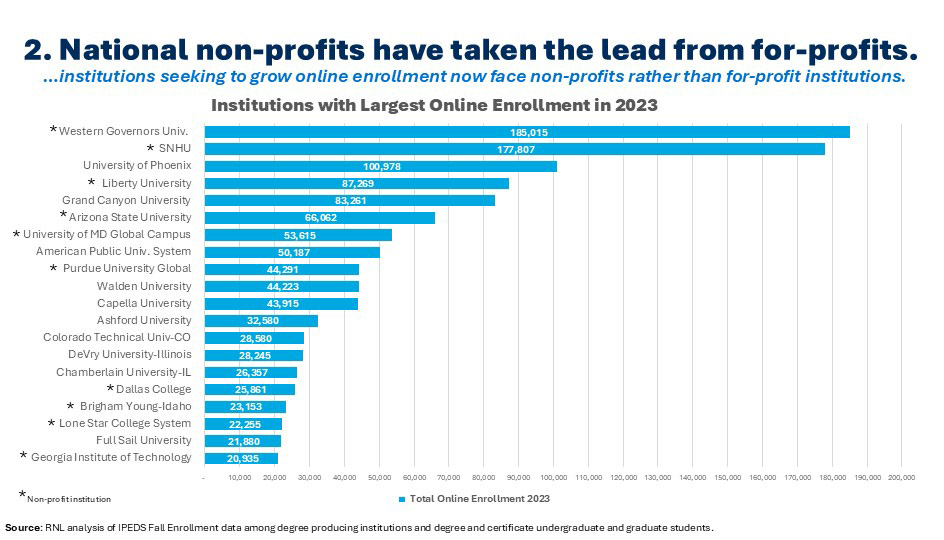

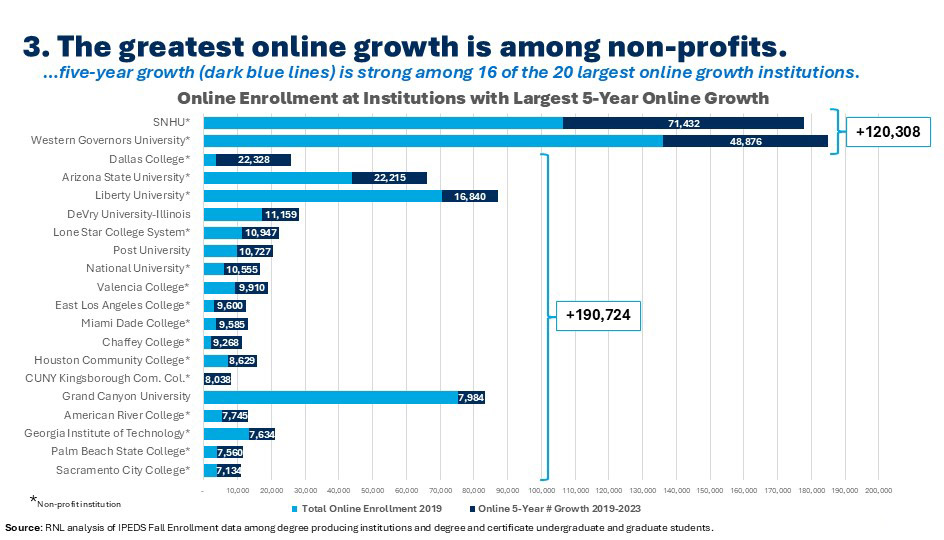
Seventeen of the 20 institutions reporting the greatest growth in online enrollment over the last five years are nonprofit institutions—a mix of ambitious public and private institutions and national non-profits. What is more, the total growth among institutions after the two behemoths far exceeds Southern New Hampshire University and Western Governors University. These nimble and dynamic institutions include a variety of institution types (with community colleges well represented) across the higher education sector. Institutions seeking to grow online enrollment should research what these institutions are offering and how they are positioning their programs in the market and emulate some of their best practices.

In 2024, a research study by Robert Kelchen documented growth in the number of available master’s programs in the U.S. over the last 15 years. Not only did Kelchen document a massive expansion in availability (over the 15-year period, institutions launched nearly 14,000 new master’s programs on a base of about 20,000), but also that the pace of launching online or hybrid programs dramatically outpaces classroom programs. This rise in available offerings far outpaces the rate of growth of the online student market, resulting in significantly higher levels of competition for each online student. Institutions seeking to grow their online footprint must ensure that they fully understand both the specific demand dynamics for each of their programs and the specifics of what online students want in their program. A mismatch on either factor will inhibit growth.

We all know something of the power of social media today. This was reinforced for me recently by an Inside Higher Education story which focused on the 8-year rates of degree completion among the biggest online providers. The story was triggered by a widely read Linked IN post and followed up by numerous other stories and posts and comments across the platform. This is just the kind of exposure that is most likely to generate real scrutiny of the outcomes of online learning – which were already taking shape over the last year or more. In fact, this focus on outcomes ended up as one of the unfulfilled priorities of the Biden Education Department. I have long said that institutions seeking to enter the online space have an opportunity to tackle some of the quality issues that first plagued the for-profits, now challenge the national online non-profits, and will confront others if not addressed soon.
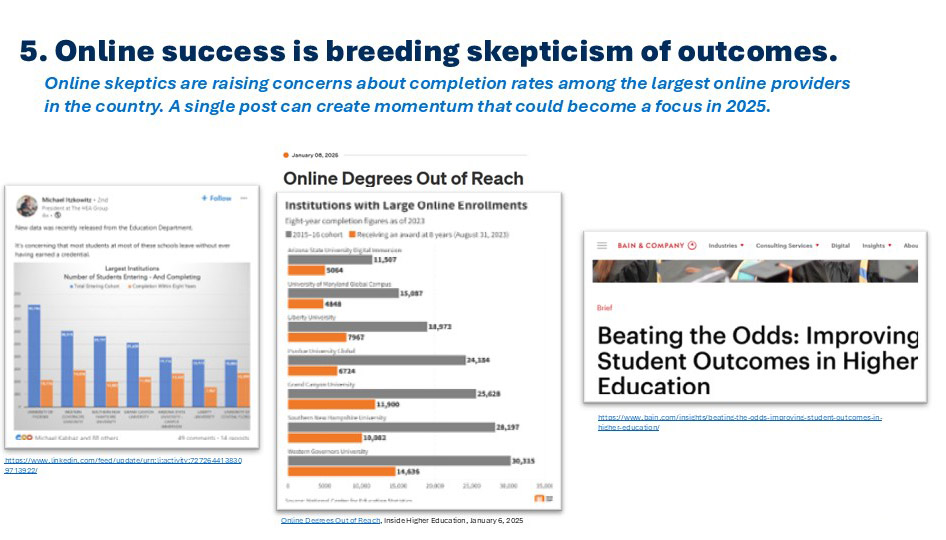

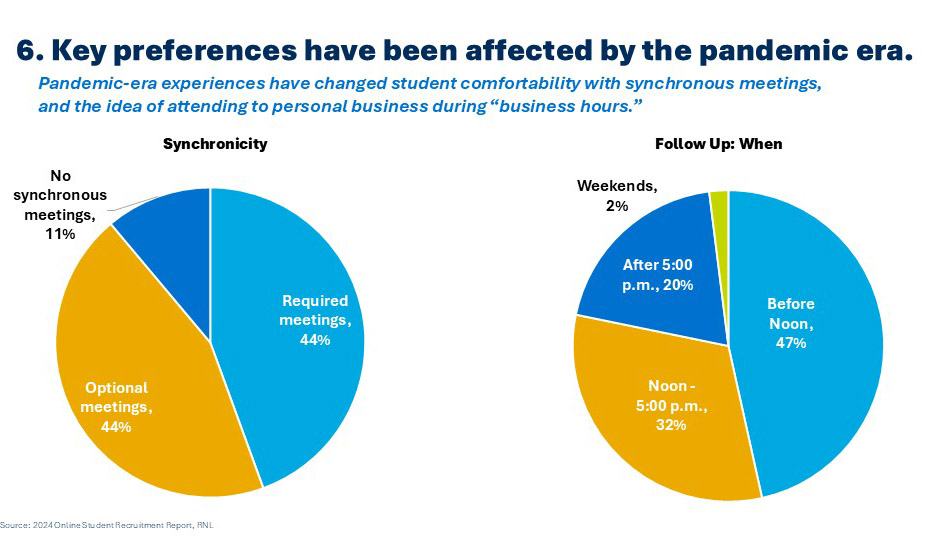
RNL’s own 2024 online student survey surfaced dozens of important findings that online leaders should consider as they chart their course. Two findings stand out as reflecting profound changes in online student preferences, and both are likely the result of pandemic-era experiences. First, all but 11 percent of online students told us that they are open to at least some synchronous activities in their program, likely the result of hundreds of online meetings during the pandemic. Similarly, they told us that the ideal time to communicate with recruiters/counselors from online programs is now during business hours. This is also likely to be related to the pandemic period, in which millions of people working from home began to regularly contend with some personal business during their day. Institutions should assess both of these factors as they think through student engagement (to address point #5), and the intense competition of the online space (to address point #3).

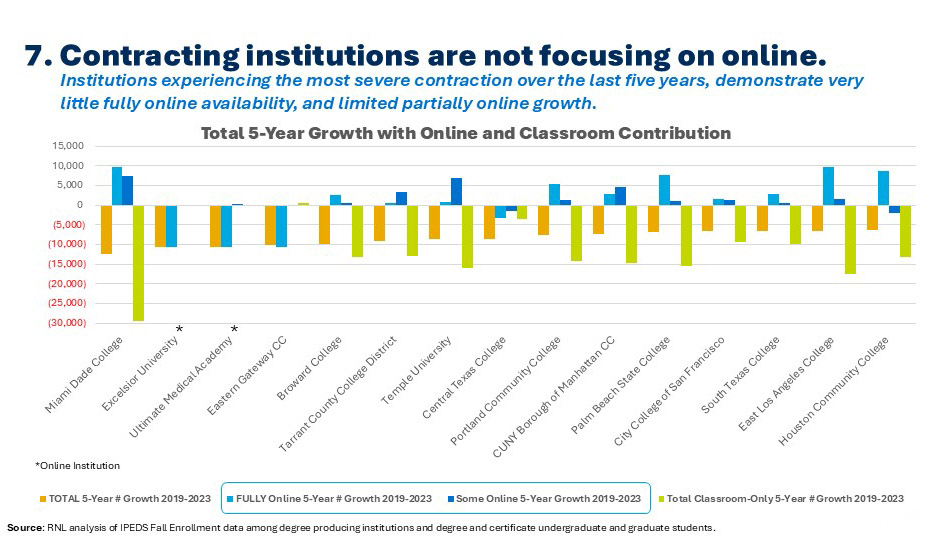
Finally, we return to the new IPEDS data to see that institutions that have experienced the greatest enrollment contraction over the last five years demonstrate almost no access to fully online study (dark blue lines in the chart below), and only limited access to programs in which students can enroll in both online and classroom courses (light blue lines). Even where there has been some online or partially online growth, these efforts have not been given adequate attention to counterbalance contraction among students enrolled in classroom-only programs (green lines). These data again make it clear (as stated in point #1) that institutions facing classroom-only contraction must either amend their goals to account for reduced enrollment or determine which online or hybrid programs would be most attractive to students in their region and then ensure that such offerings are visible in a highly competitive higher education market.


Join us for a deeper dive into trends during our webinar, 5 Enrollment Trends You Need to Know for 2025. This discussion with me and a number of my RNL expert colleagues will look at research and trends that should shape strategic and tactical planning over the next 12 months. Particularly, as we enter what has been identified as the first year of the “demographic cliff,” data-informed decision-making will be more important to enrollment health than ever before. Register now.

Dear Commons Community,
Patsy Moskal and I have decided to be guest editors for Education Sciences for a special edition entitled,
“Trends in the Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence for Digital Learning.” (See below for a longer description.)
It is a most timely topic of deep interest to many in the academy. We would love to have you contribute an article for it. Your submission can be research, practitioner, or thought-based. It also does not have to be a long article (4,000-word minimum). Final articles will be due no later than July 1, 2025.
You can find more details at: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/education/special_issues/6UHTBIOT14#info
Thank you for your consideration!
Tony

We are at a pivotal point in higher education, the Era of the Modern Learner. This new era, shaped by evolving technology, changing cultural dynamics, and shifting student priorities, is revolutionizing how colleges and universities engage with students.
Modern Learners are not who they used to be. They are:
To succeed in the Era of the Modern Learner, institutions must adapt and embrace a Unified Enrollment Approach that seamlessly integrates marketing and communications across the campus, ensuring a consistent brand message reaches all audiences. This means moving beyond traditional demographic-driven strategies and embracing the commonalities that bind today’s diverse student population as Modern Learners.
The 2025 Marketing and Enrollment Management Benchmarks Report offers higher education leaders with the knowledge and insights needed to effectively navigate the landscape.
A growing number of students prefer to explore college options privately, submitting applications directly without engaging with admissions offices beforehand. This trend, known as stealth applying, presents a challenge for institutions to connect with these elusive prospects, requiring refined media spending strategies to justify investments and adapt to this evolving application behavior.
Analysis of site traffic reveals significant shifts in program demand. Healthcare and vocational training programs are experiencing a surge in interest, reflecting a growing societal focus on healthcare careers and a shift towards practical skills and direct employment pathways. Conversely, traditional arts and humanities fields are facing declines, suggesting students are prioritizing fields perceived as more job ready.
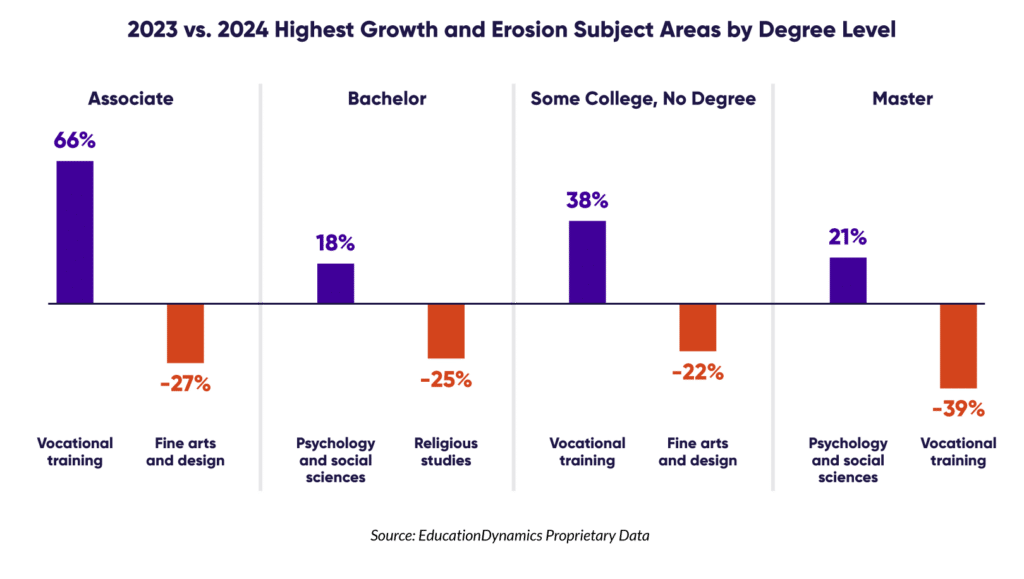
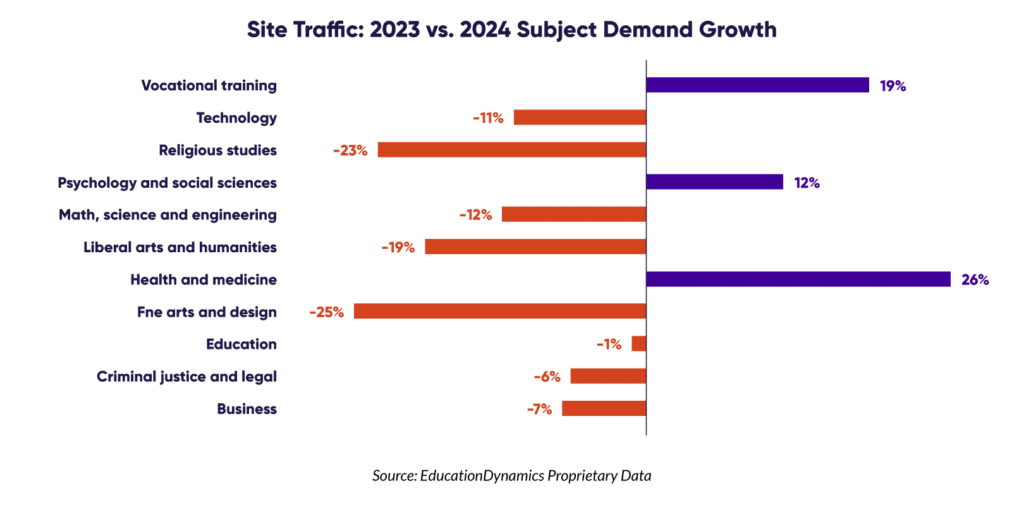
Organic search remains a highly cost-effective way to attract prospective students, with over a third of all education website visits originating from organic search. Institutions need to prioritize website performance and optimize their online presence to capture this valuable traffic source.
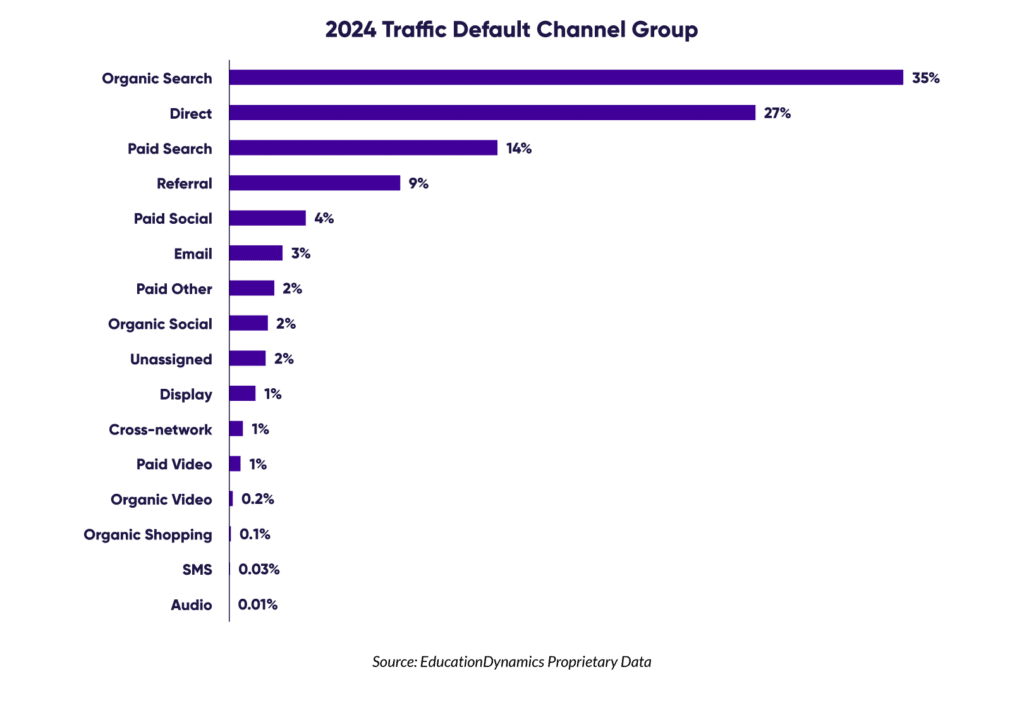
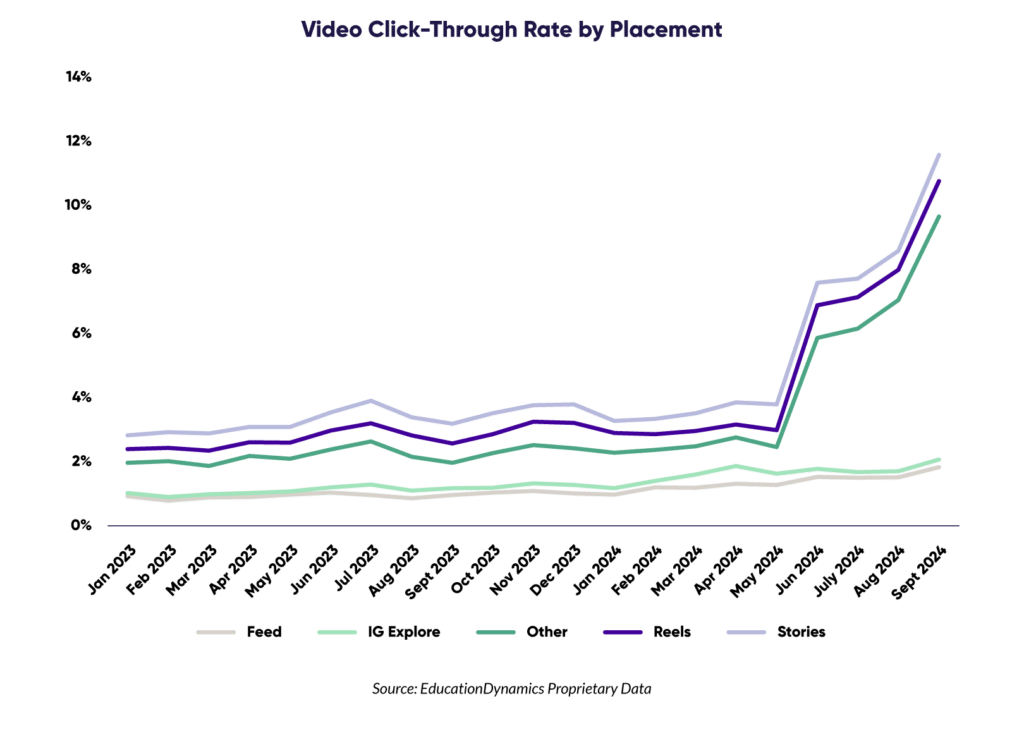
Institutions are strategically increasing their investment in digital advertising, particularly across platforms like Google, social media, and mobile video. This shift reflects the Modern Learner’s digital-first consumption habits and the effectiveness of these channels in driving awareness and conversions.
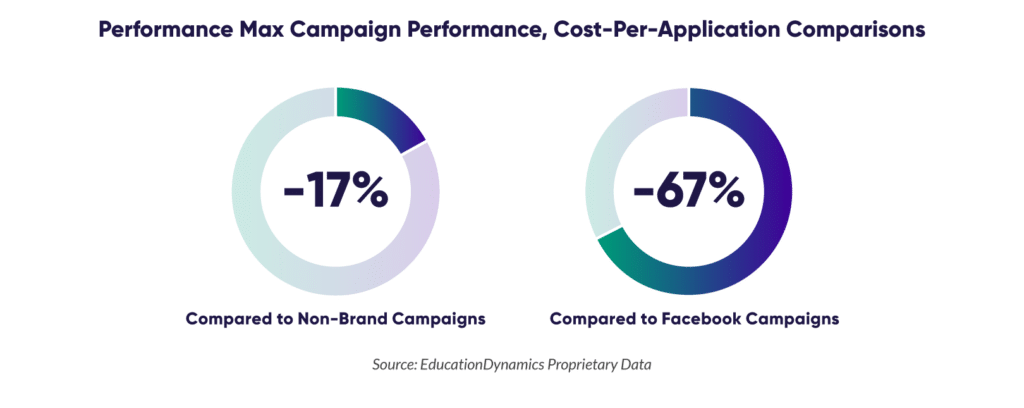
AI-powered tools, such as Google’s Performance Max, are transforming how institutions optimize advertising campaigns and personalize content delivery. These tools leverage machine learning to enhance ad performance across multiple Google channels, leading to more efficient and effective outreach.
By understanding these trends and proactively adapting strategies, higher education institutions can effectively engage Modern Learners, navigate the evolving landscape, and achieve enrollment success in 2025 and beyond.
For a more in-depth analysis of the current higher education marketing and enrollment landscape, download our comprehensive Marketing and Enrollment Management report. It’s packed with EducationDynamics’ proprietary data, insights and actionable strategies to help you grow enrollment.
EducationDynamics is dedicated to helping colleges and universities navigate these complex challenges. We offer proven solutions to help you implement these key recommendations and achieve your enrollment goals. Contact us today to learn how we can partner with you to reach the Modern Learner and thrive in the evolving higher education environment.